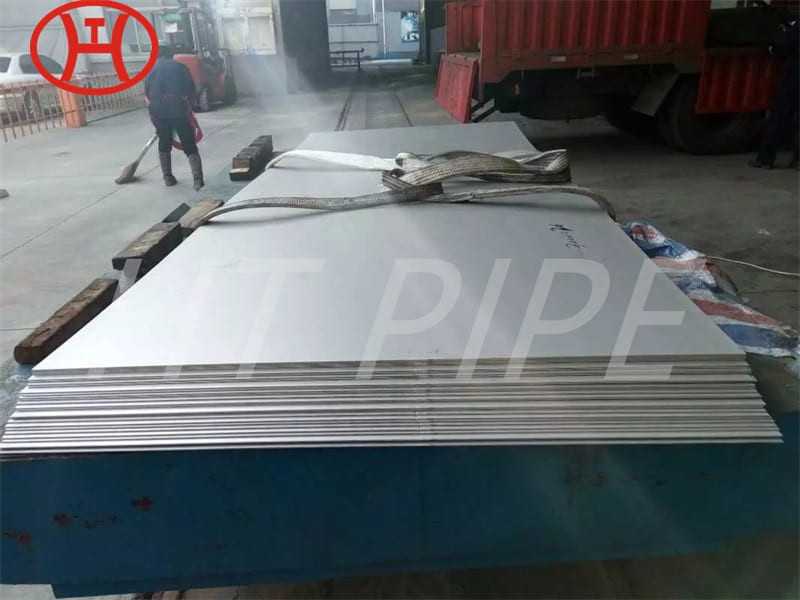
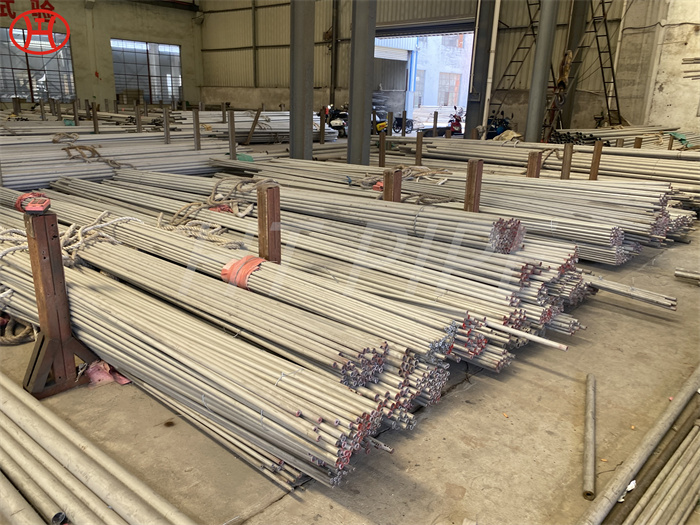
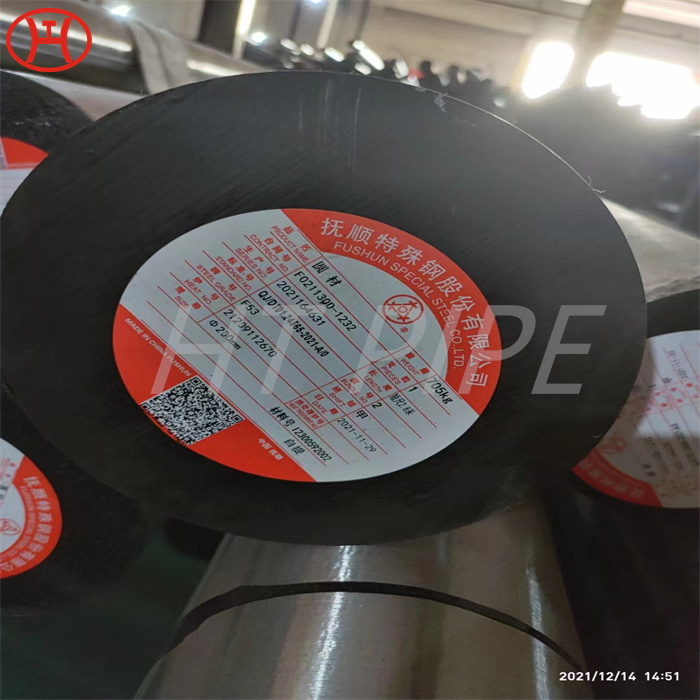
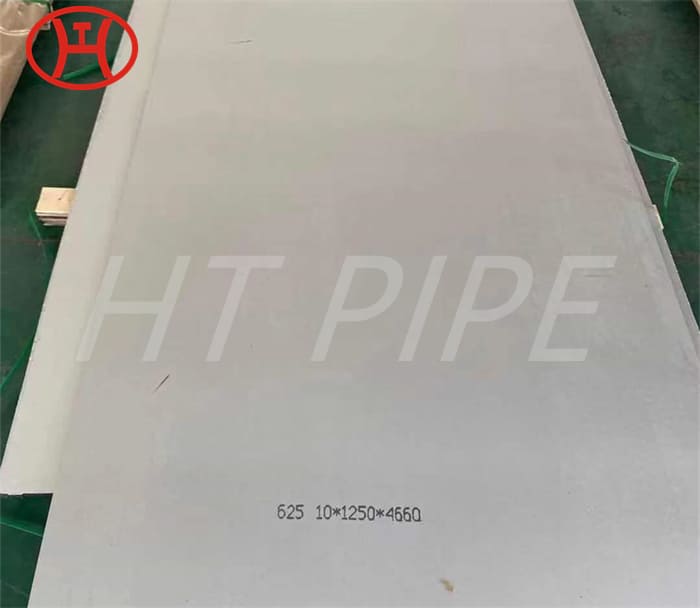
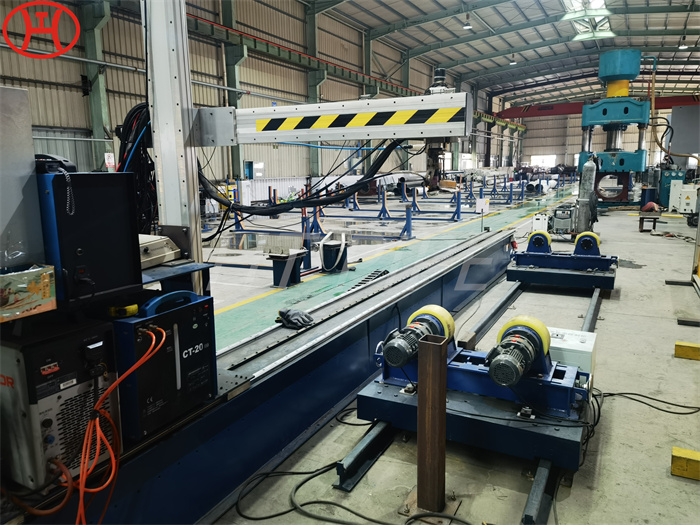
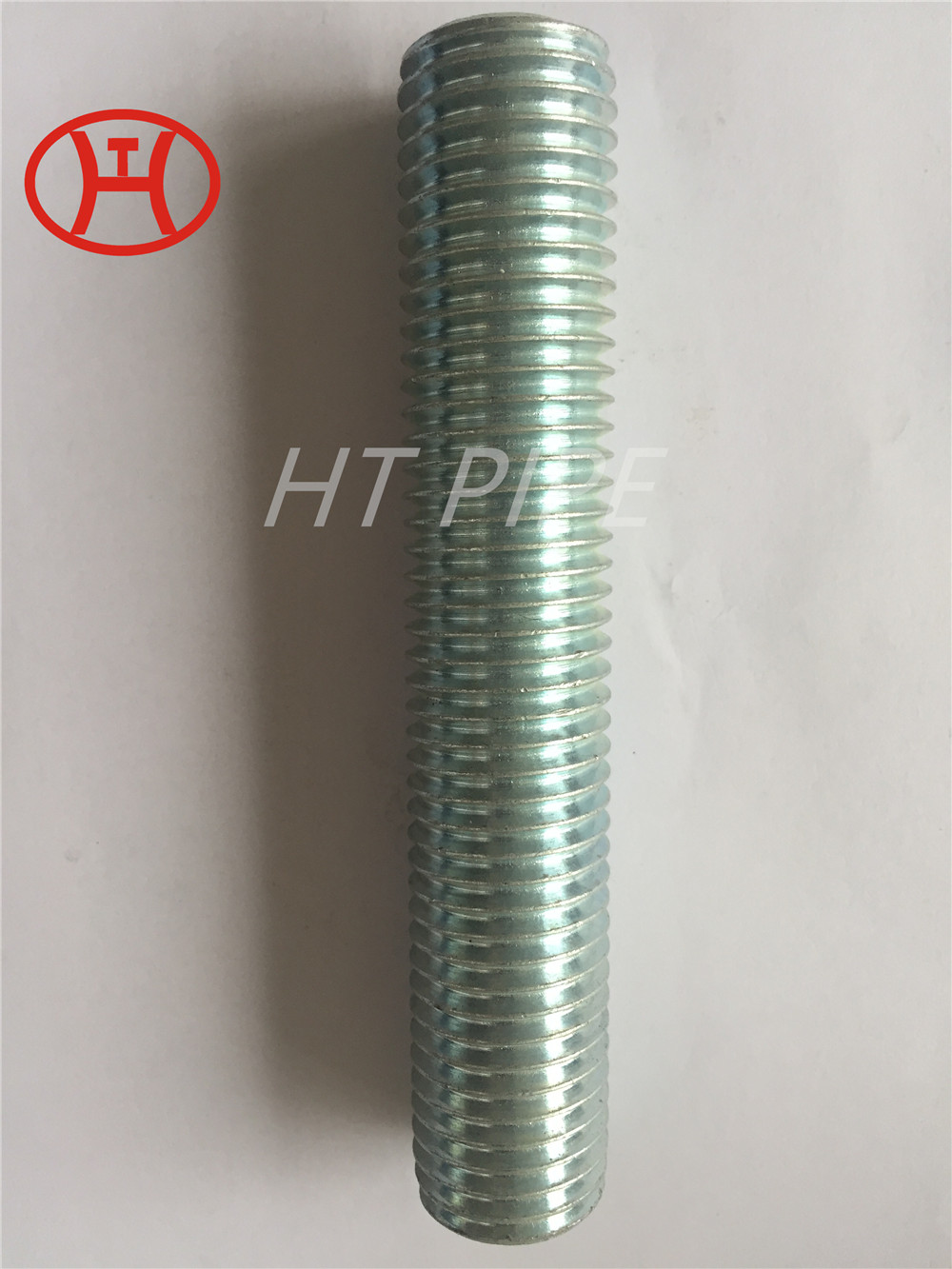
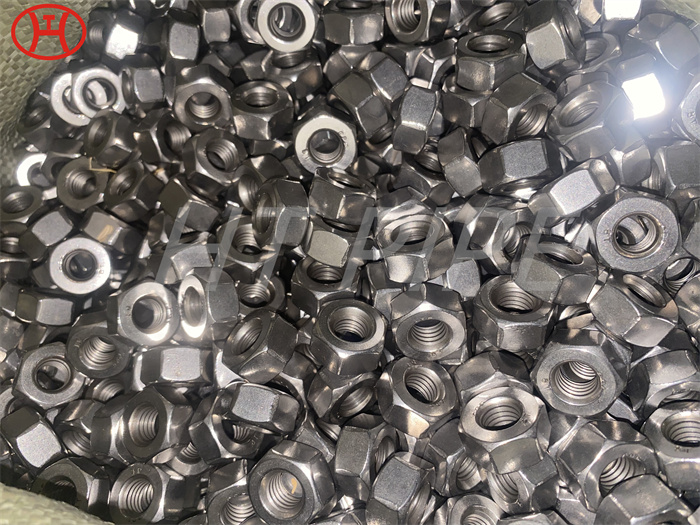
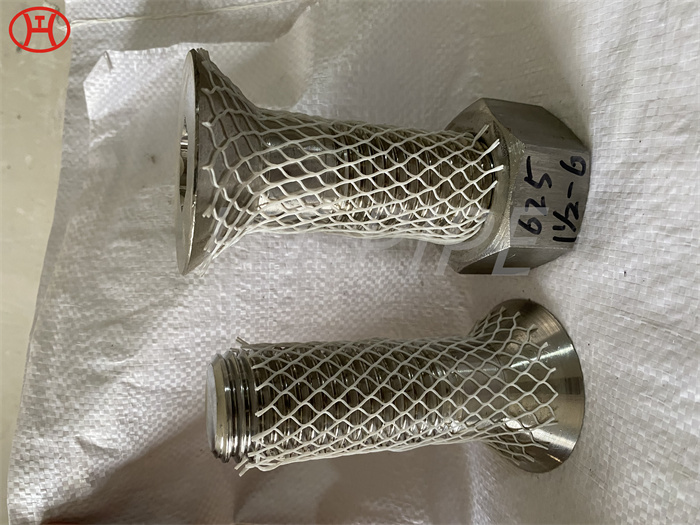
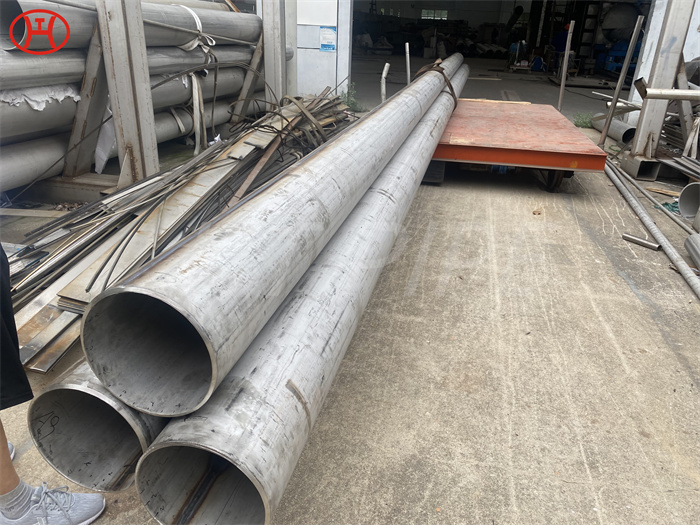
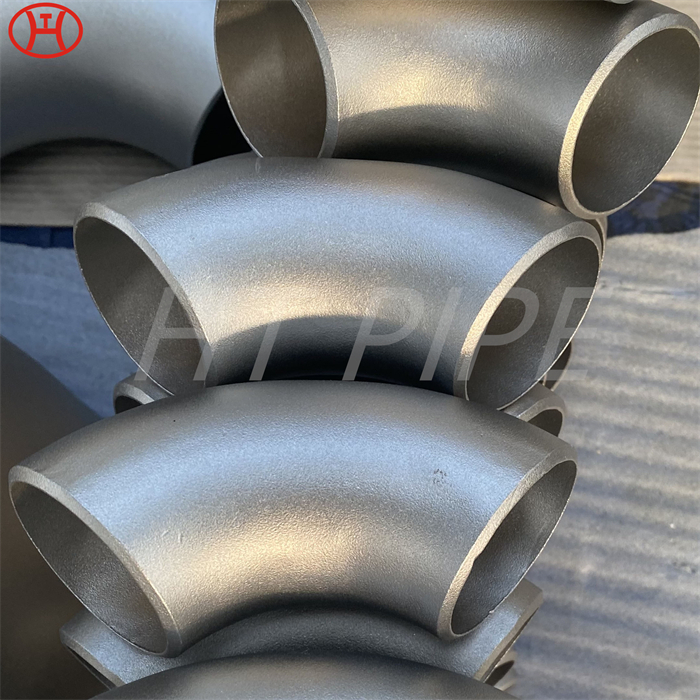
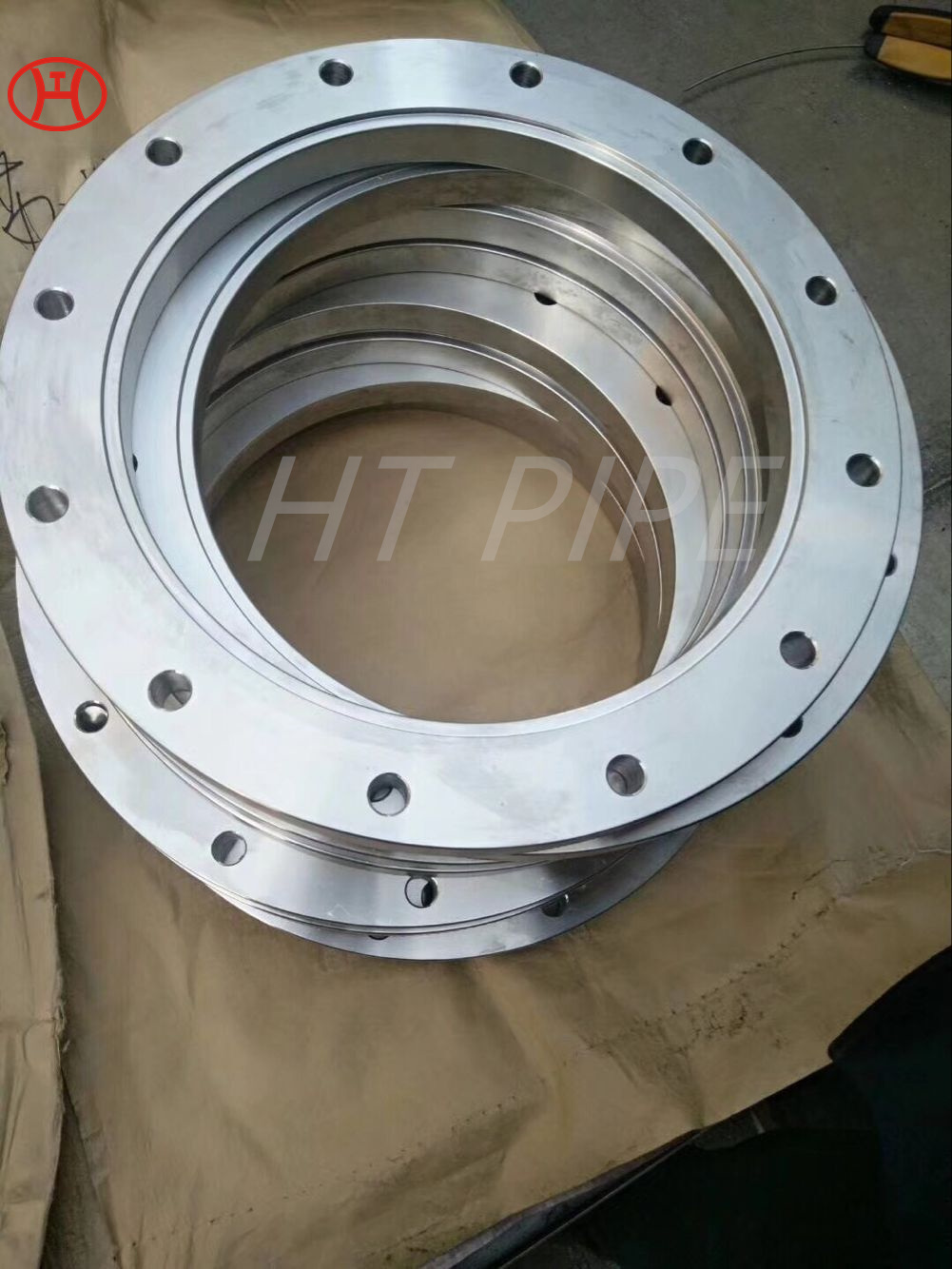
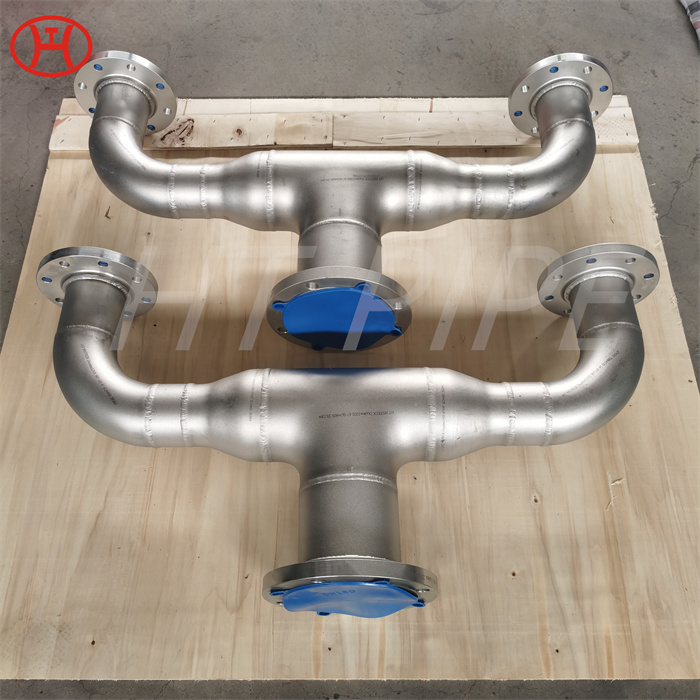
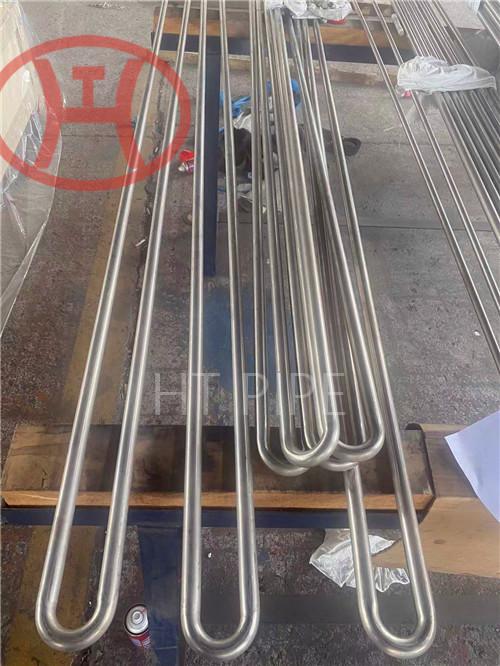
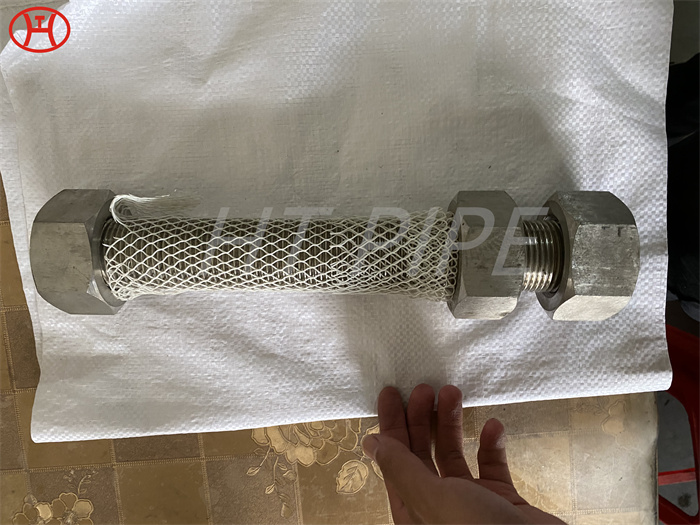
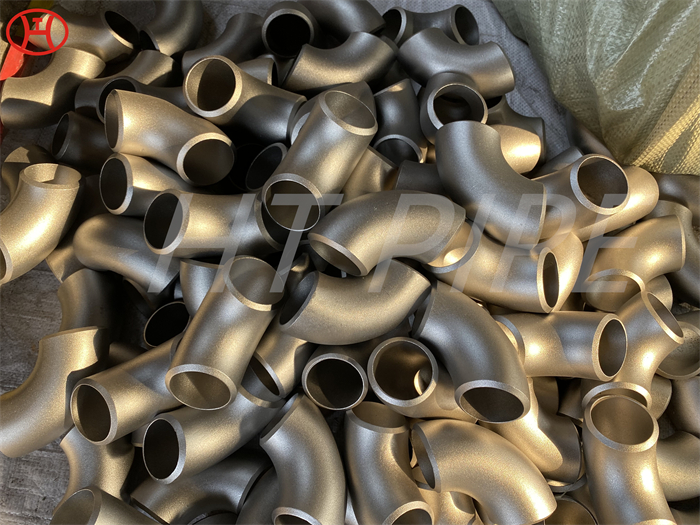
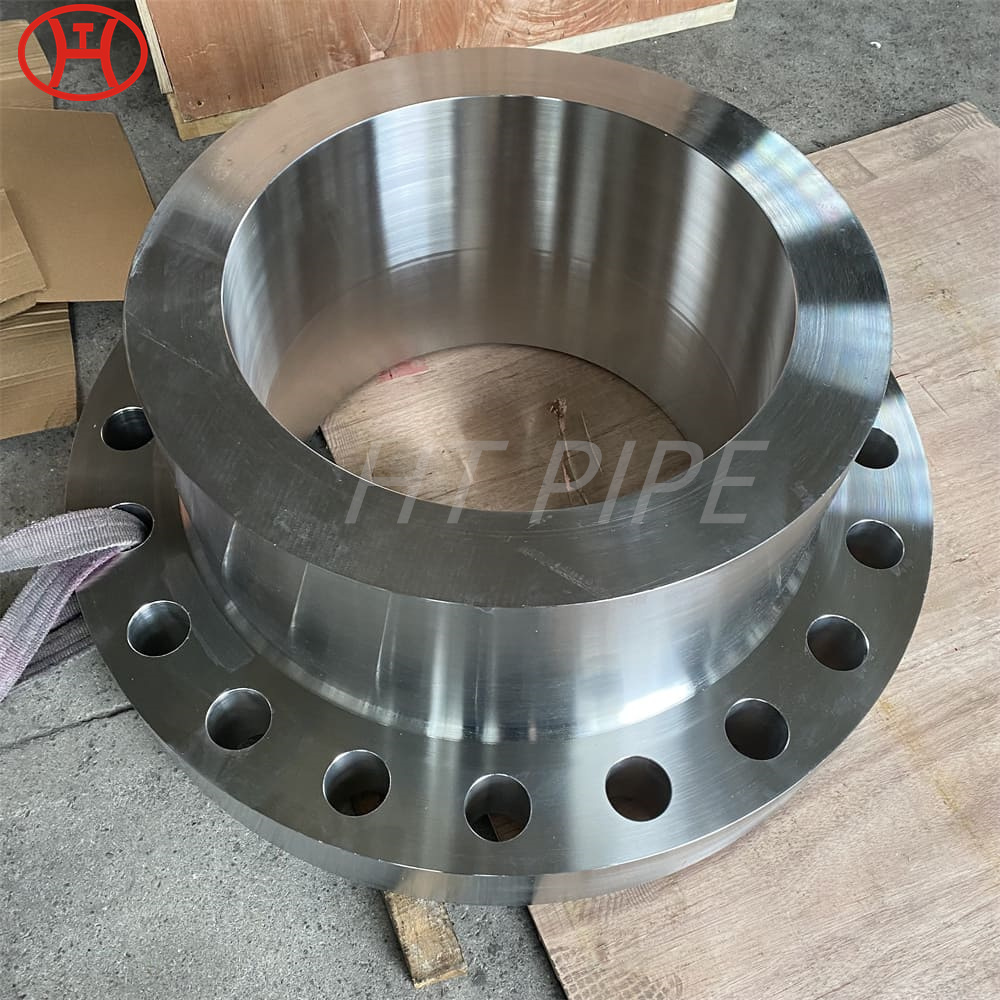
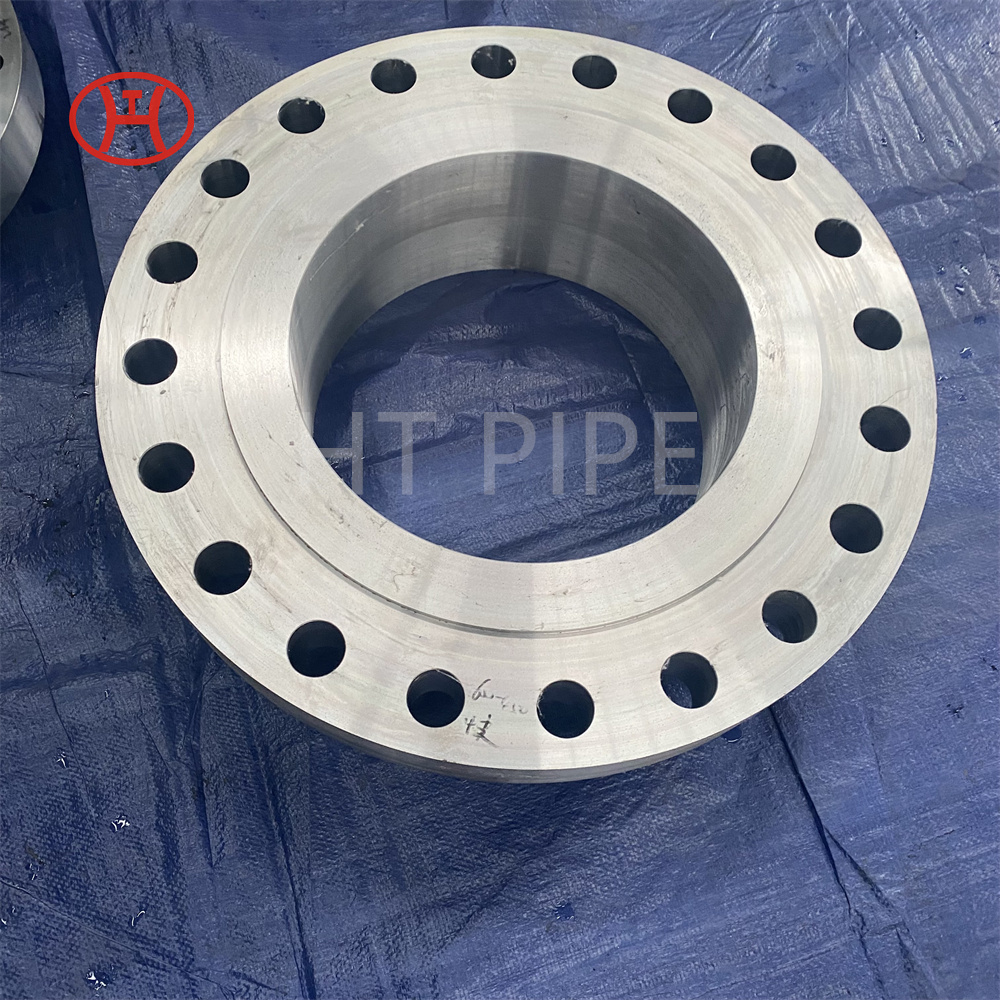
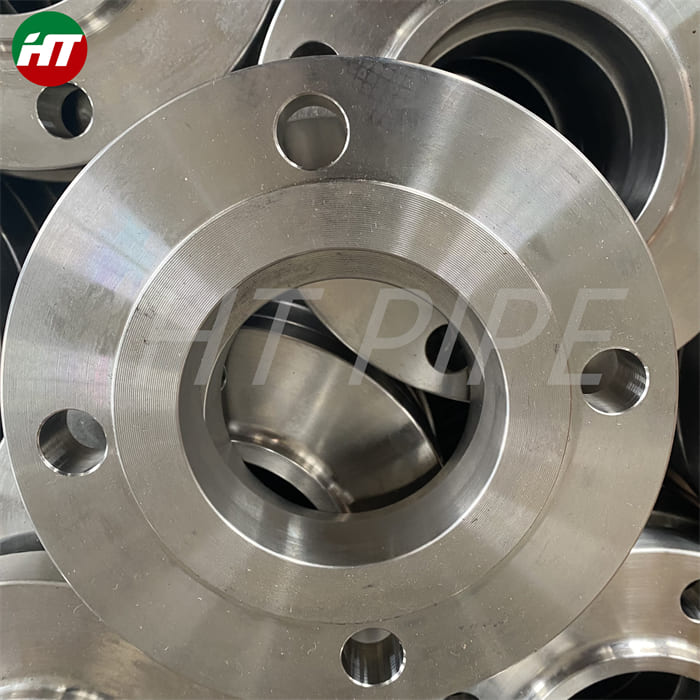
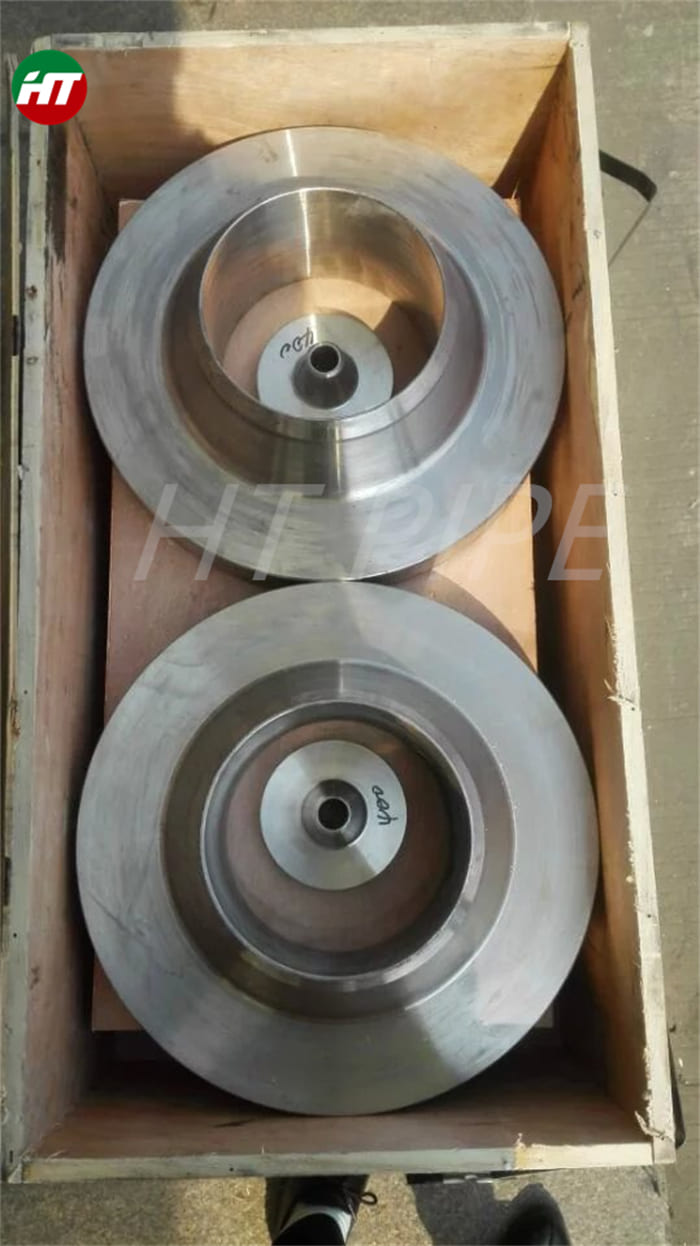
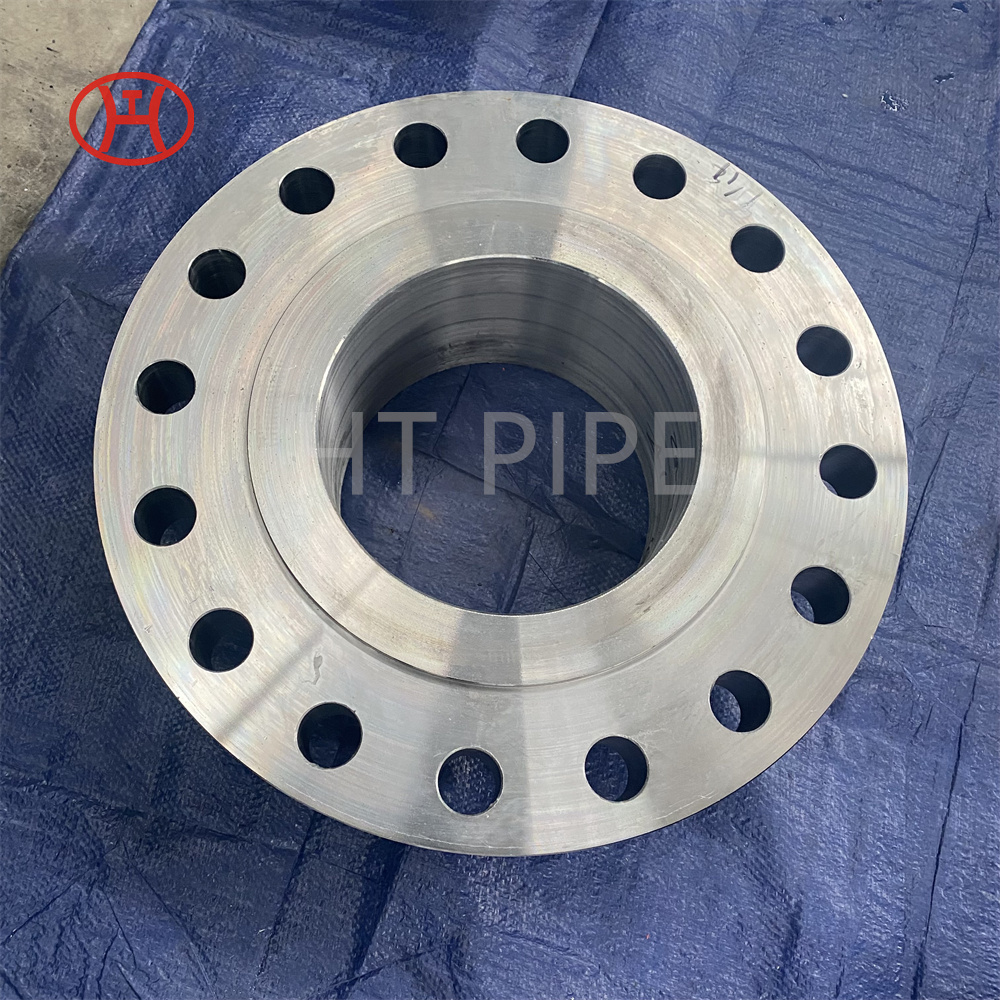
Heat treatment of inconel 625 flanges for Chemical process equipment for reducing
Tempering: The quenched workpiece is heated to an appropriate temperature below the critical point AC1 for a certain period of time, and then cooled by a method that meets the requirements to obtain the required structure and properties.
Quenching and tempering: It is generally customary to combine heat treatment with quenching and high temperature tempering as quenching and tempering. Quenching and tempering treatment is widely used in various important structural parts, especially those connecting rods, bolts, gears and shafts that work under alternating loads. The tempered sorbite structure is obtained after quenching and tempering treatment, and its mechanical properties are better than the normalized sorbite structure with the same hardness. Its hardness depends on the high temperature tempering temperature and is related to the tempering stability of the steel and the size of the workpiece section, generally between HB200-350.