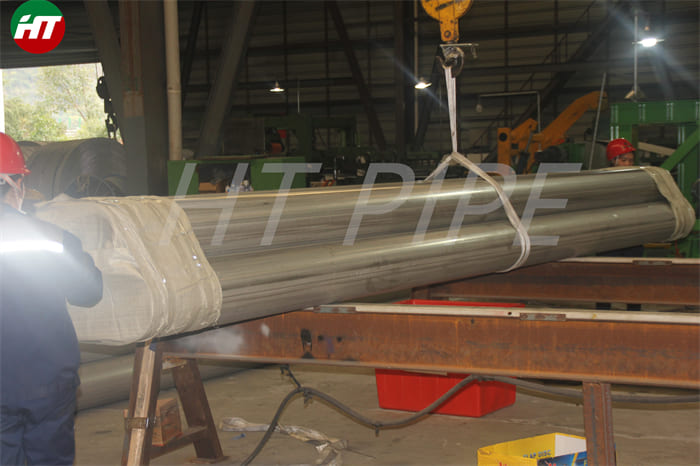
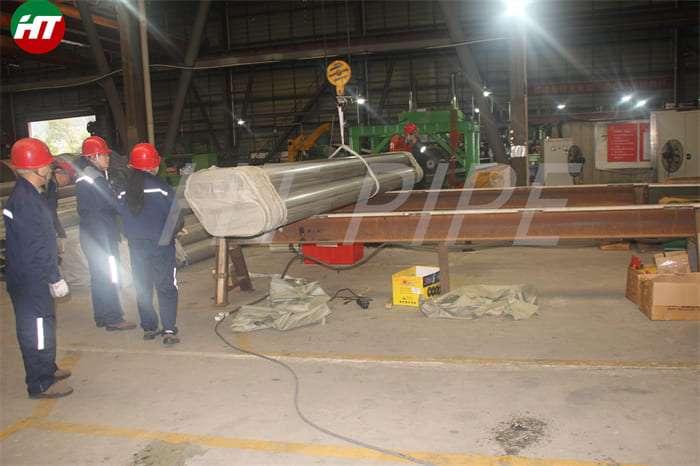
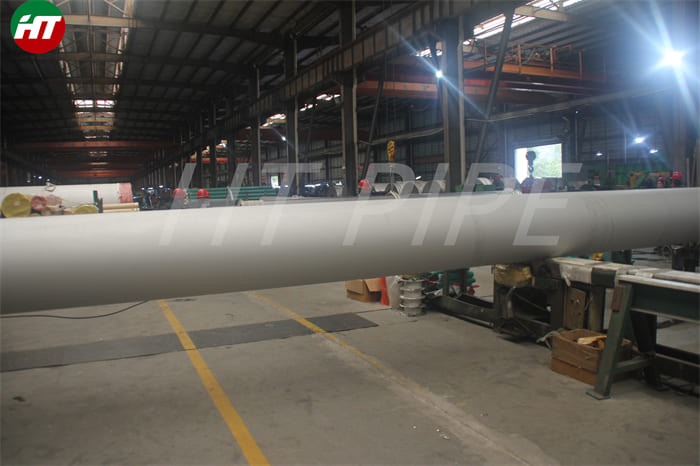
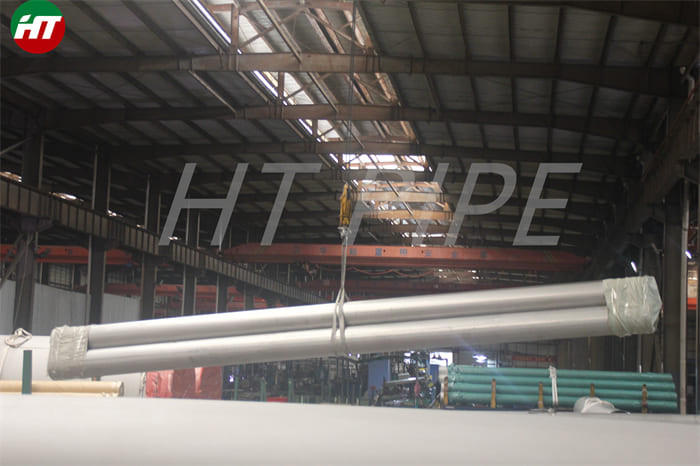
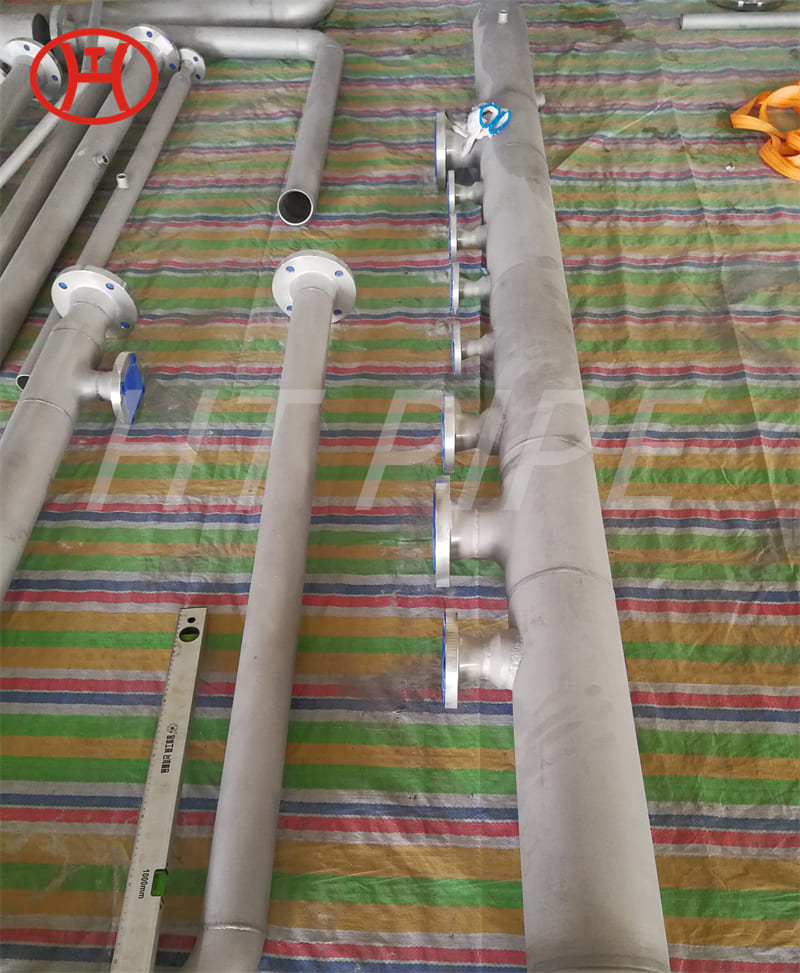
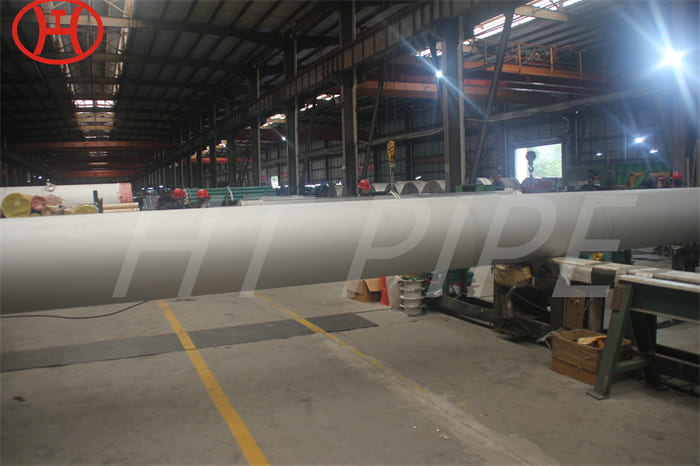
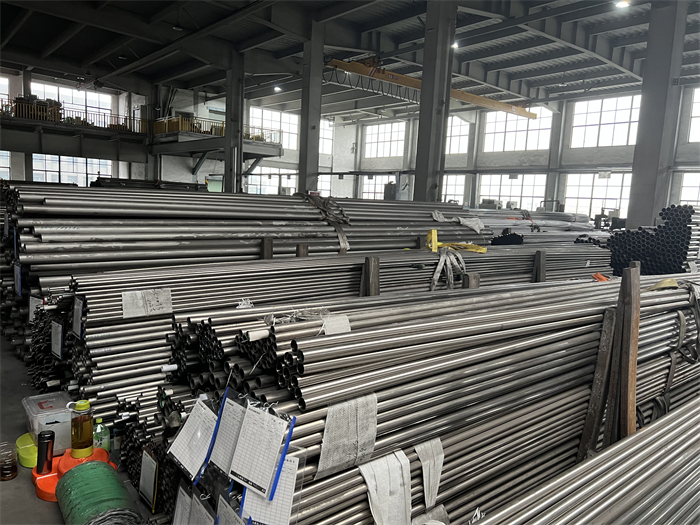
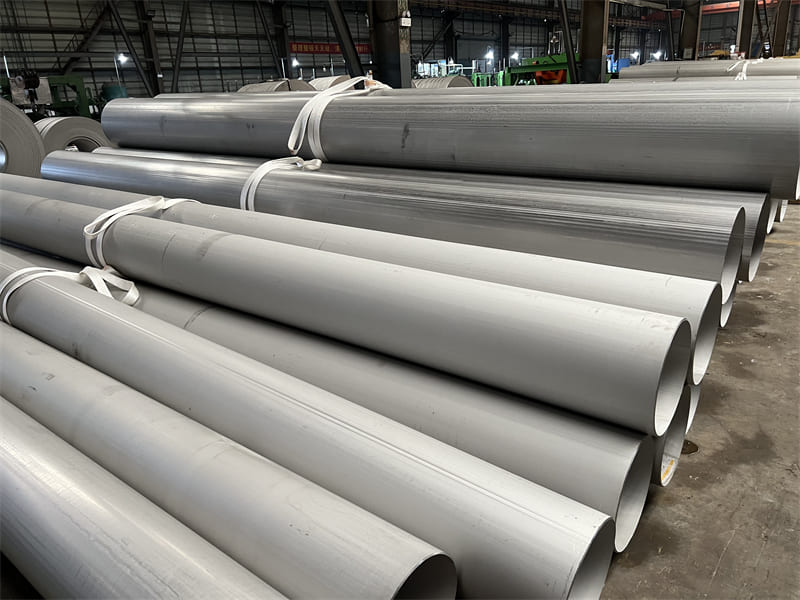
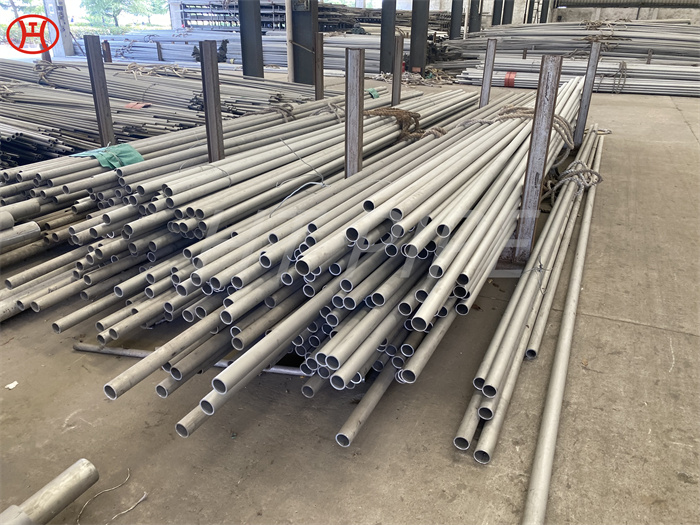
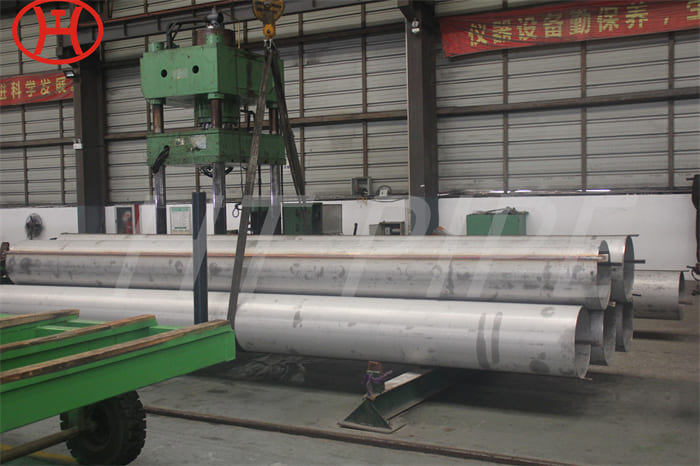
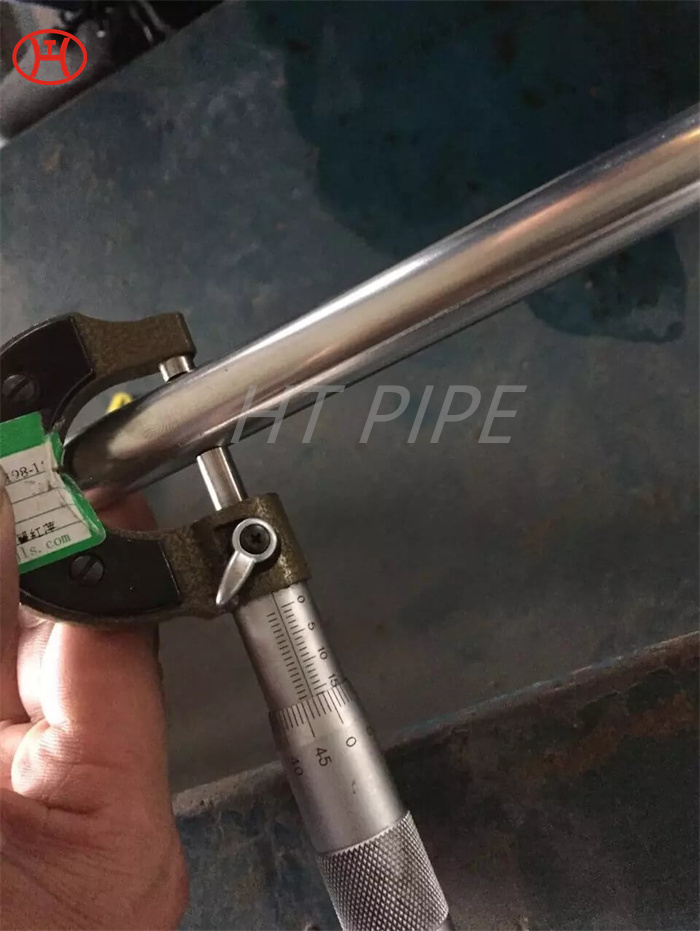
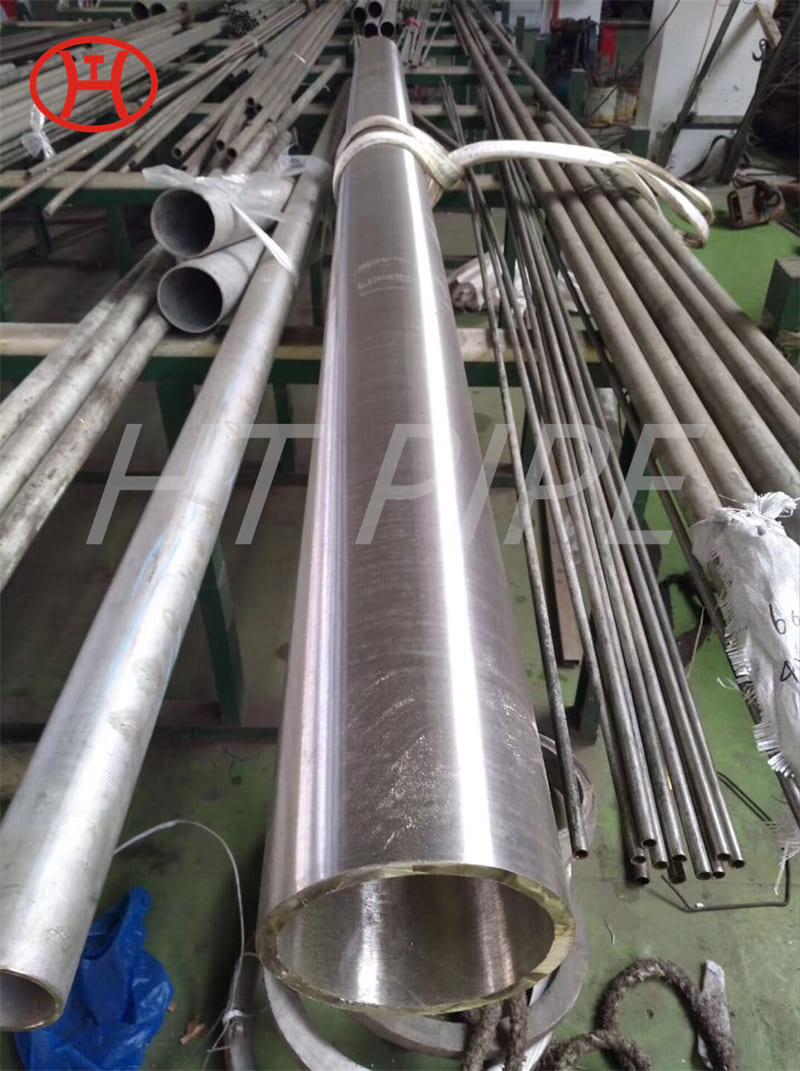
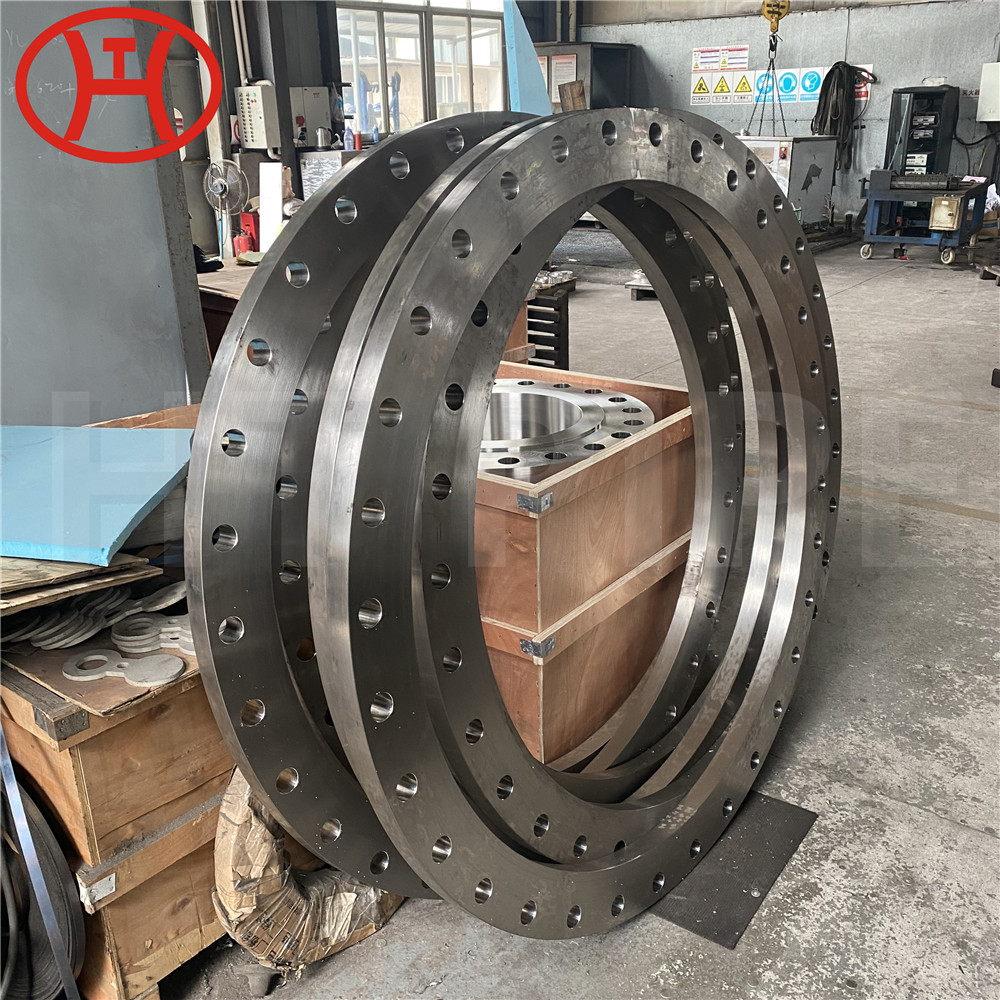
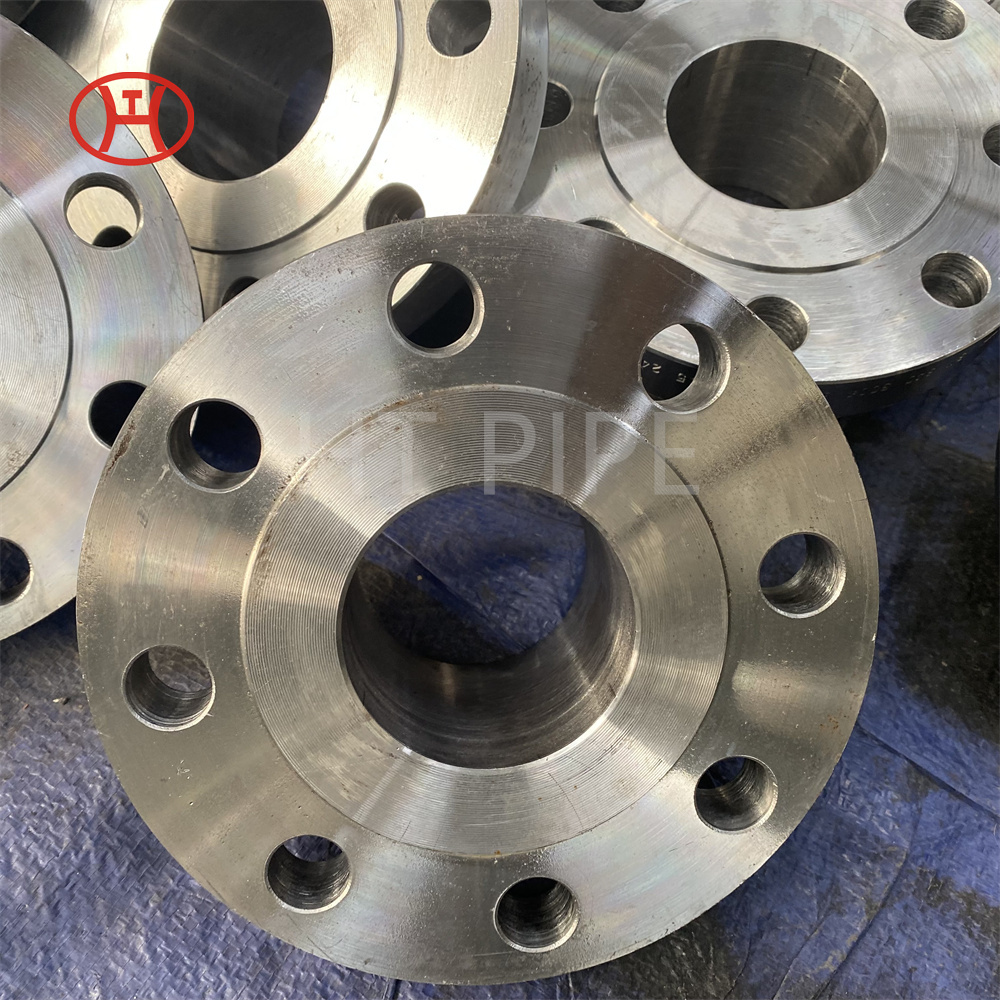
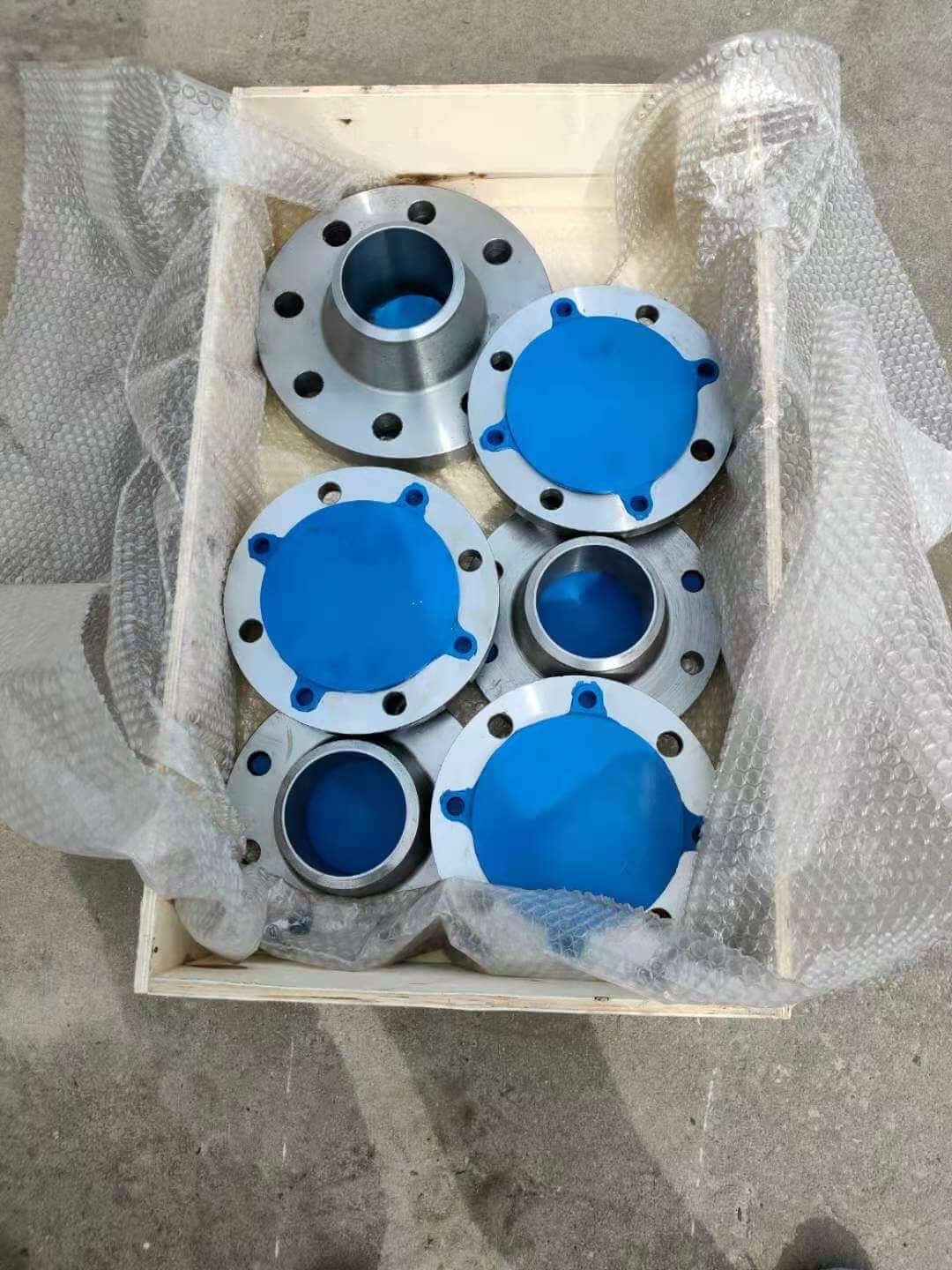
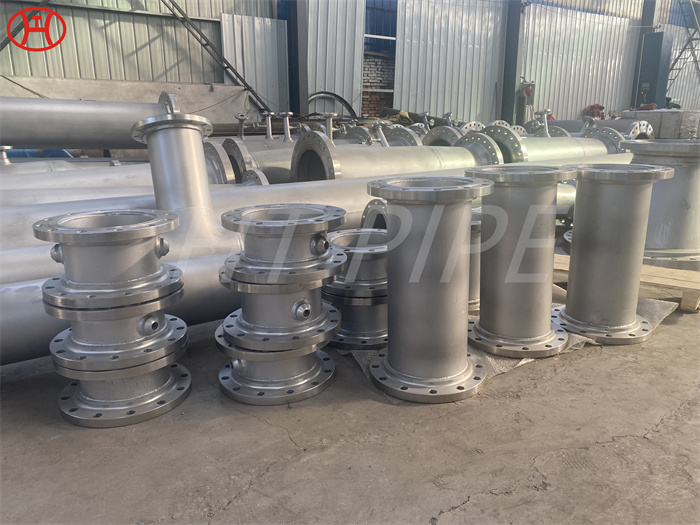
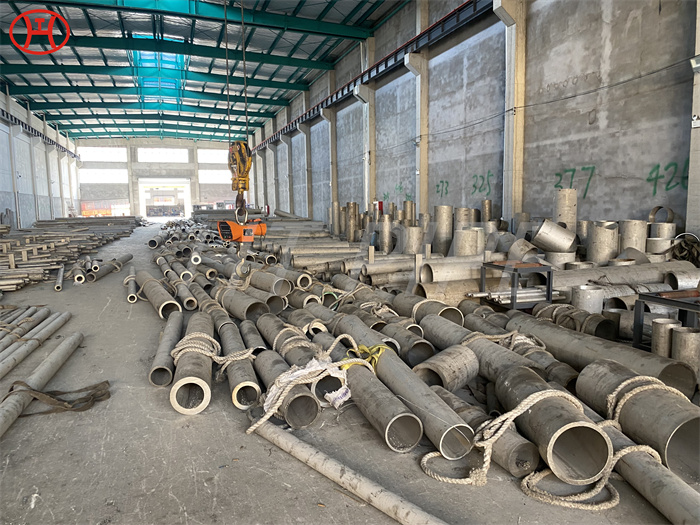
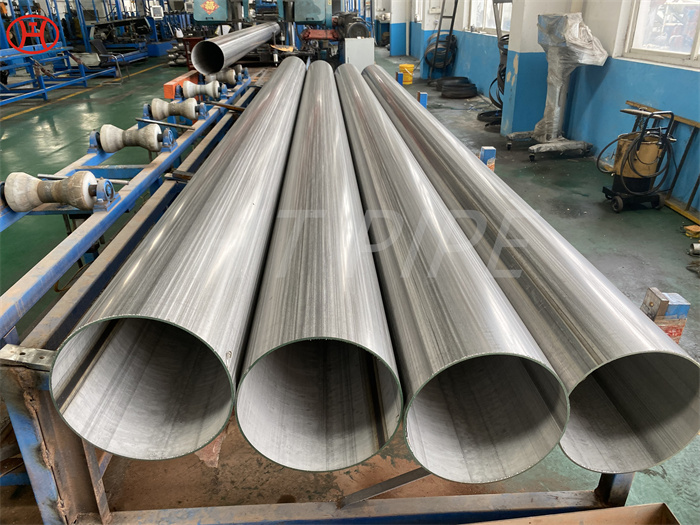
DN 1400 316 Stainless Steel Pipe 316L Stainless Steel Seamless Tube
Type 316 stainless steel is particularly effective in sour environments. This grade of steel is effective against corrosion caused by sulfuric, hydrochloric, acetic, formic and tartaric acids, as well as acidic sulfates and basic chlorides.
316L Stainless Steel Seamless Pipe | 316L Stainless Steel Seamless Tube | 316L Stainless Steel ERW Pipe | 316L Stainless Steel EFW Tube | 316L Stainless Steel Welded Pipe and Tubes in ASTM A213 / A312 / A269 / A358
Type 316L is the low carbon version of 316 stainless. With the addition of molybdenum, the 316L stainless steel pipe is popular for use in severe corrosion environments due to the materials immunity from boundary carbide precipitation (sensitisation). The 316L stainless steel pipe is widely used in heavy gauge welded components and weld annealing is only required where the material is for use in high stress environments. 316L stainless steel pipe has an extensive variety of uses especially in marine applications due to the materials high corrosion resistance.

These processes use various kinds of salts and soaps or chemical solutions which if exposed to grade 304, would surely be susceptible to getting corroded. On the other hand, the highly resilient behaviour and superior tensile strength properties of ASTM A312 tp 316 seamless pipe make this alloy grade an amazing addition to the textile industry. Moreover, the dyeing of different textile fibres often uses an assortment of techniques with varying chemicals. Some of the fibres such as nylon or silk use acids like acetic acid to facilitate the increase of dye uptake by the cloth.

Since 316 Stainless Steel seamless pipe offers good resistance to acetic acid and phosphoric acid, they can be involved in the dyeing process as well. Other fibres like cotton can increase the uptake of dye by adding salts to their dyeing bath. As the SS 316 seamless pipe is resistant to salt solutions, they can be used in several processing operations of the textile industry.
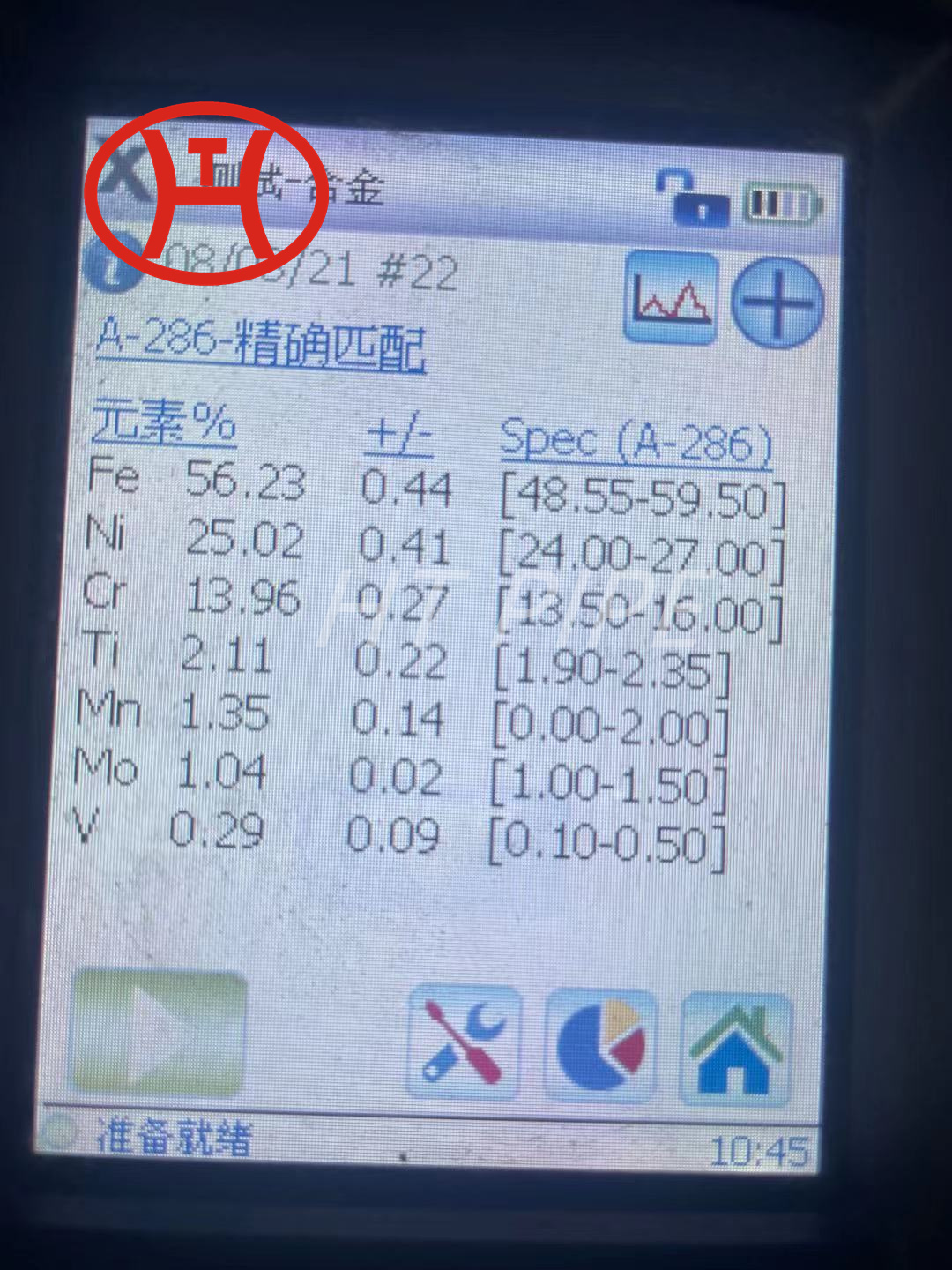
Composition of 316L Stainless Steel Pipes and Tubes
Table 1. Composition ranges for 316 grade of stainless steels.
| Grade | C | Mn | Si | P | S | Cr | Mo | Ni | N | |
| 316 | Min | – | – | – | 0 | – | 16.0 | 2.00 | 10.0 | – |
| Max | 0.08 | 2.0 | 0.75 | 0.045 | 0.03 | 18.0 | 3.00 | 14.0 | 0.10 | |
| 316L | Min | – | – | – | – | – | 16.0 | 2.00 | 10.0 | – |
| Max | 0.03 | 2.0 | 0.75 | 0.045 | 0.03 | 18.0 | 3.00 | 14.0 | 0.10 | |
| 316H | Min | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0 | – | – | 16.0 | 2.00 | 10.0 | – |
| max | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.75 | 0.045 | 0.03 | 18.0 | 3.00 | 14.0 | – |
Mechanical Properties of 316L Stainless Steel Pipes and Tubes
Table 2. Mechanical properties of 316 grade stainless steels.
| Grade | Tensile Str (MPa) min |
Yield Str 0.2% Proof (MPa) min |
Elong (% in 50mm) min |
Hardness | |
| Rockwell B (HR B) max | Brinell (HB) max | ||||
| 316 | 515 | 205 | 40 | 95 | 217 |
| 316L | 485 | 170 | 40 | 95 | 217 |
| 316H | 515 | 205 | 40 | 95 | 217 |