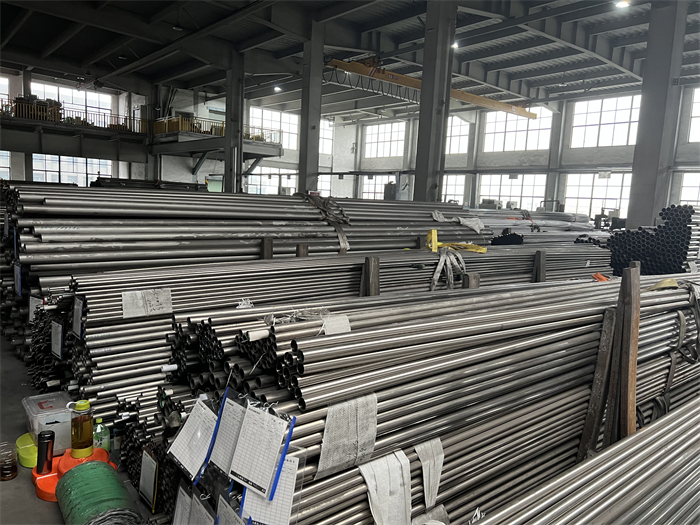
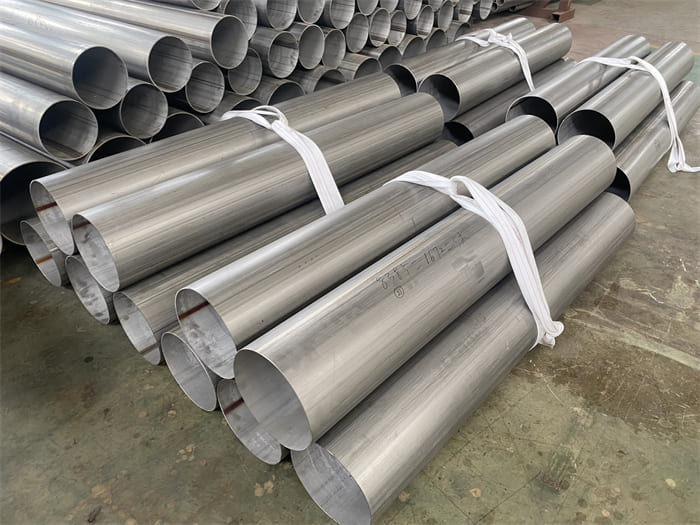
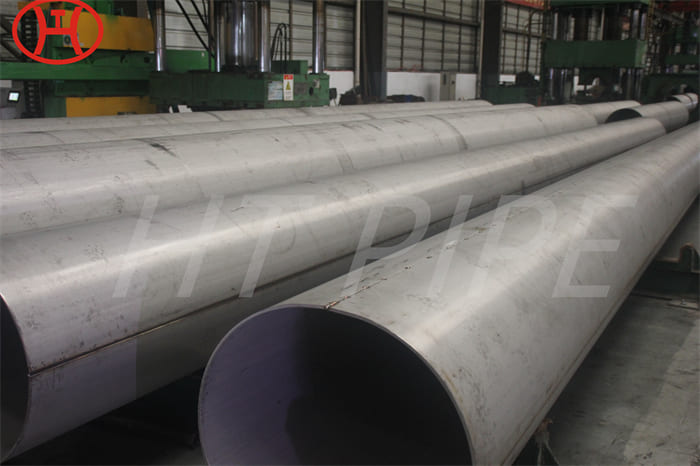
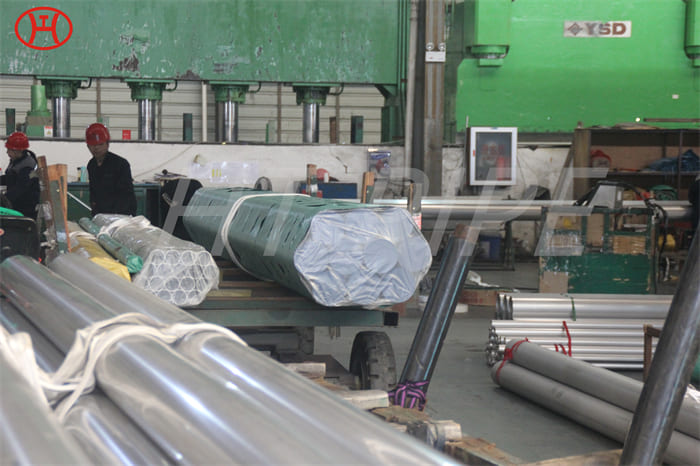
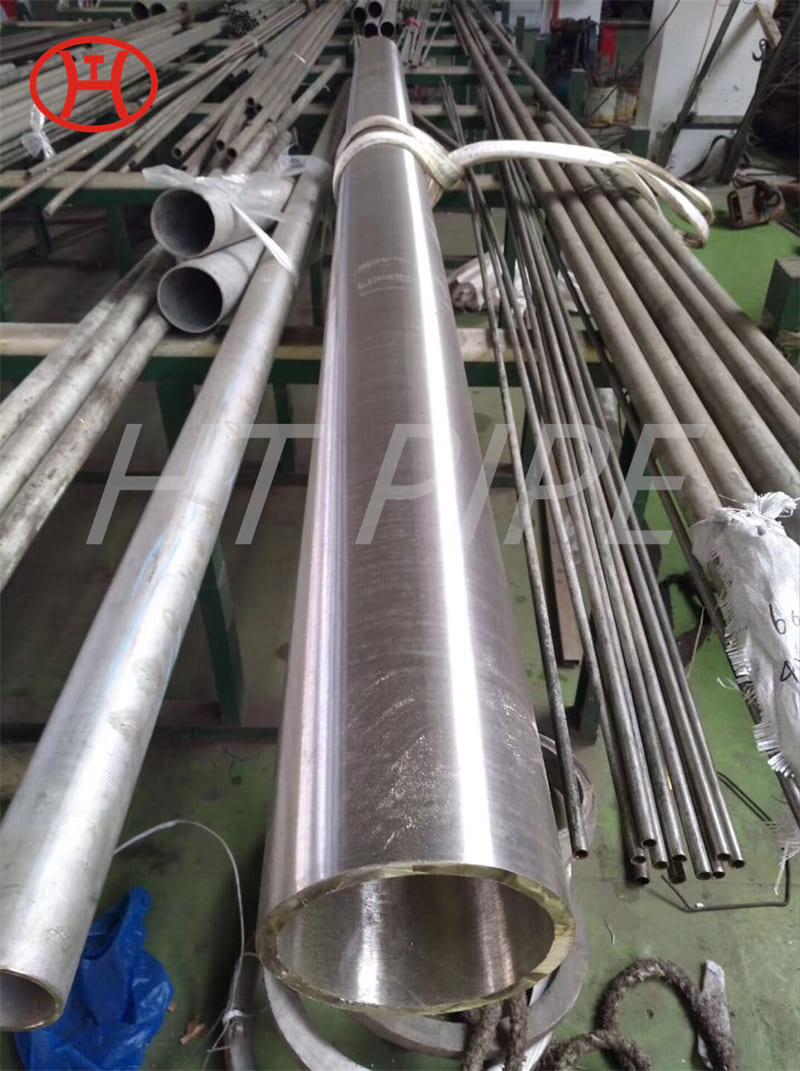
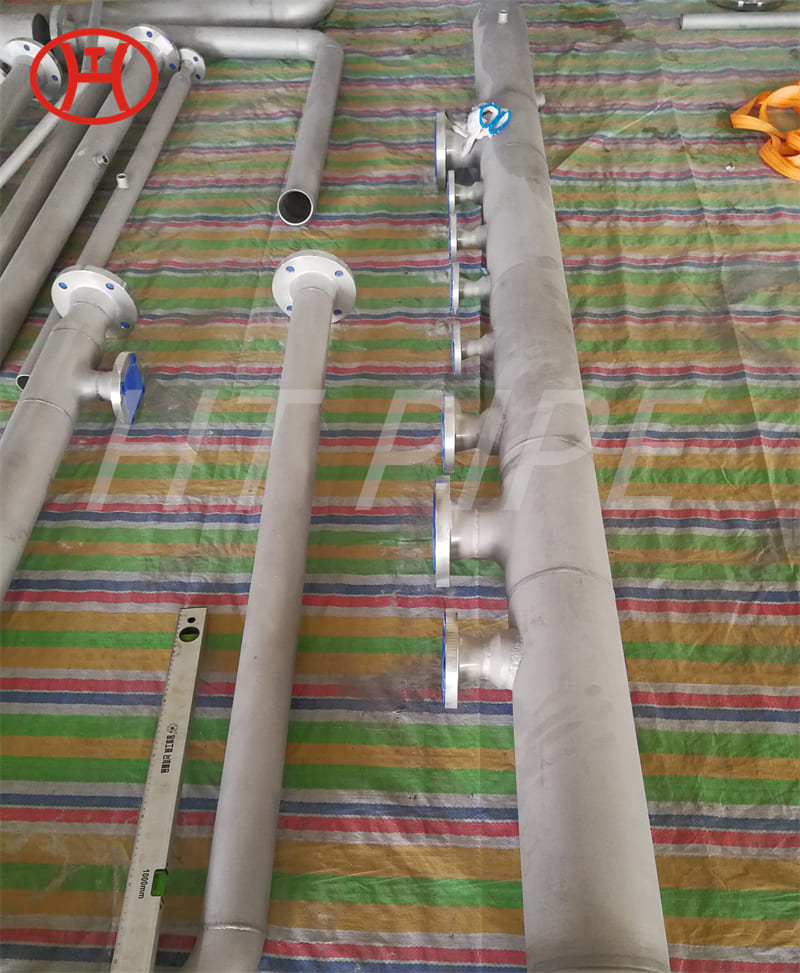
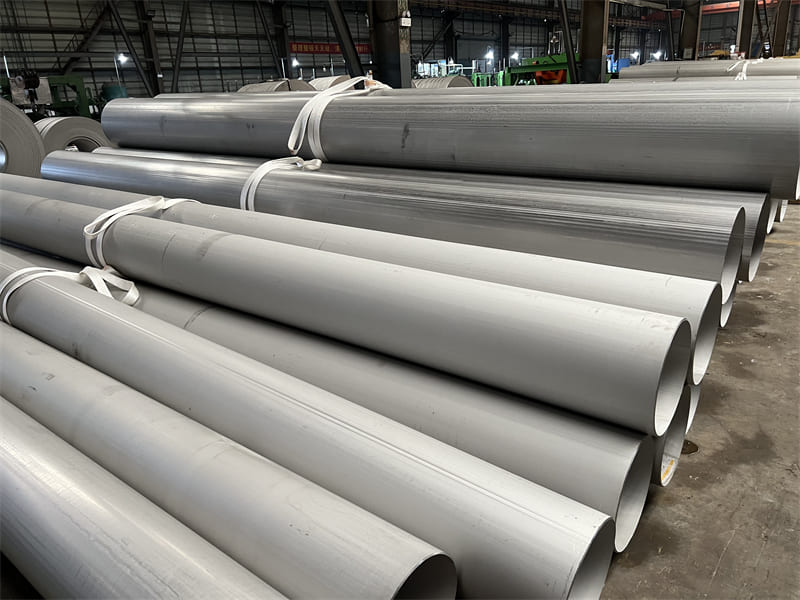
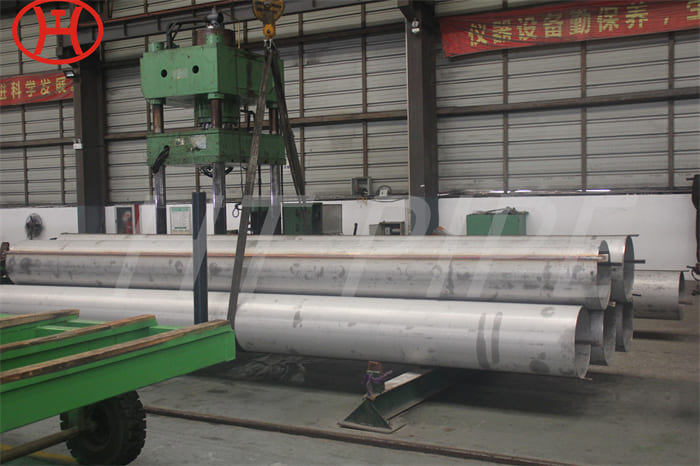
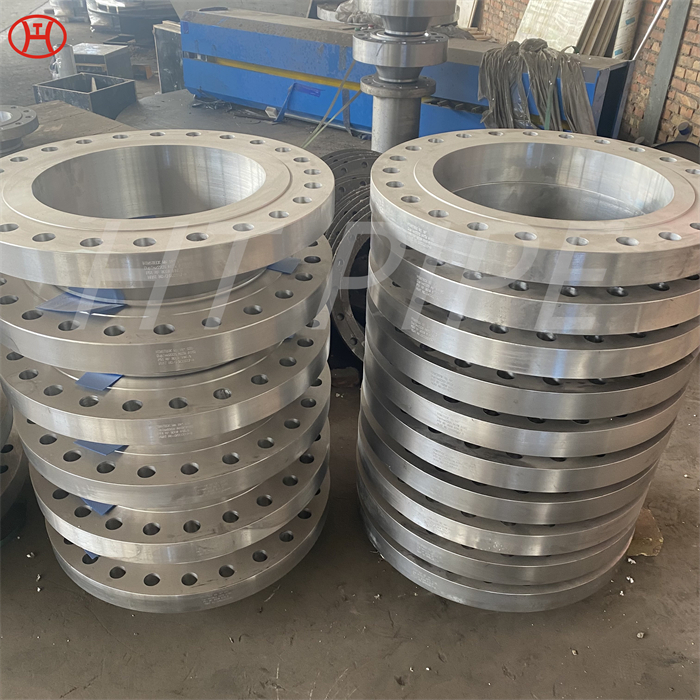
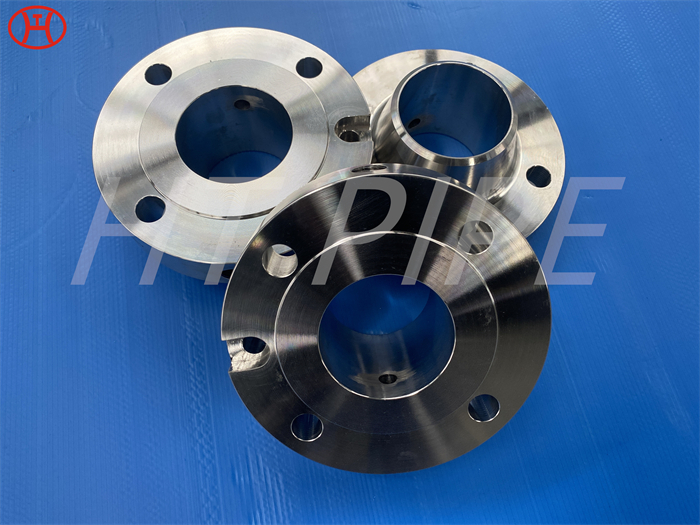
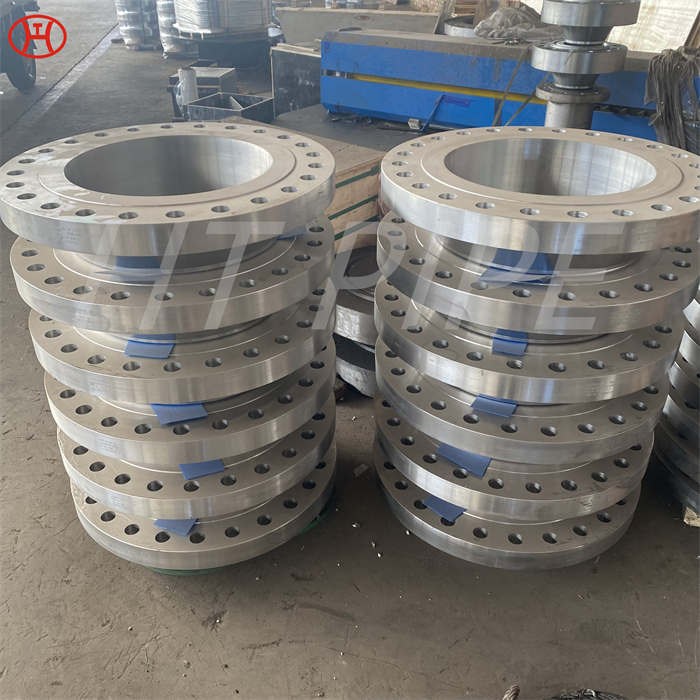
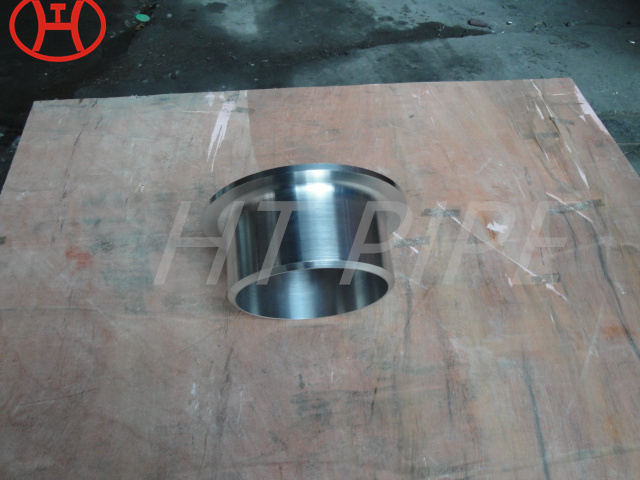
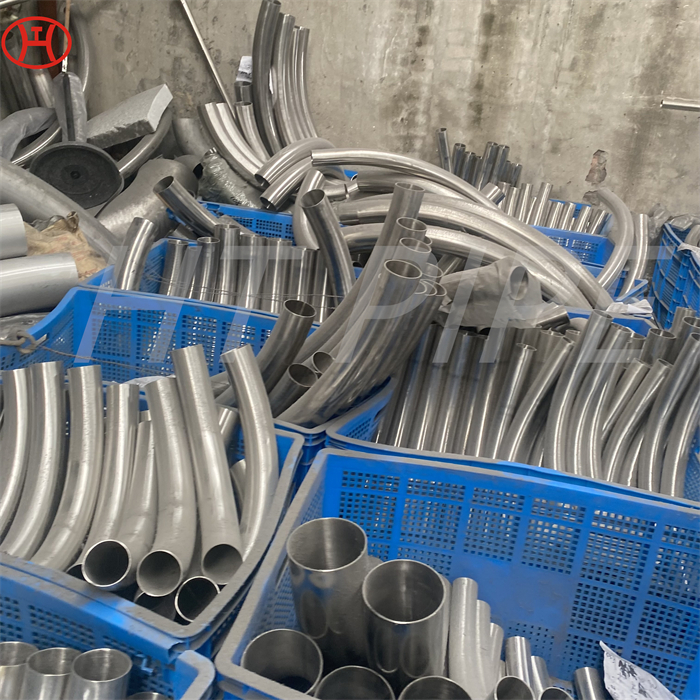
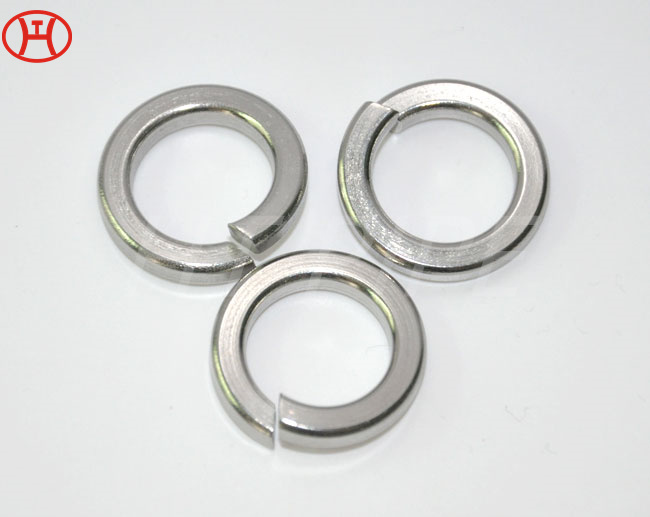
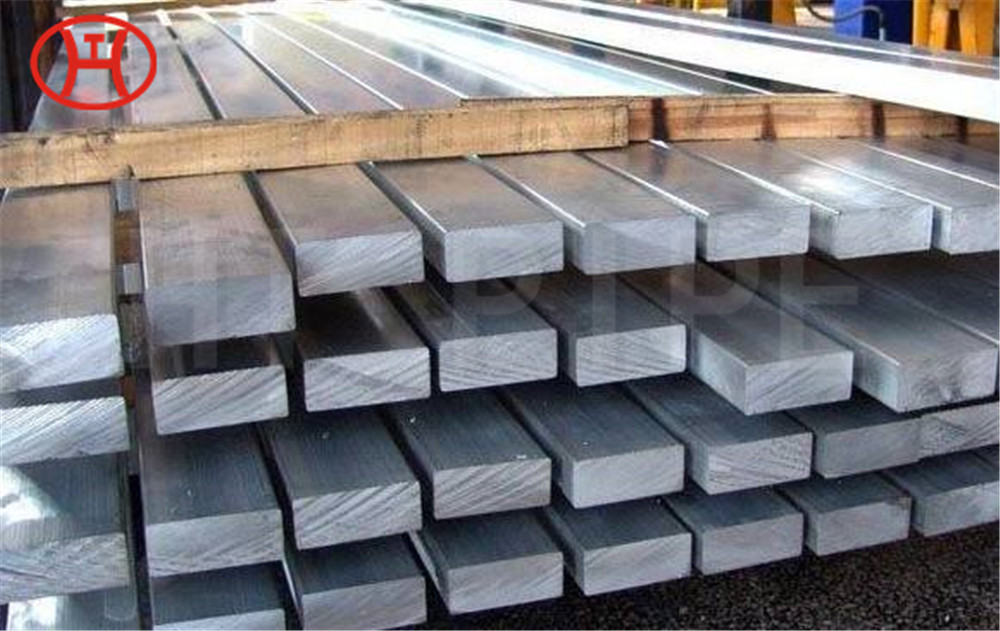
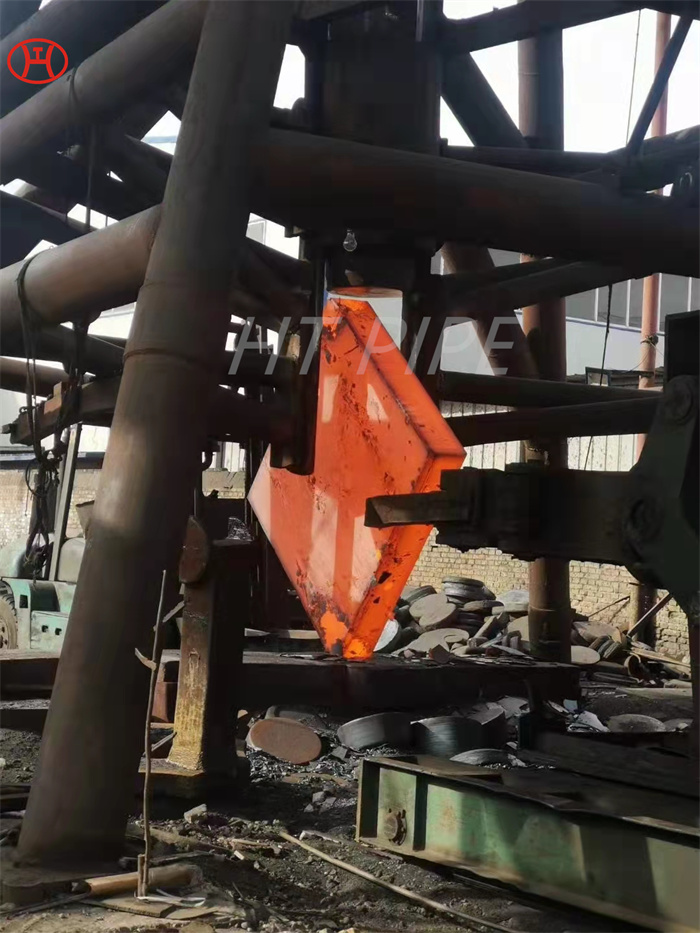
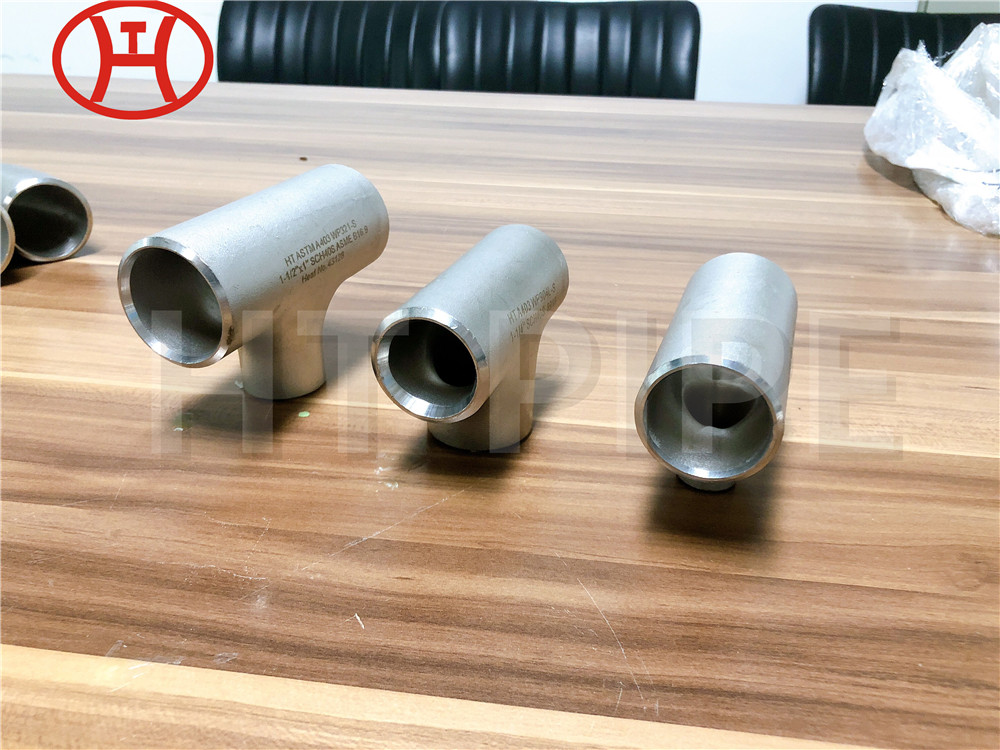
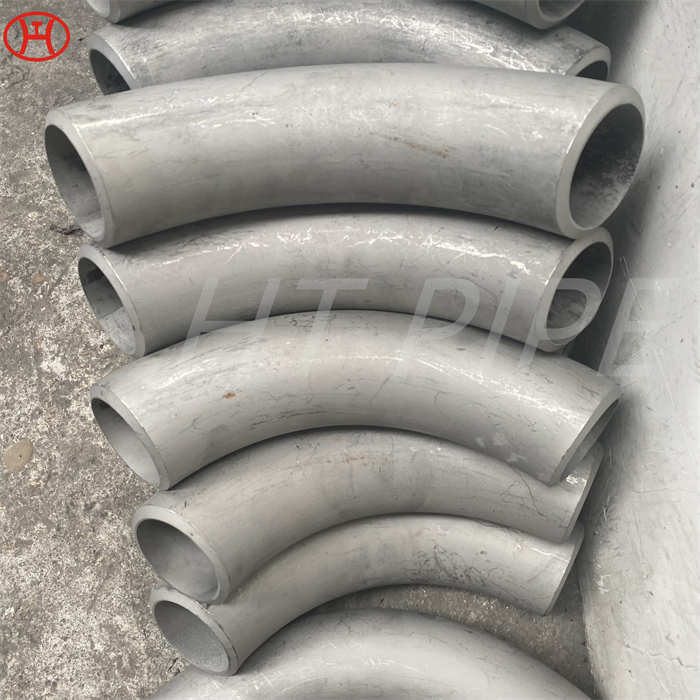
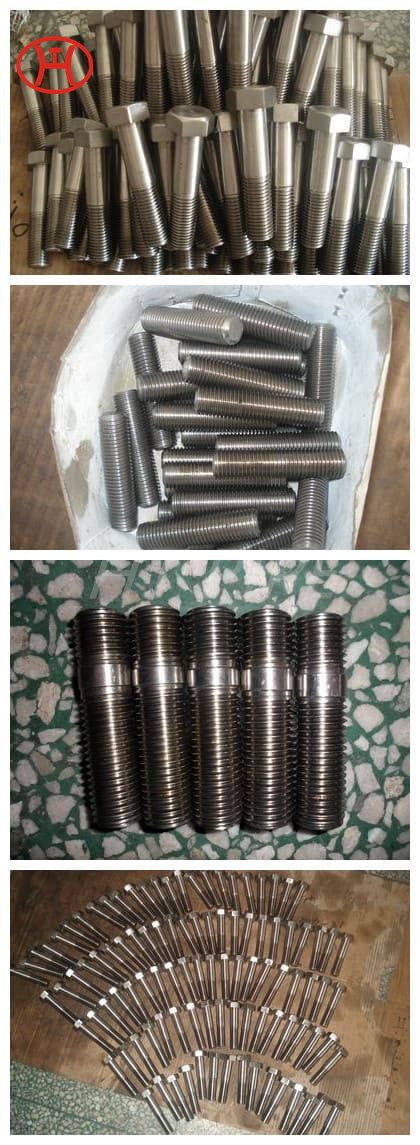
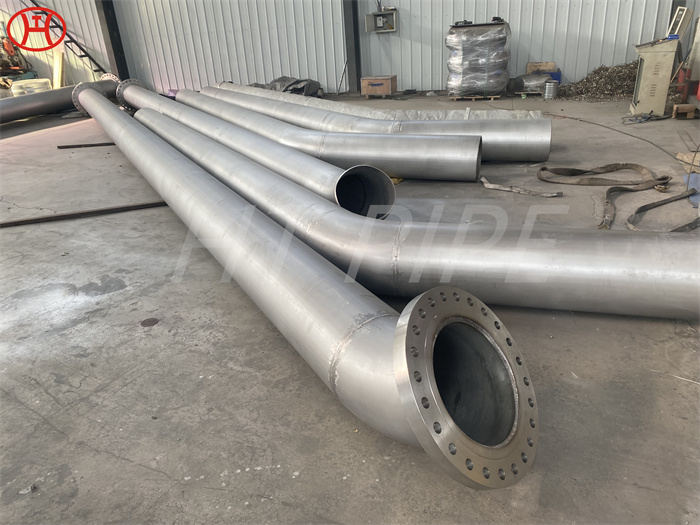
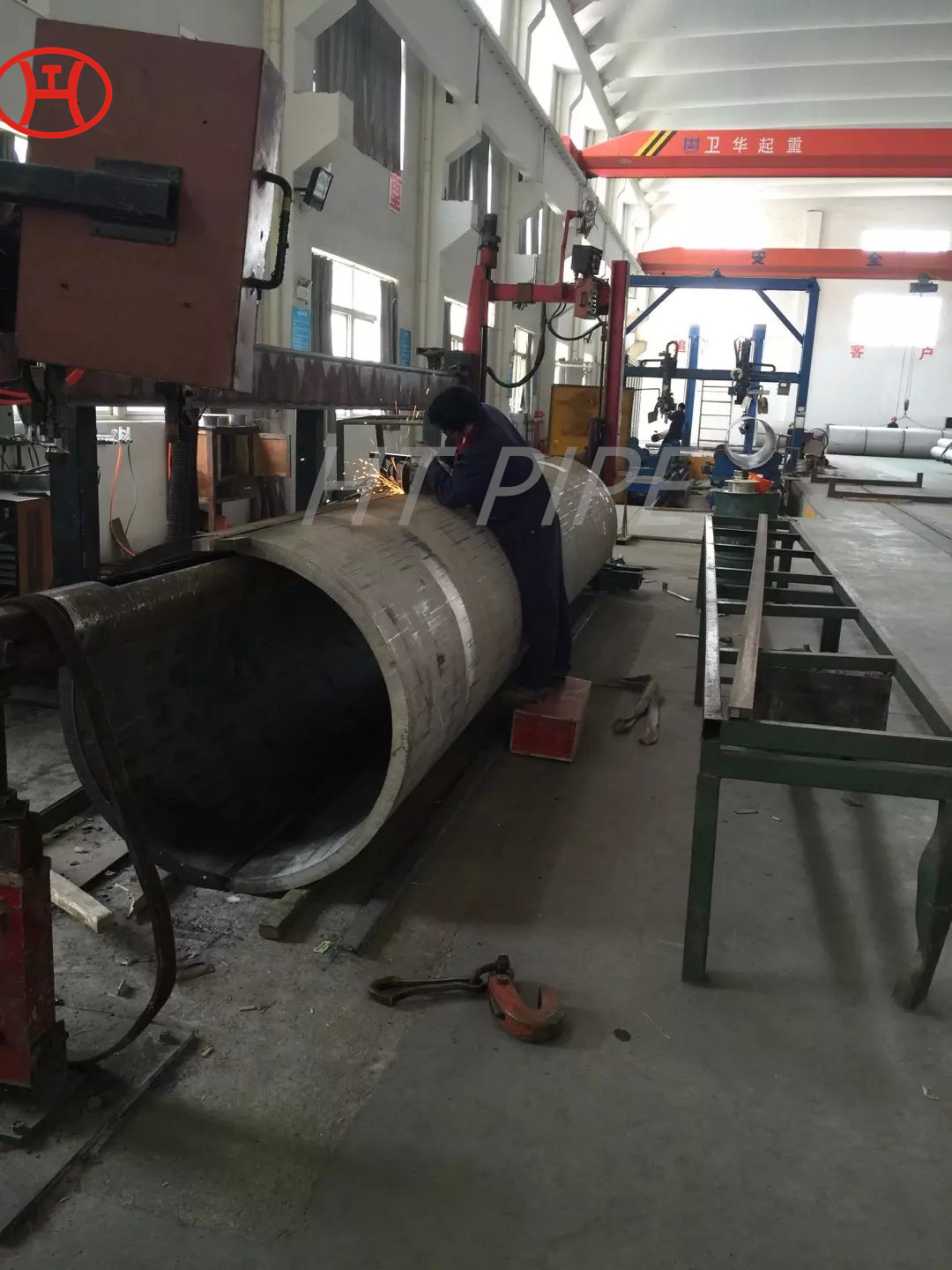
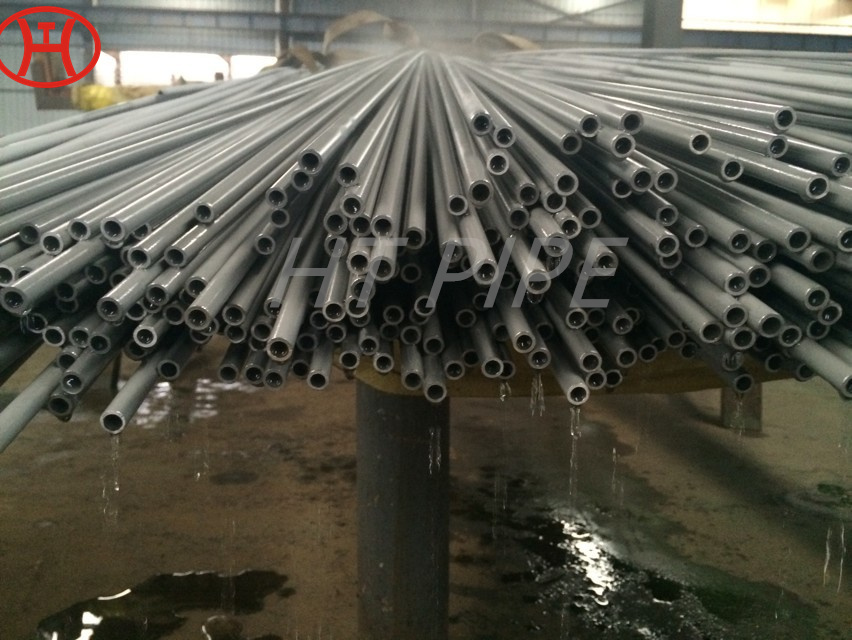
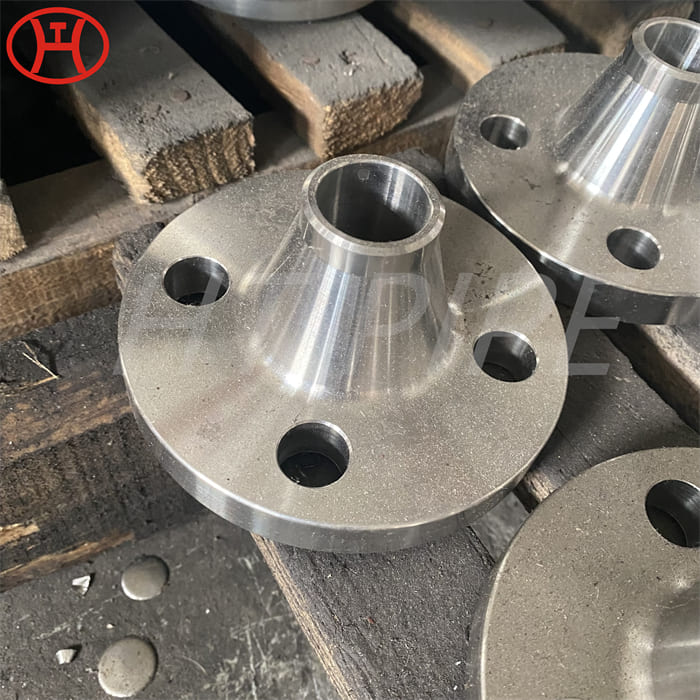
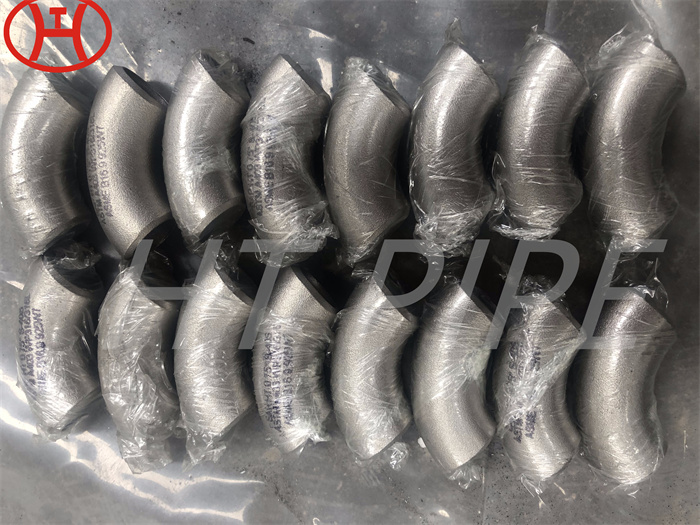
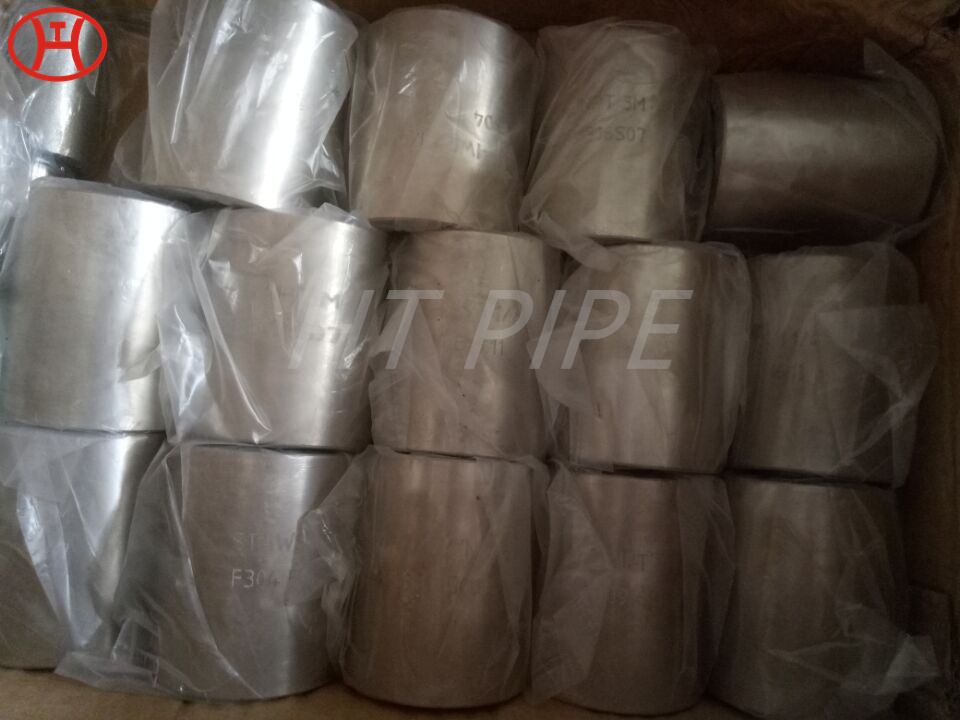
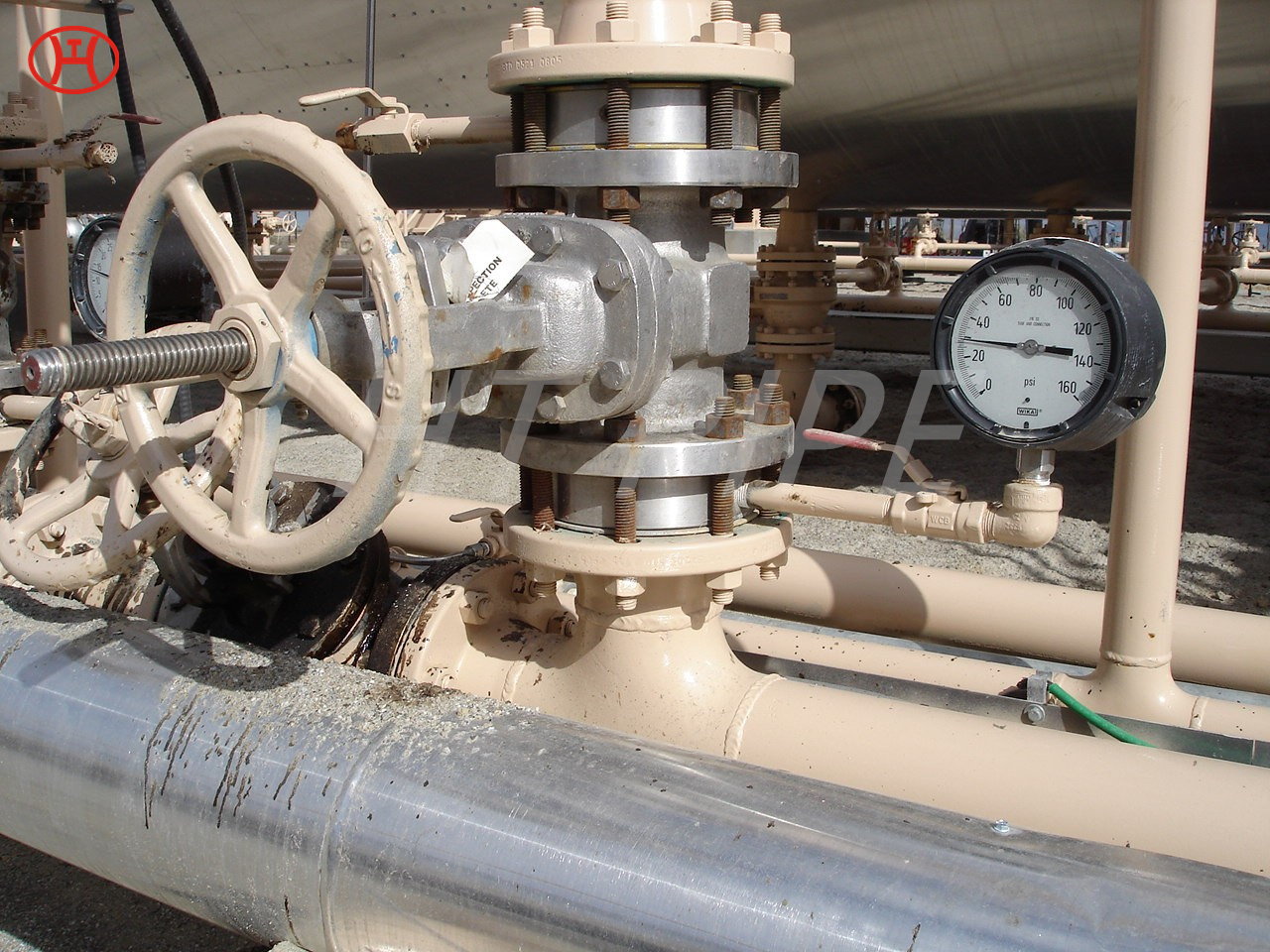
A182 F316L special flange potentially corrosive chemicals
Typical applications for steel include: food preparation equipment, laboratory equipment, chemical containers for transportation, springs, heat exchangers, mining screens, coastal building paneling, railings, trim, marine fittings, quarrying and water filtration. One of the main differences between 316l stainless steel and 316 stainless steel is that the carbon content of the former is as high as 0.03%, and the carbon content of the latter is as high as 0.08%. These differences give them different properties. Let’s learn more about the 316l stainless steel alloy.
Types 316/316L have excellent strength and toughness at low temperatures. Type 316/316L is non-magnetic in the annealed condition, but may become weak due to severe cold working. 316 is an austenitic chromium-nickel stainless steel containing 2% to 3% molybdenum. The molybdenum content improves corrosion resistance, increases pitting resistance in chloride ion solutions, and improves high temperature strength.