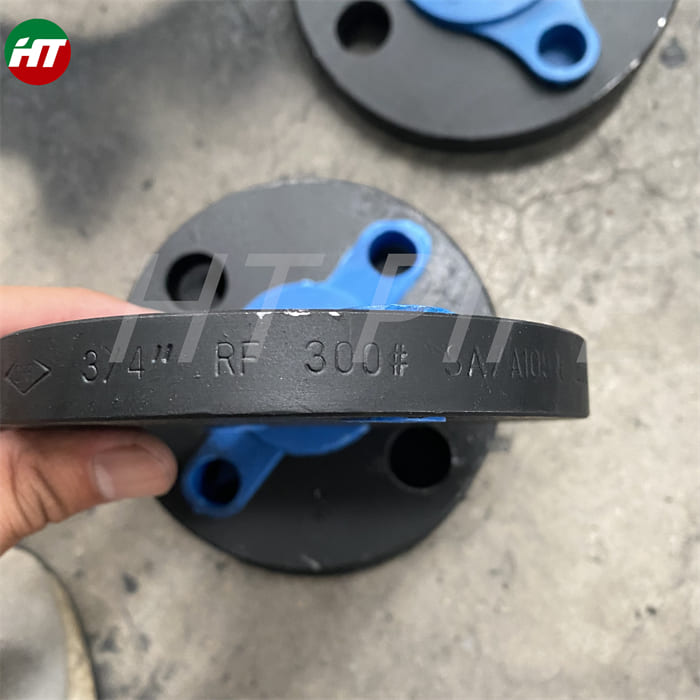
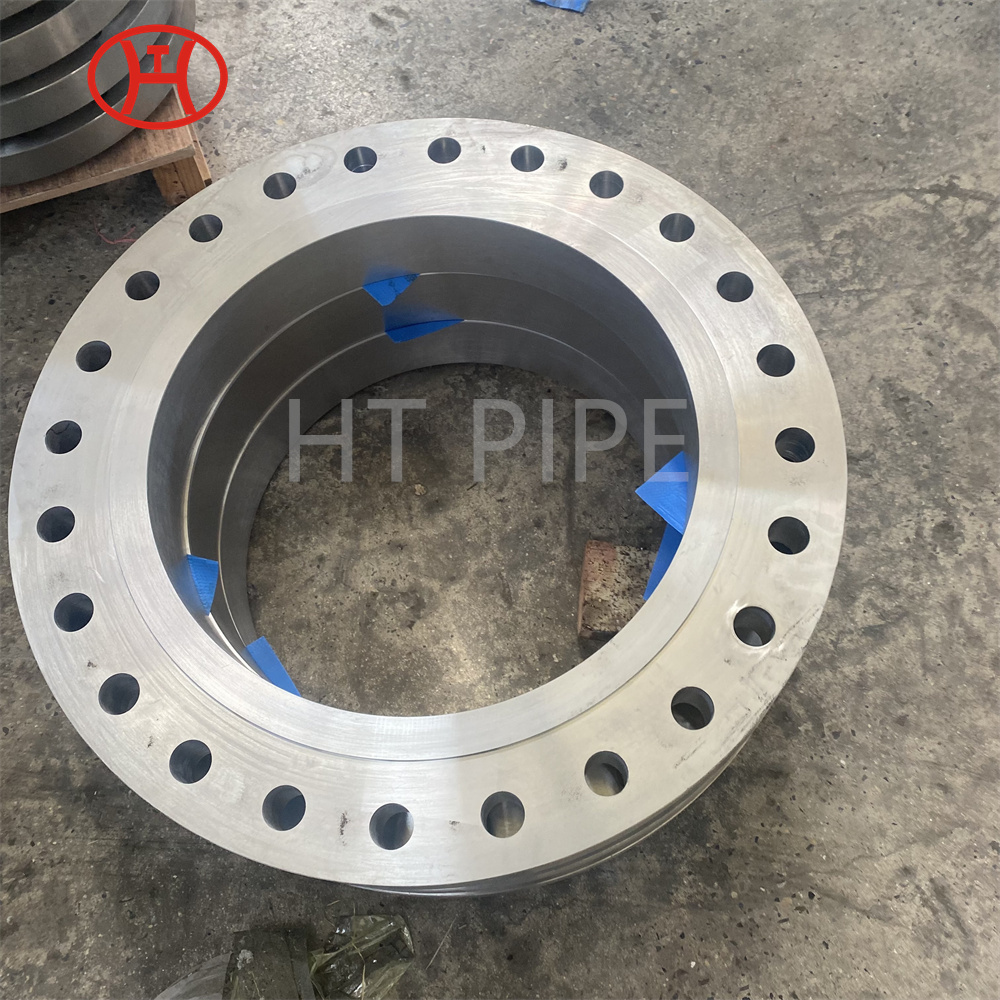
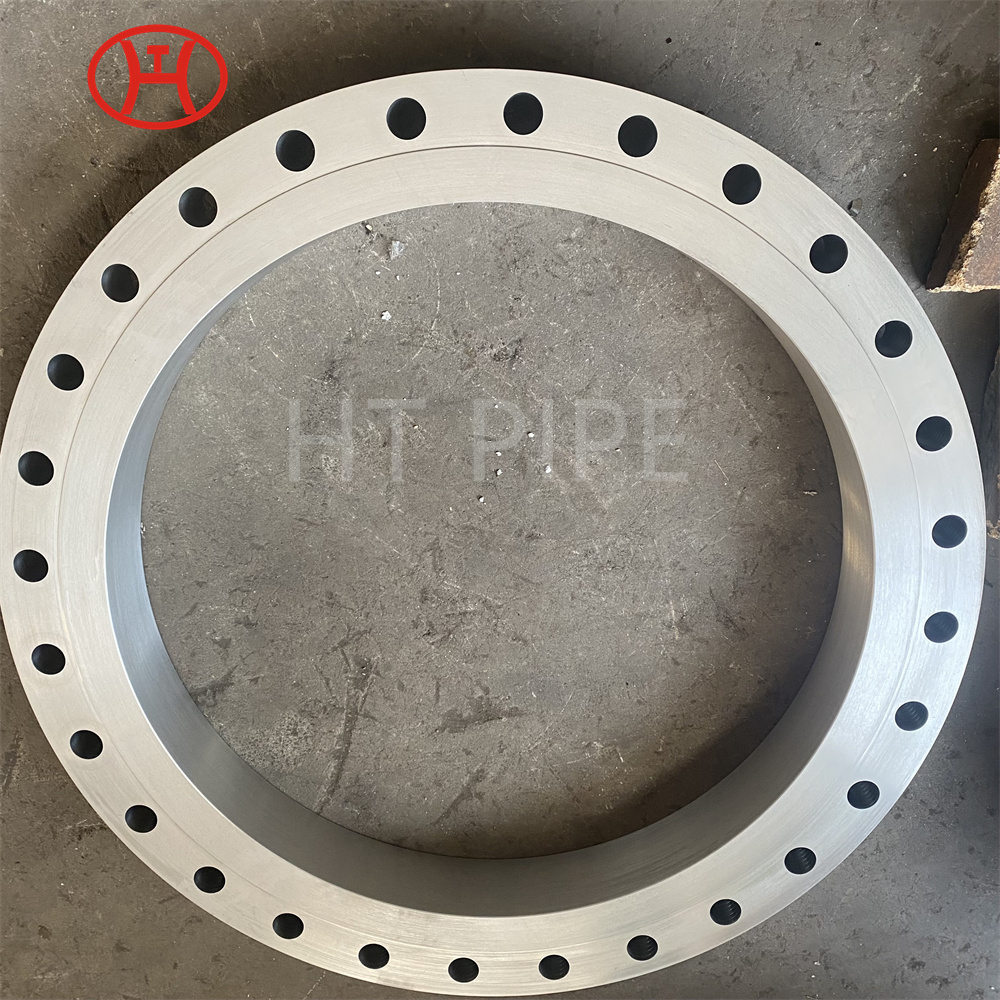
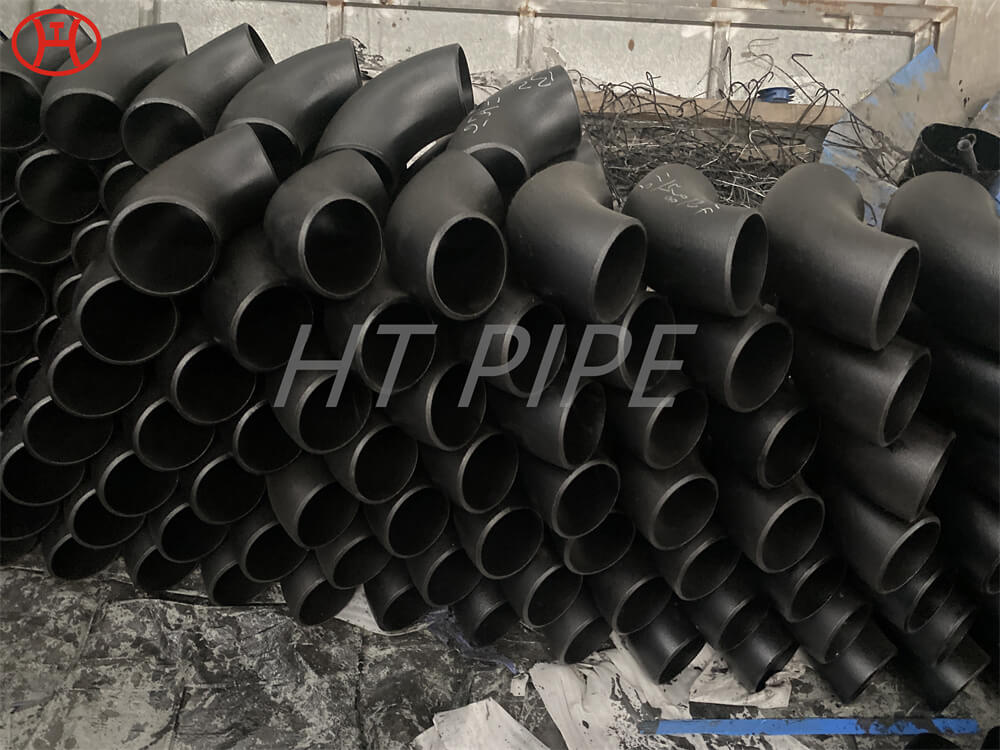
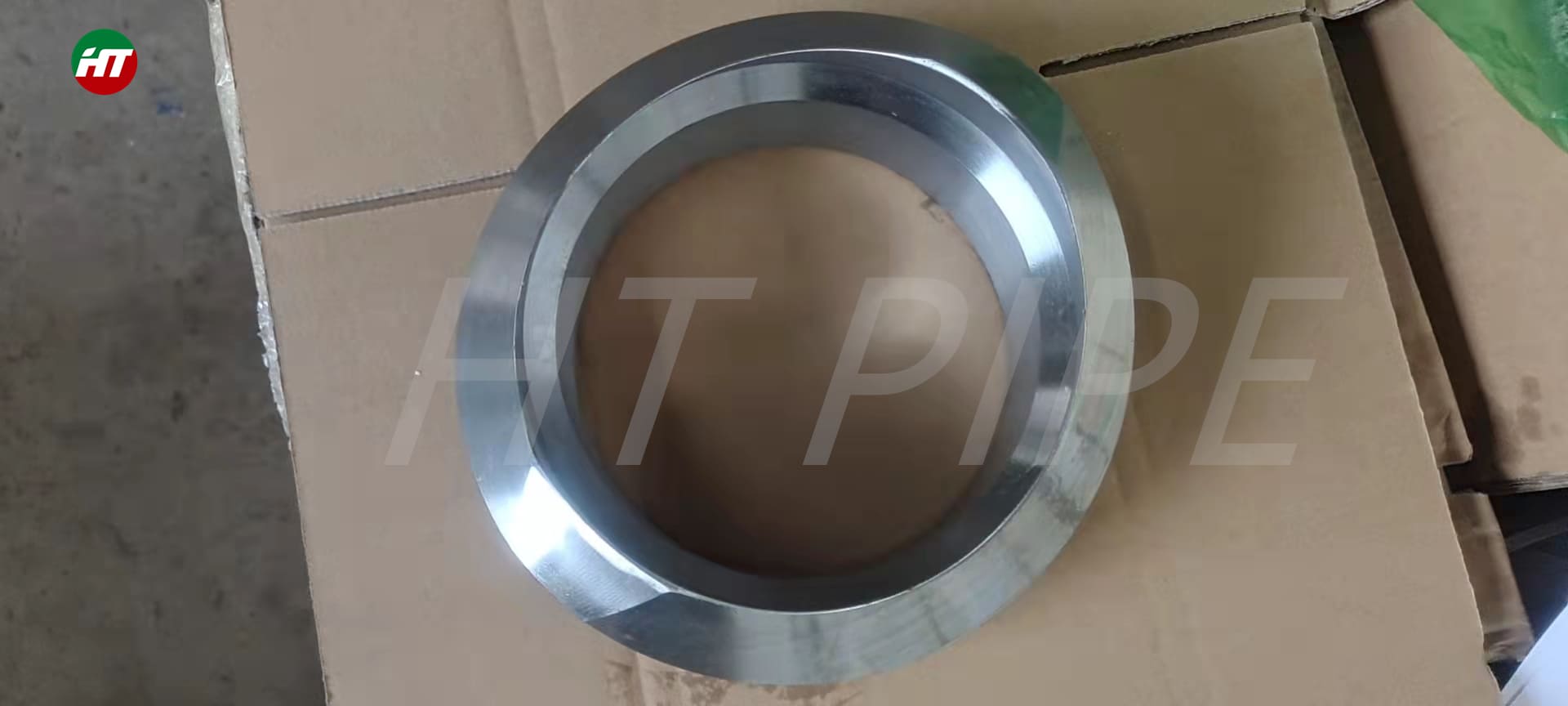
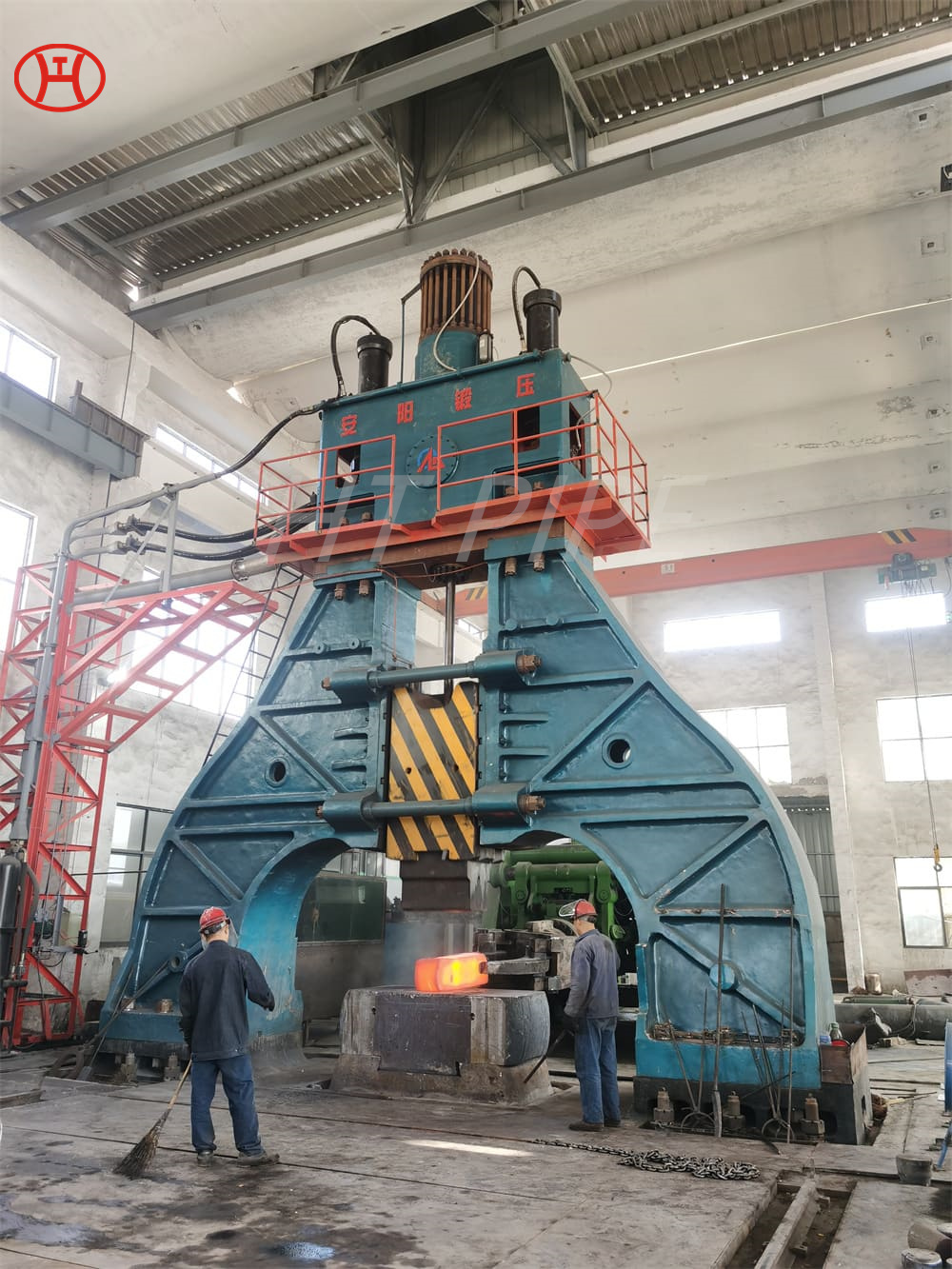
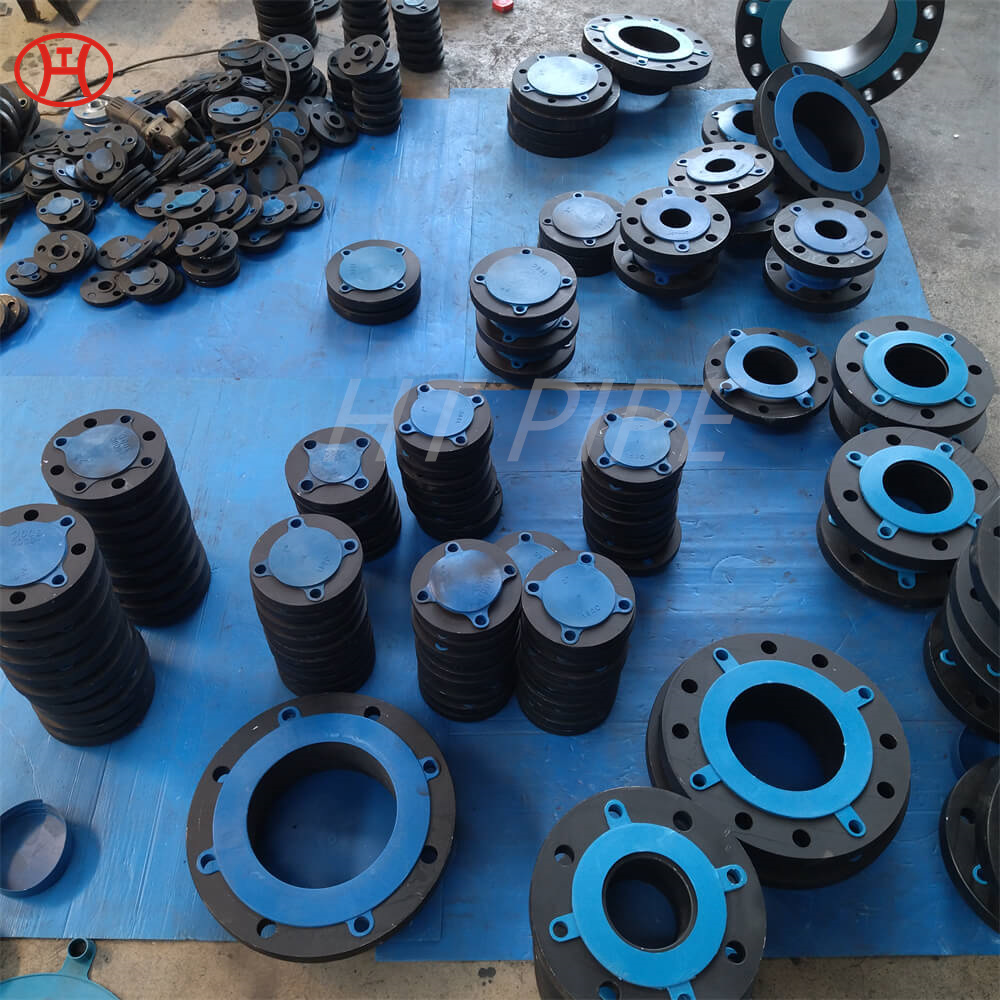
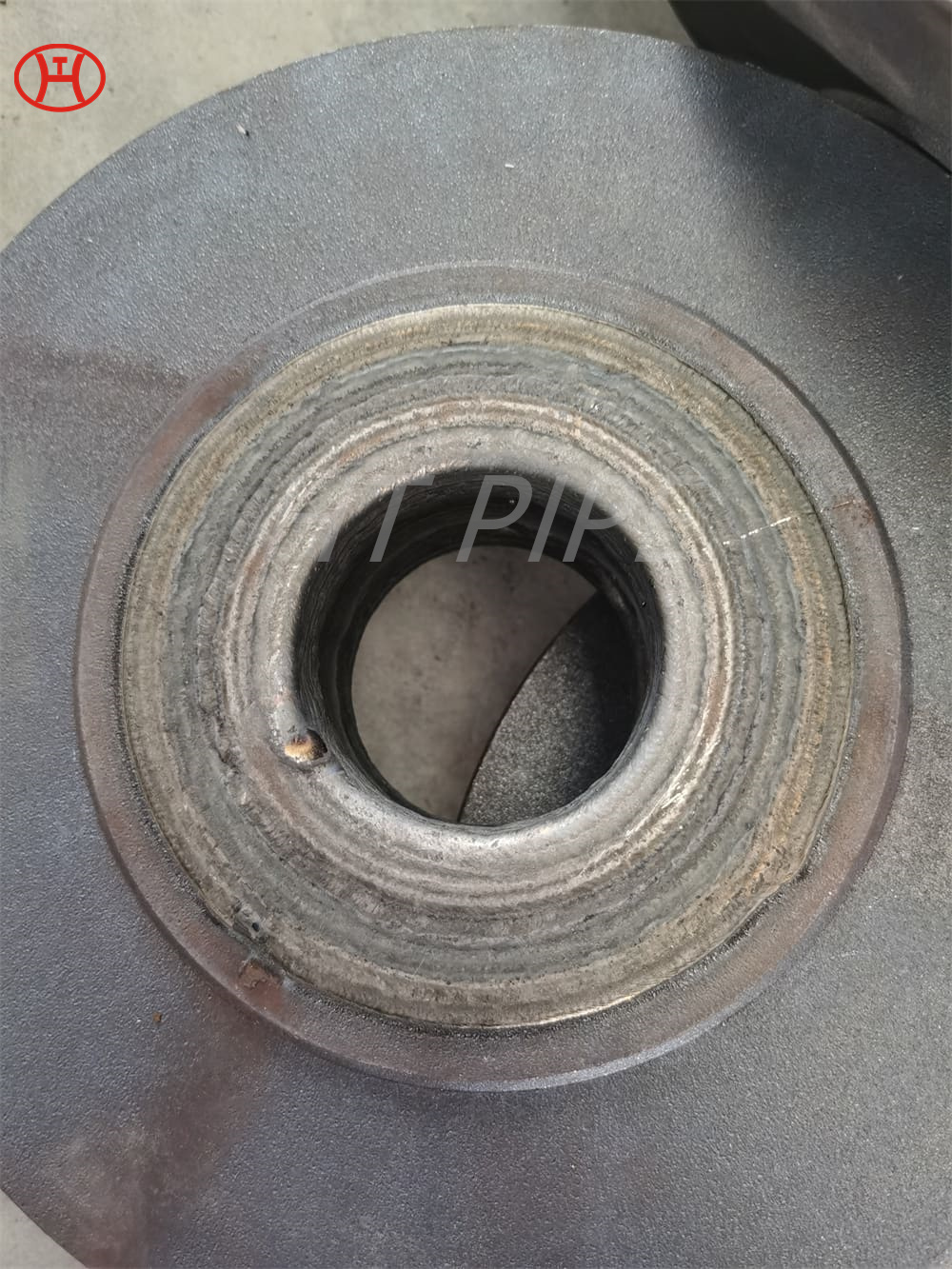
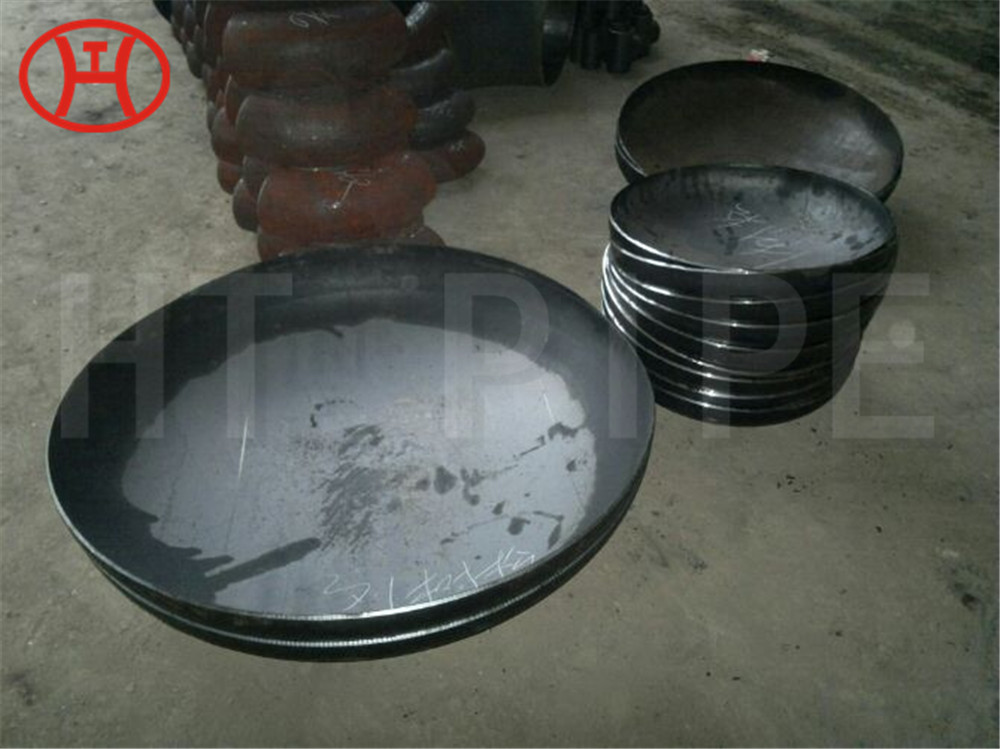
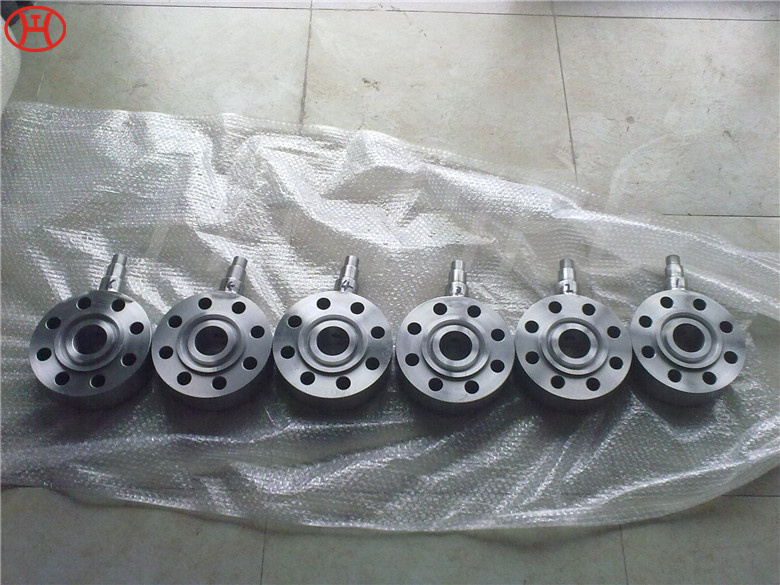
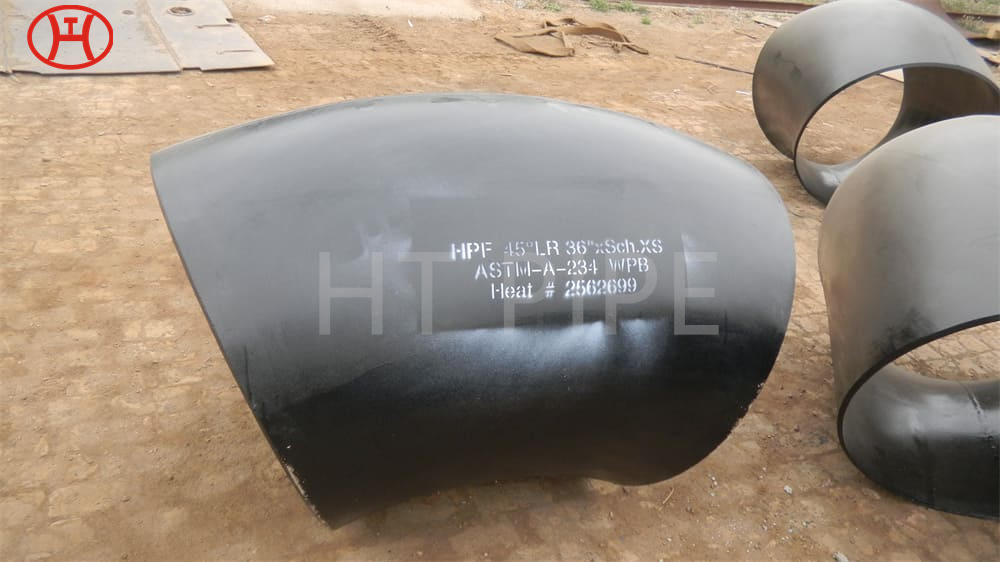
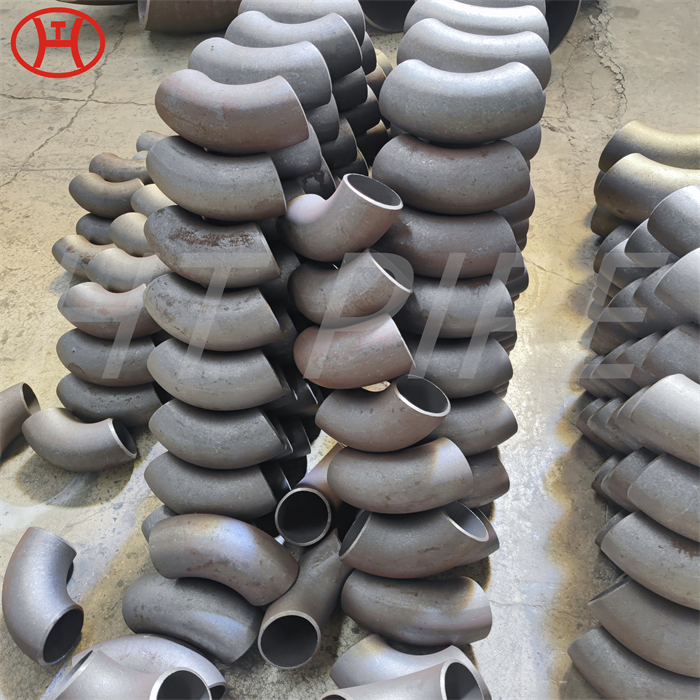
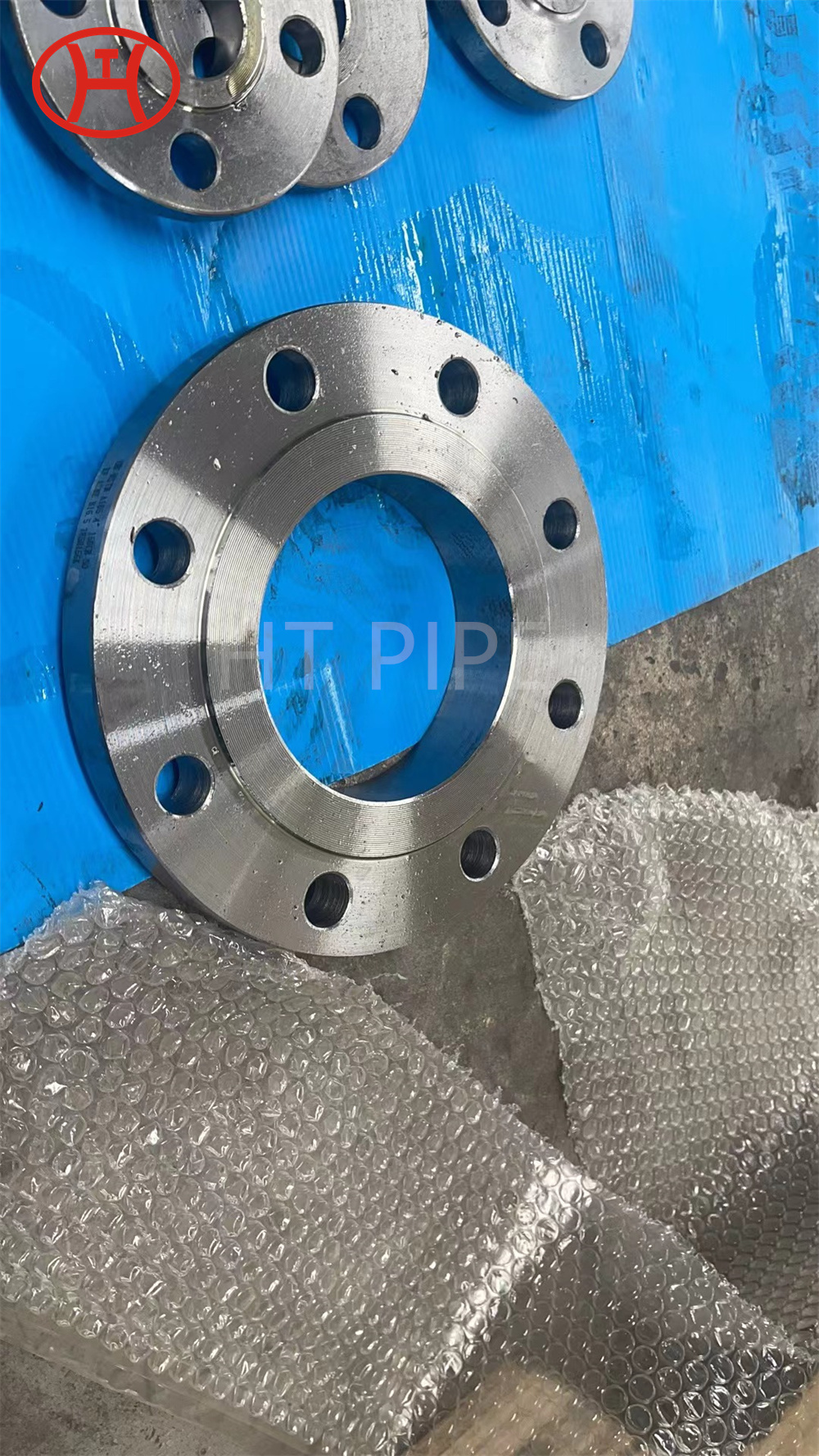
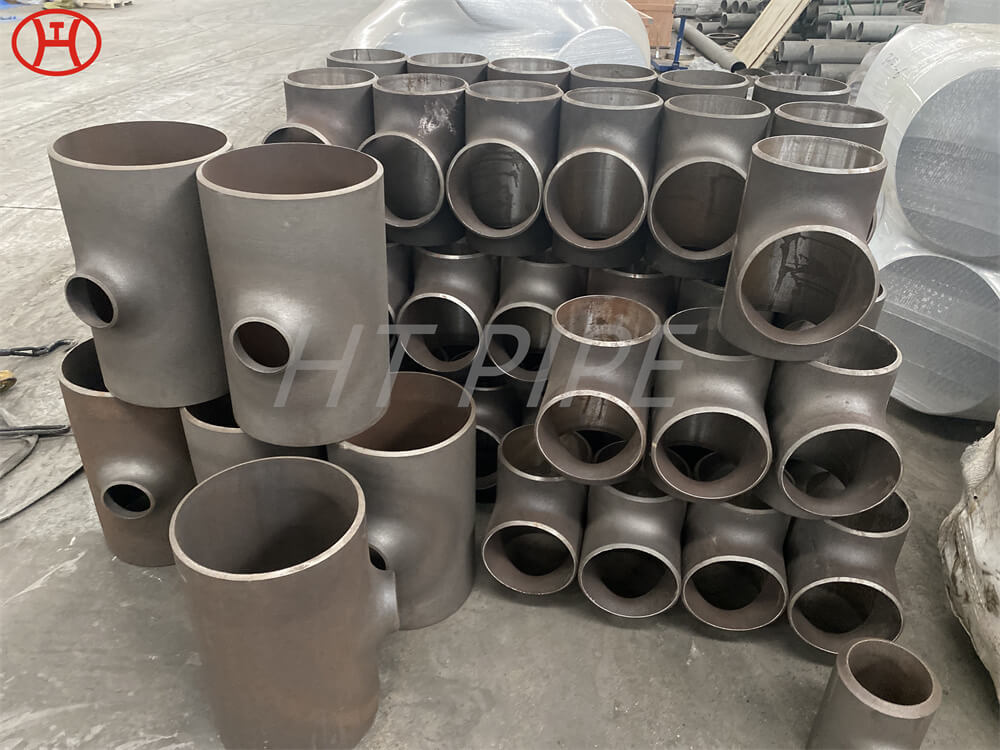
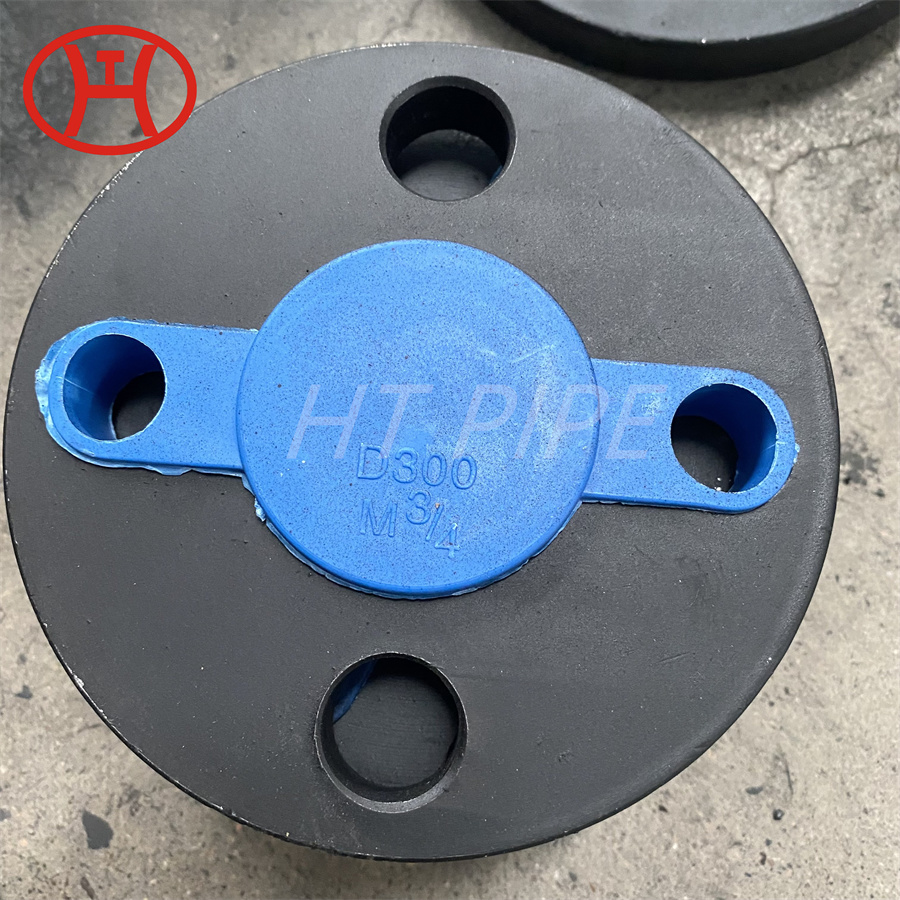
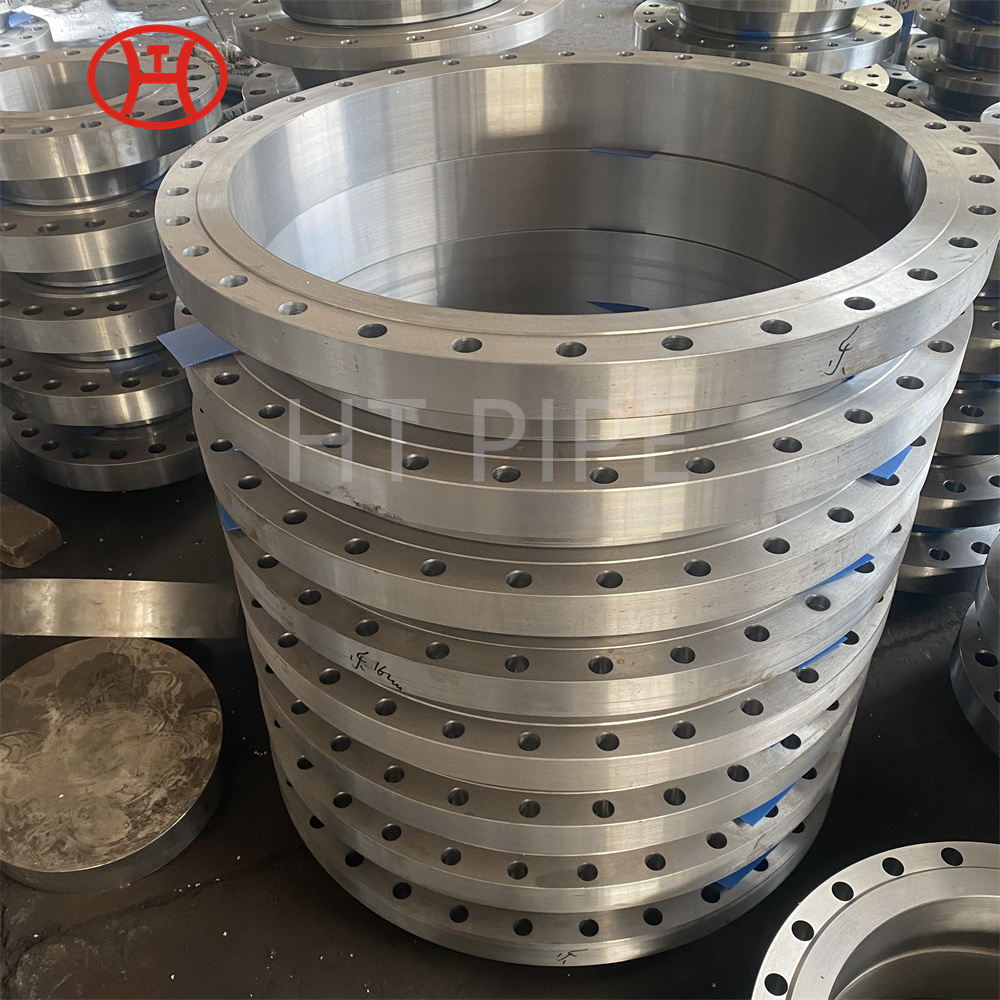
Carbon Steel Threaded Flange A105 Carbon steel flange
As carbon element content increases, the steel will become harder and stronger after heat treatment. On the contrary, it become less ductile. Where if without heat treatment, higher carbon will reduce weldability.
ASTM standards define the specific manufacturing process of the material and determine the exact chemical composition of pipes, fittings and flanges, through percentages of the permitted quantities of carbon, magnesium, nickel, etc., and are indicated by “Grade”.
For example, a carbon steel pipe can be identified with Grade A or B, a stainless-steel pipe with Grade TP304 or Grade TP321, a carbon steel fitting with Grade WPB etc.
Flanges ASTM A182 Grade F304, F304L F316L
Pipes ASTM A312 Grade TP304, TP304L, TP3016L
Fittings ASTM A403 Grade WP304, WP304L, WP316L
Furthermore, a table with frequently used ASTM Grades, arranged on Pipes, Fittings, Flanges, Valves, Bolts and Nuts, which belong together as a group.
As you may be have noted, in the table below, ASTM A105 has no Grade. Sometimes ASTM A105N is described;
N stands not for Grade, but for normalized. Normalizing is a type of heat treatment, applicable to ferrous metals only. The purpose of normalizing is to remove the internal stresses induced by heat treating, casting, forming etc.