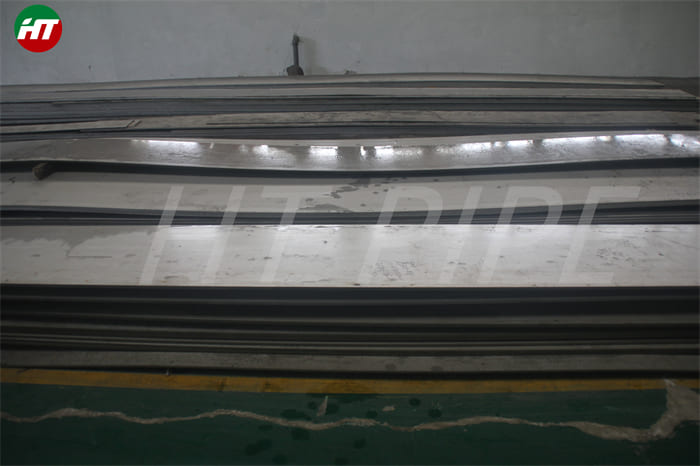
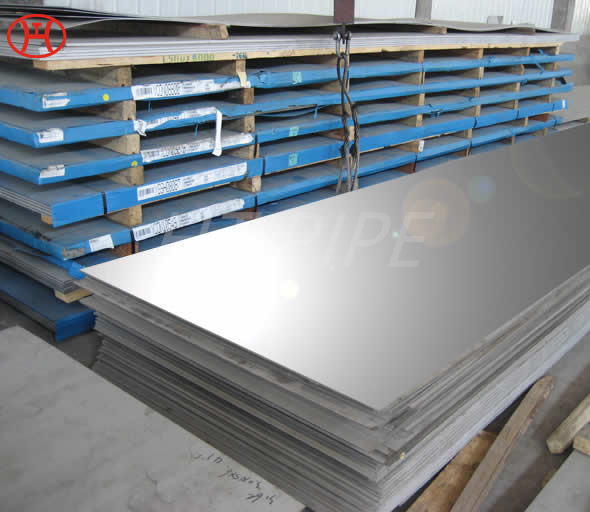
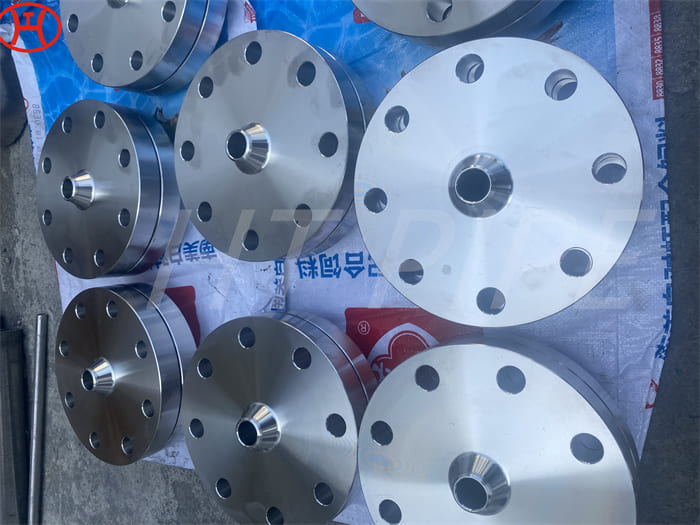
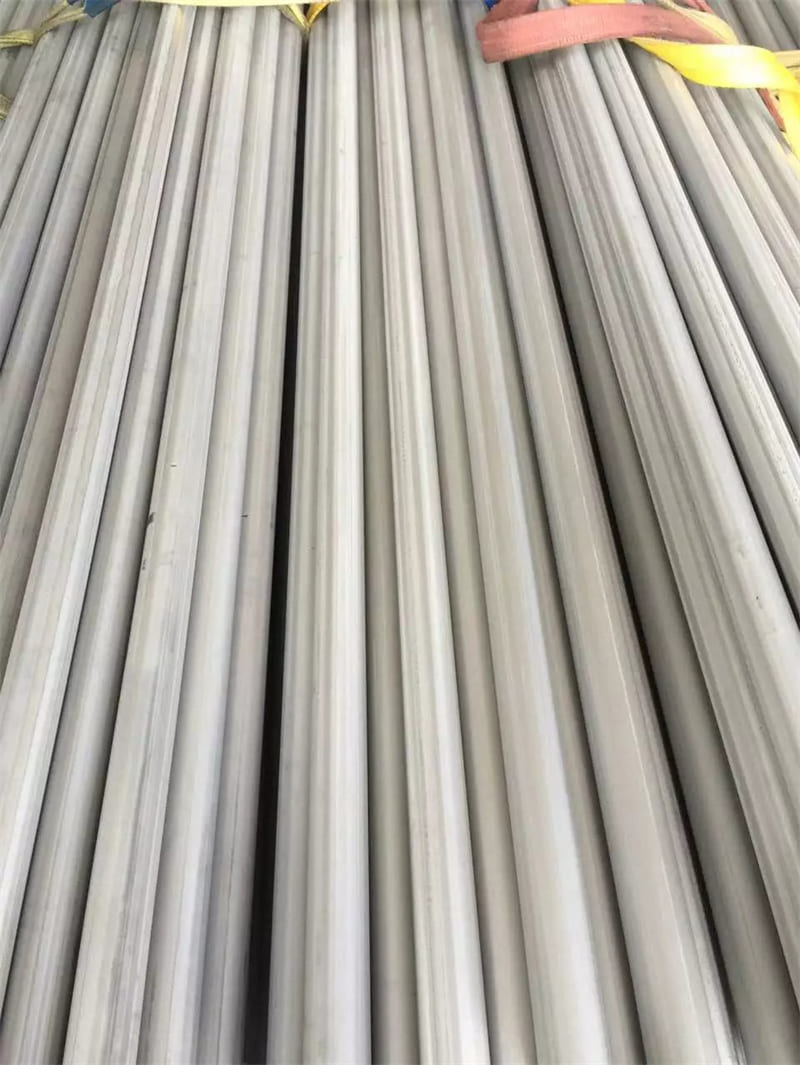
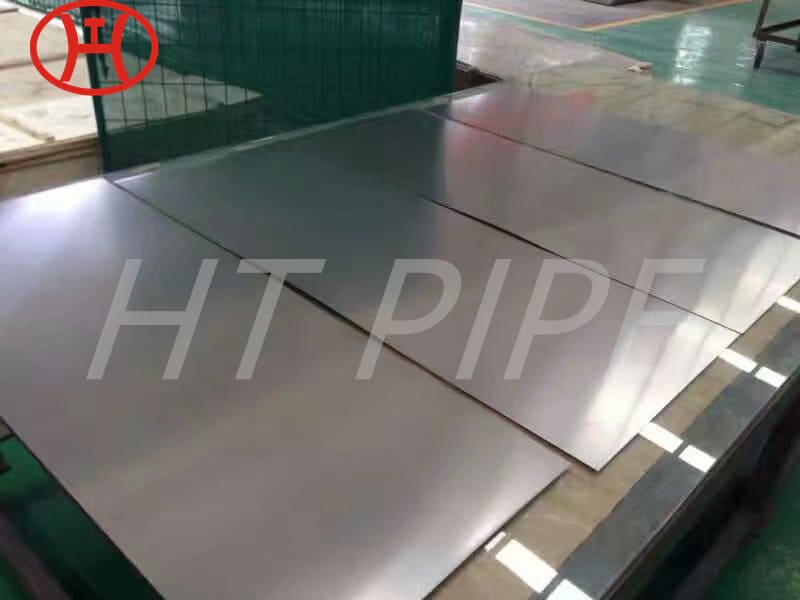
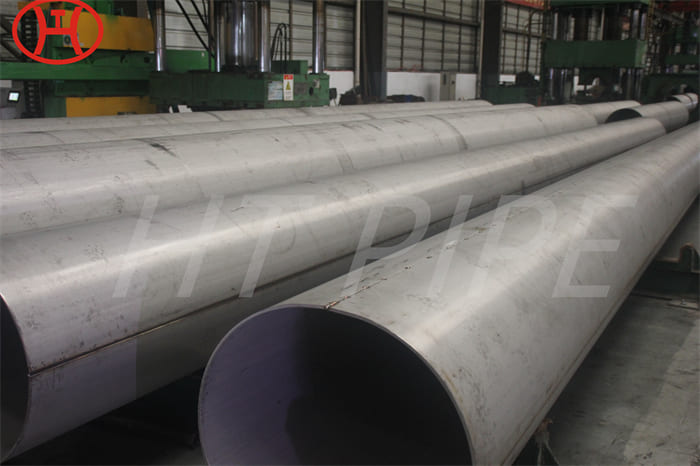
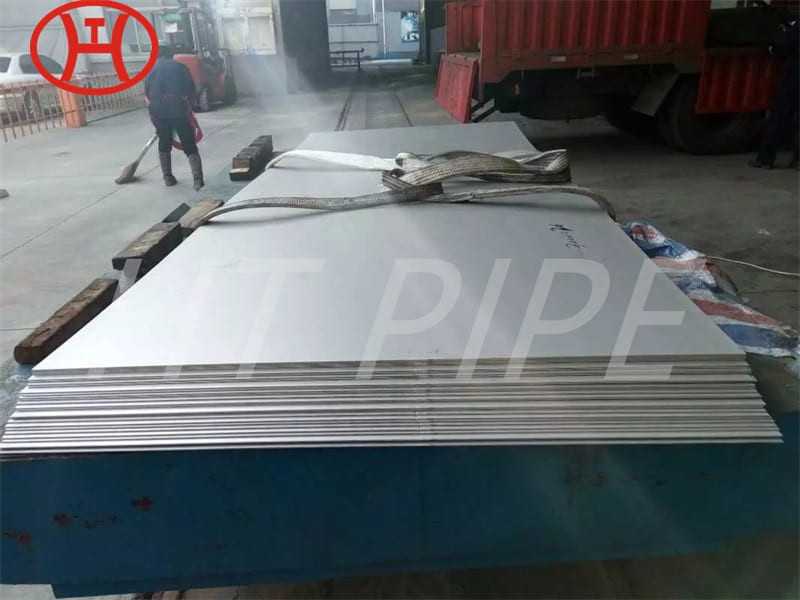
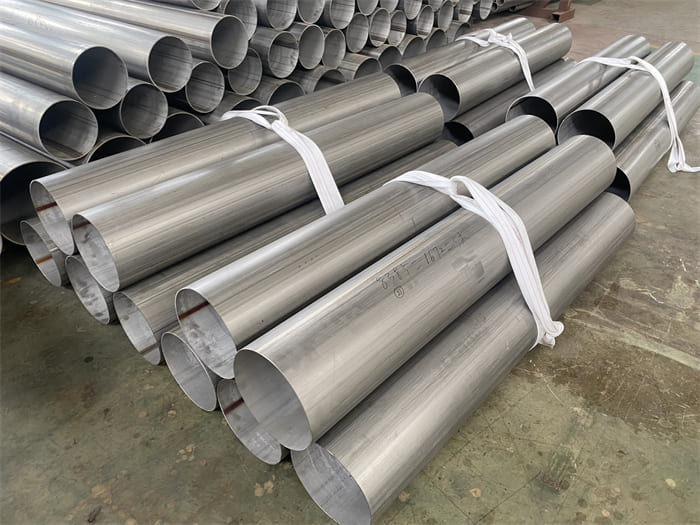
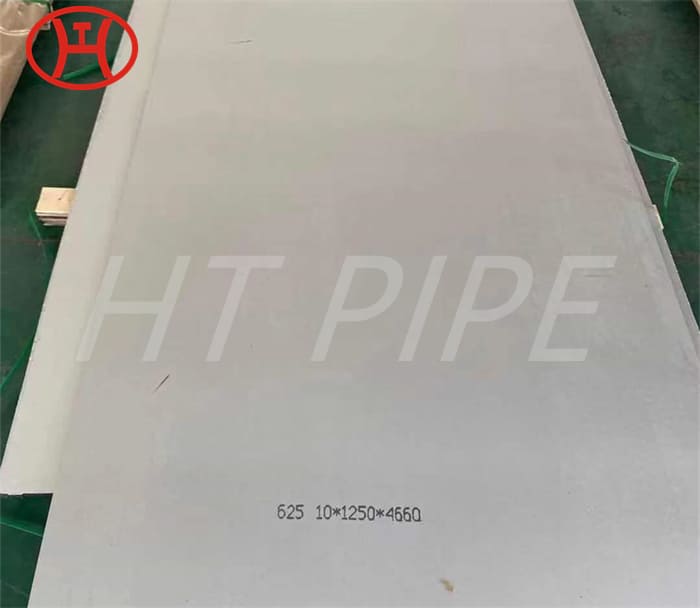
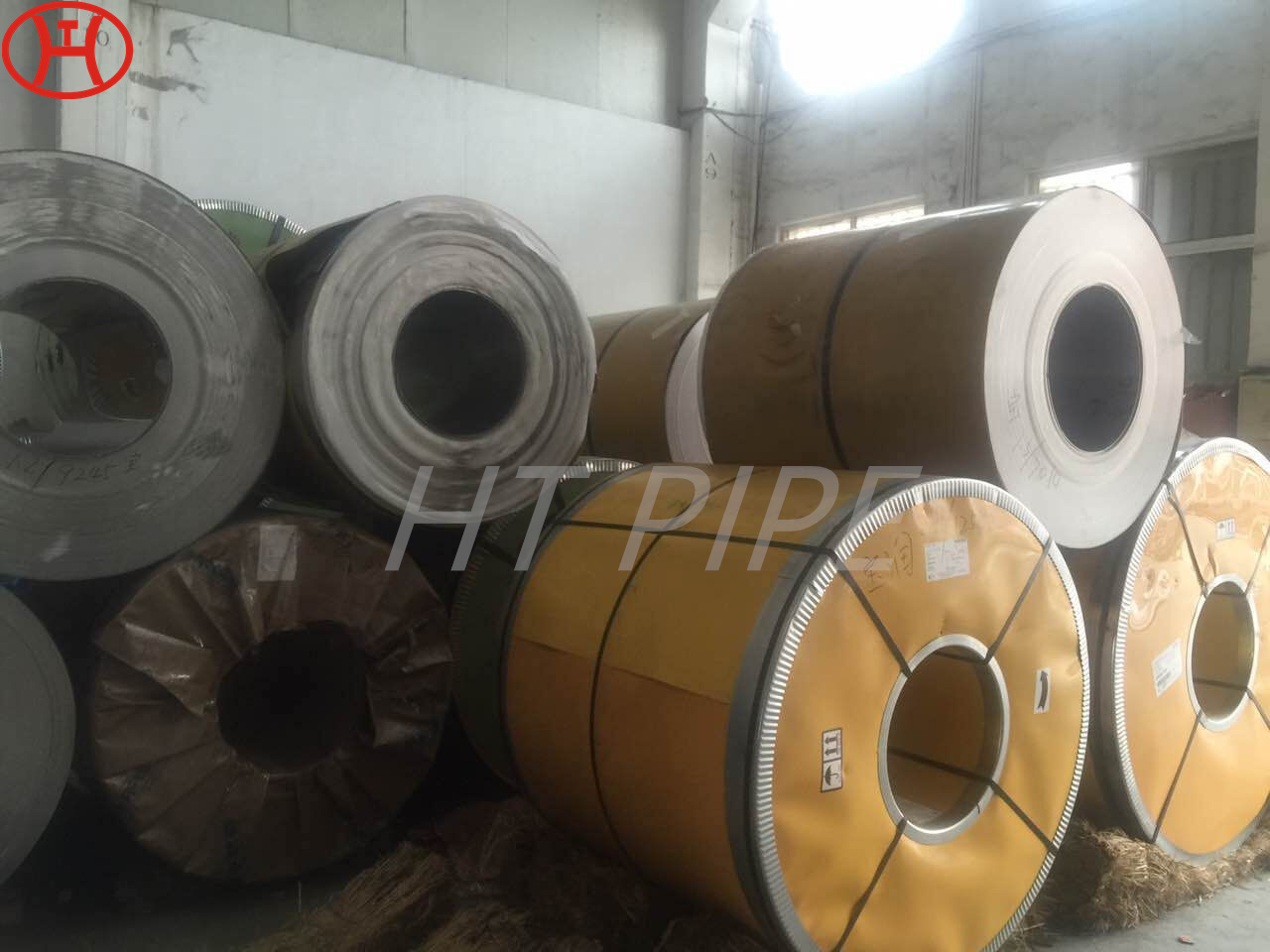
Astm A240 316L 1.4404 1.4435 Stainless Steel Sheet And 1.5Mm Plate Ss Slit Coil 304
Stainless steel also contains varying amounts of carbon, silicon and manganese. Other elements, such as nickel and molybdenum, can be added to impart other useful properties such as enhanced formability and enhanced corrosion resistance.
Alloy 316 / 316L (UNS S31600/S31603) is a chromium-nickelmolybdenum austenitic stainless steel developed to provide improved corrosion resistance to Alloy 304 / 304L in moderately corrosive environments. Stainless Steel 316L Plate is often utilized in process streams containing chlorides or halides. The addition of molybdenum improves general corrosion and chloride pitting resistance. It also provides higher creep, stress-to-rupture and tensile strength at elevated temperatures.

Stainless Steel 316L Plate is common practice for 316L to be dual certified as 316 and 316L. The low carbon chemistry of 316L combined with an addition of nitrogen enables 316L to meet the mechanical properties of 316.
Stainless Steel 316L Plate resists atmospheric corrosion, as well as, moderately oxidizing and reducing environments. Stainless Steel 316L Plate also resists corrosion in polluted marine atmospheres. The alloy has excellent resistance to intergranular corrosion in the as-welded condition. Alloy 316 / 316L sheet has excellent strength and toughness at cryogenic temperatures.

Stainless Steel 316L Plate is non-magnetic in the annealed condition, but can become slightly magnetic as a result of cold working or welding. UNS S31600 / S31603 plate can be easily welded and processed by standard shop fabrication practices.
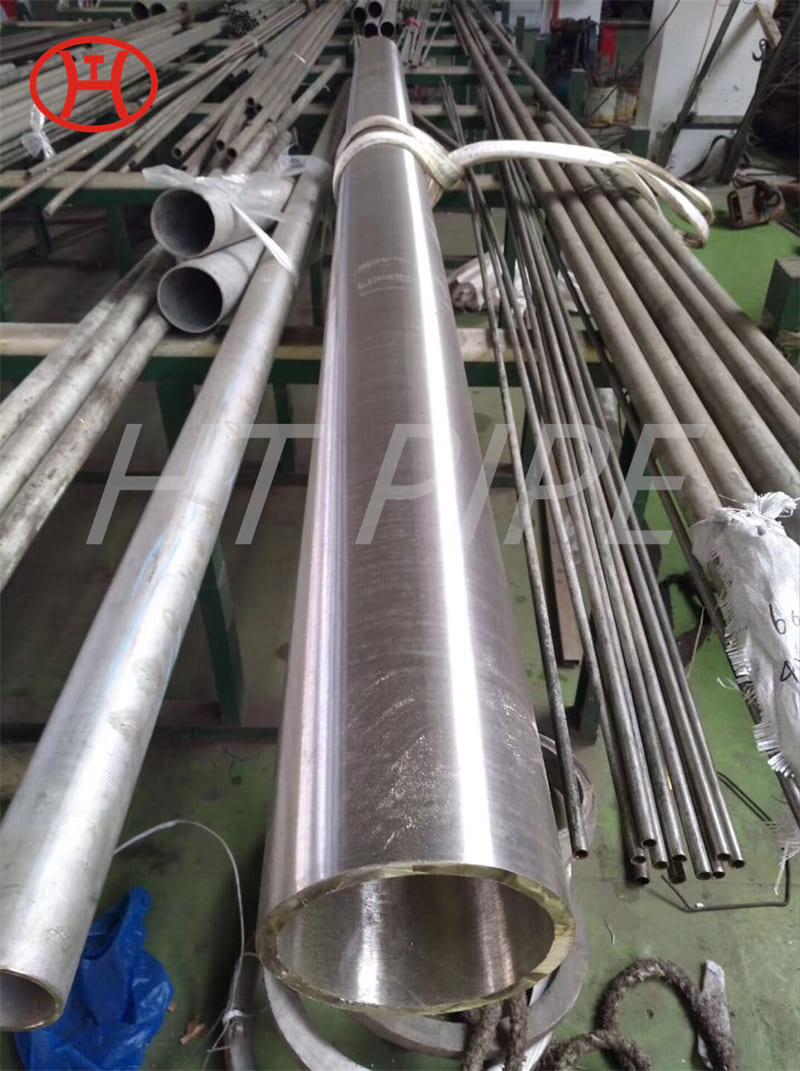
Grade 316L stainless steel sheet is available in many types and thicknesses. The main types of SS 316L sheet are perforated sheet, checkered sheet, gasket, strip, coil, foil, flat and round. ss 316 sheet is produced by two manufacturing processes, hot rolling and cold working. When the strength grade of low carbon stainless steel 316L plate is only a little higher than 316 steel plate. So sometimes 316l and 316 are almost the same. Another difference is that 316l coil can be used for welding treatments because of its lower carbon content.

Grade 316 Plate Properties
| GRADE | SHAPE | THICKNESS | SPECIFICATION |
| 316 | PLATE | 3/16″ – 6″ | AMS 5507 / ASTM A-240 |
| 316L | PLATE | 3/16″ – 6″ | AMS 5524 / ASTM A-240 |
Chemistry (range or maximum in %)
| GRADE |
C |
MN |
P |
S |
SI |
NI |
CR |
MO |
OTHER |
| 316 | 0.08 | 2.00 | 0.045 | 0.03 | 0.75 | 10.00/14.00 | 16.00/18.00 | 2.00 | N 0.10 MAX |
| 316L (LOW CARBON) | 0.03 | 2.00 | 0.045 | 0.03 | 0.75 | 10.00/14.00 | 16.00/18.00 | 2.00 | N 0.10 MAX |