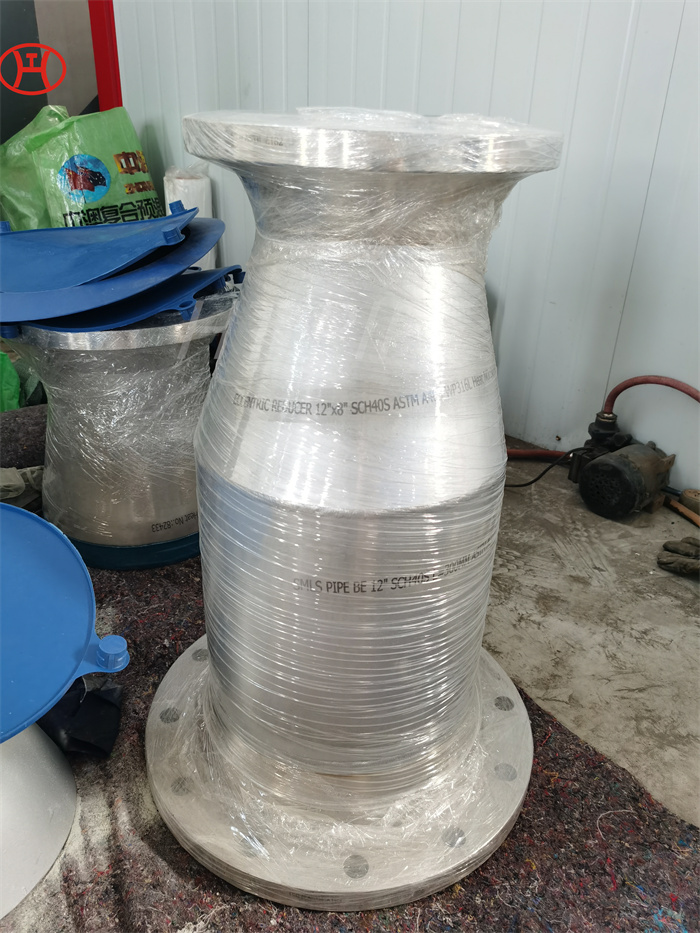
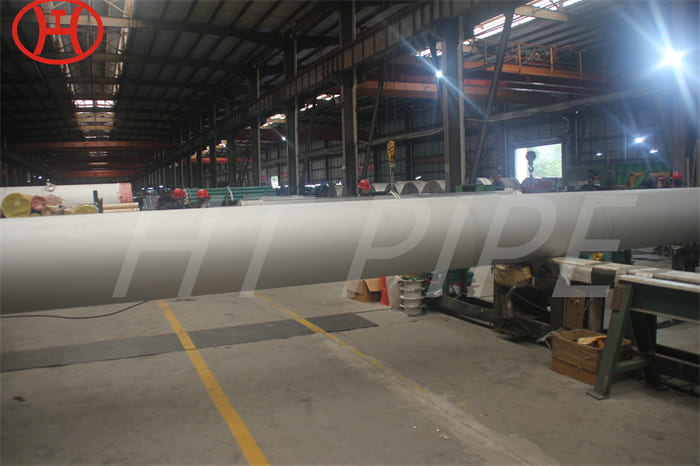
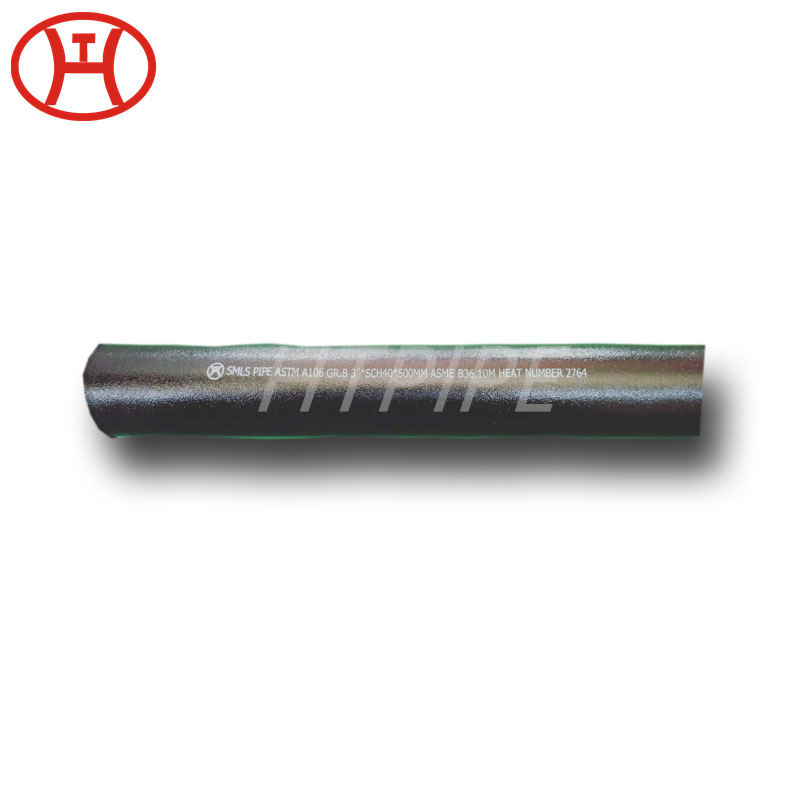
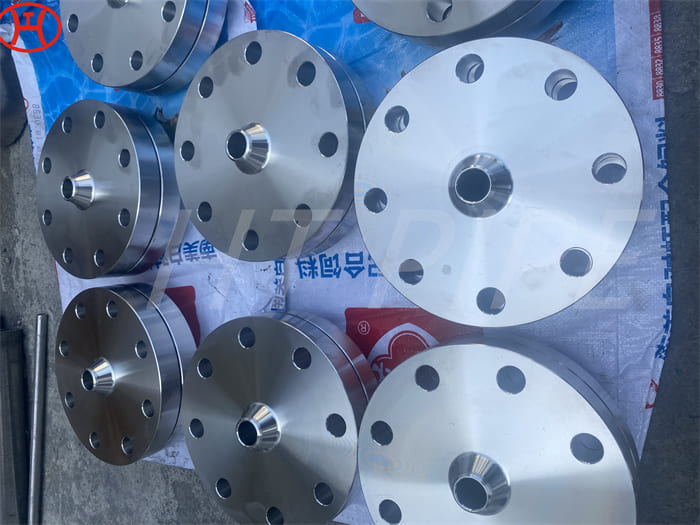
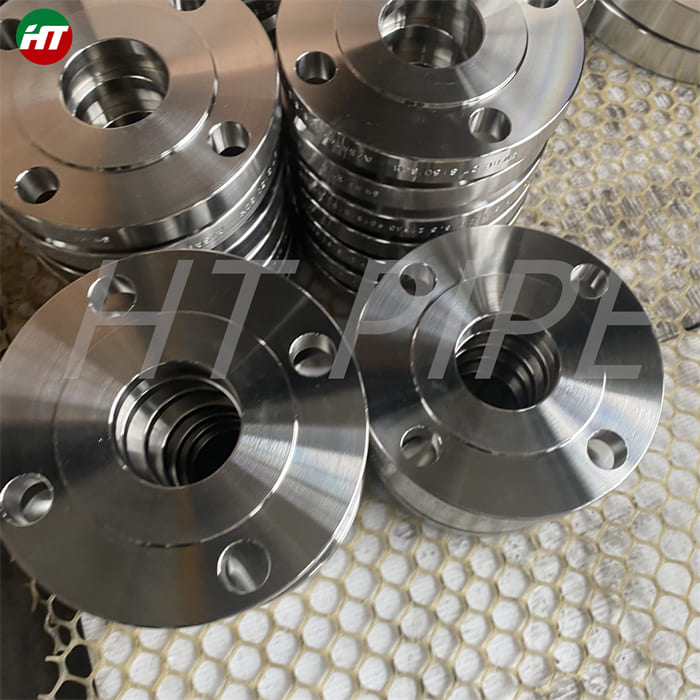
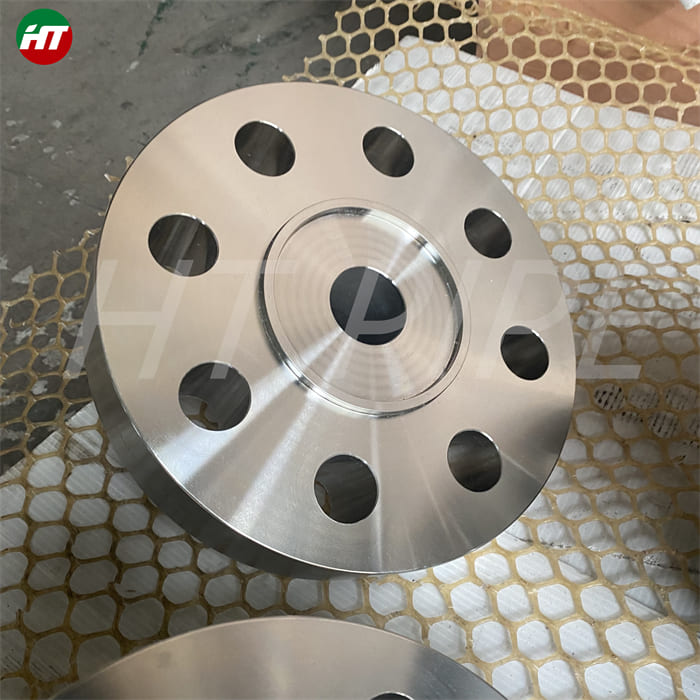
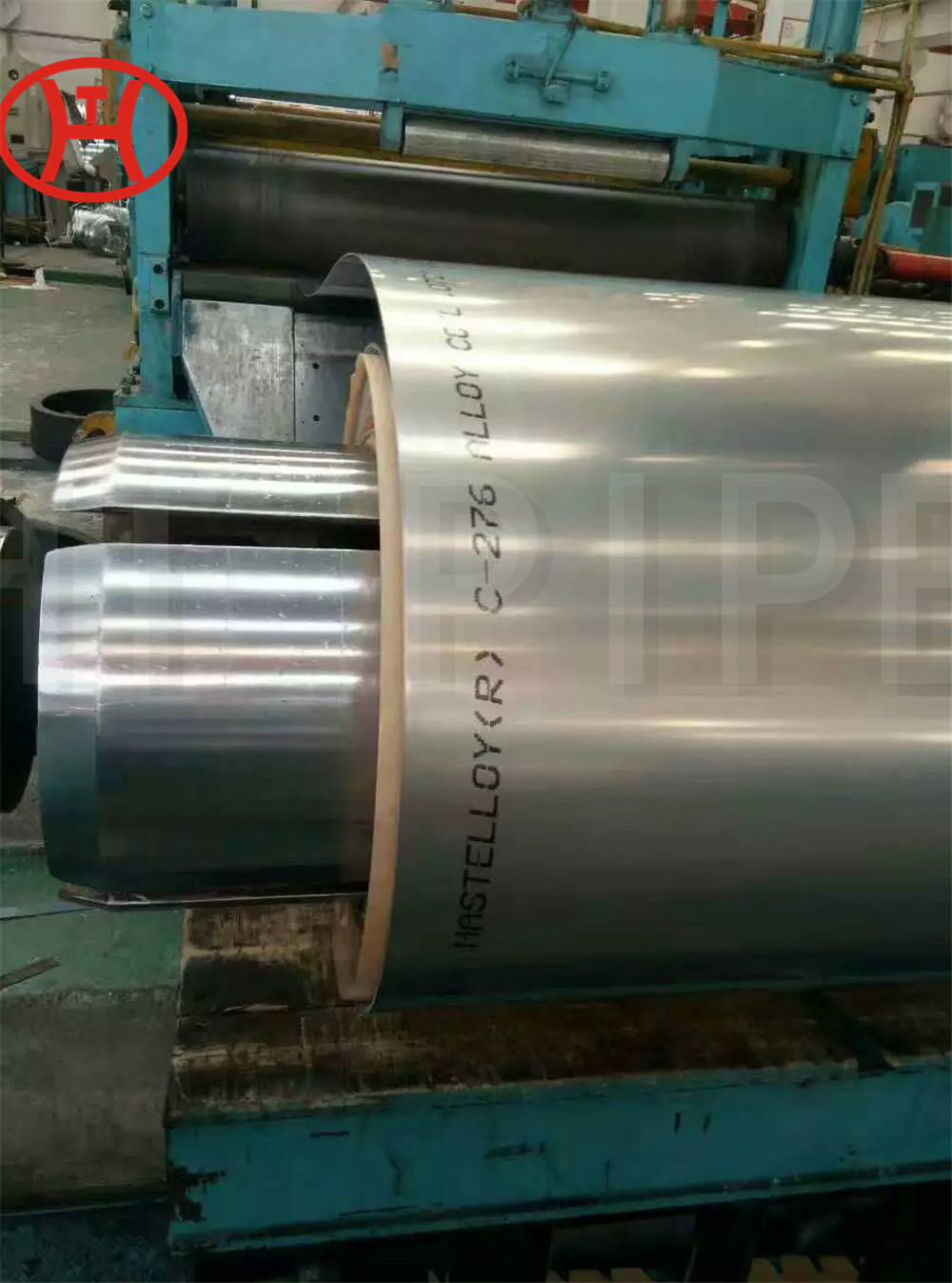
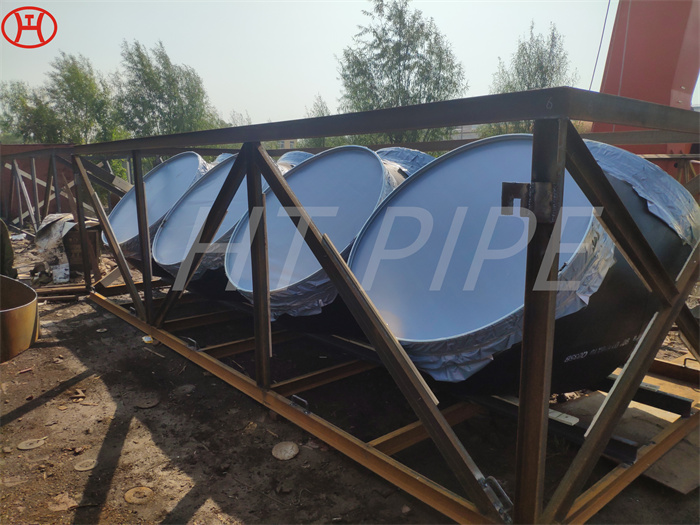
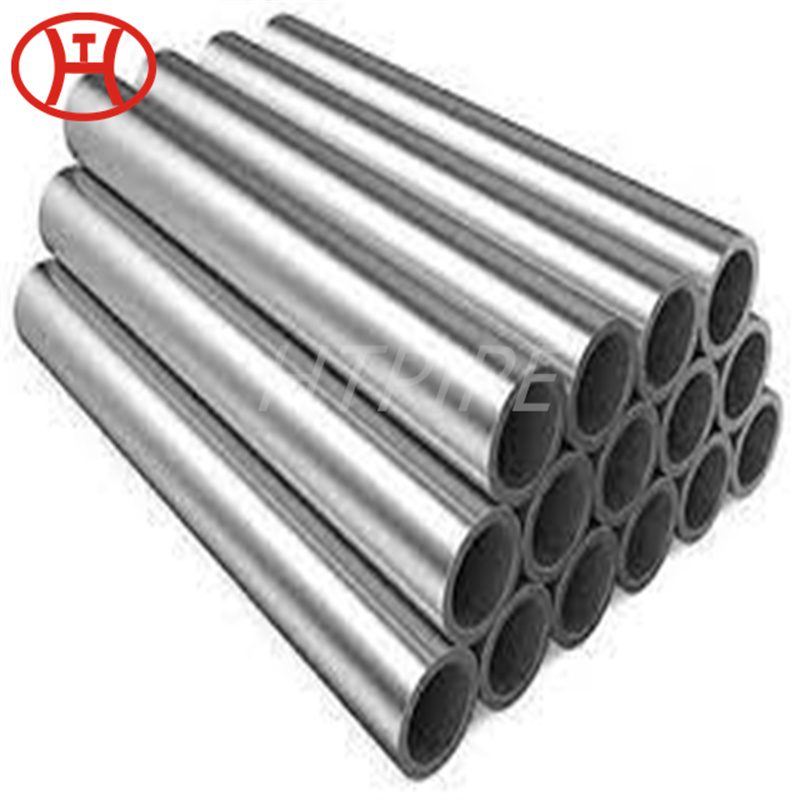
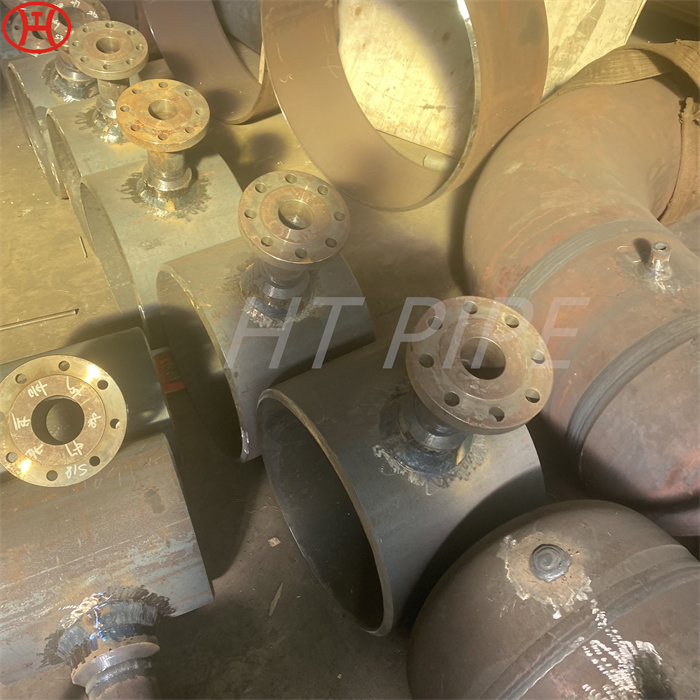
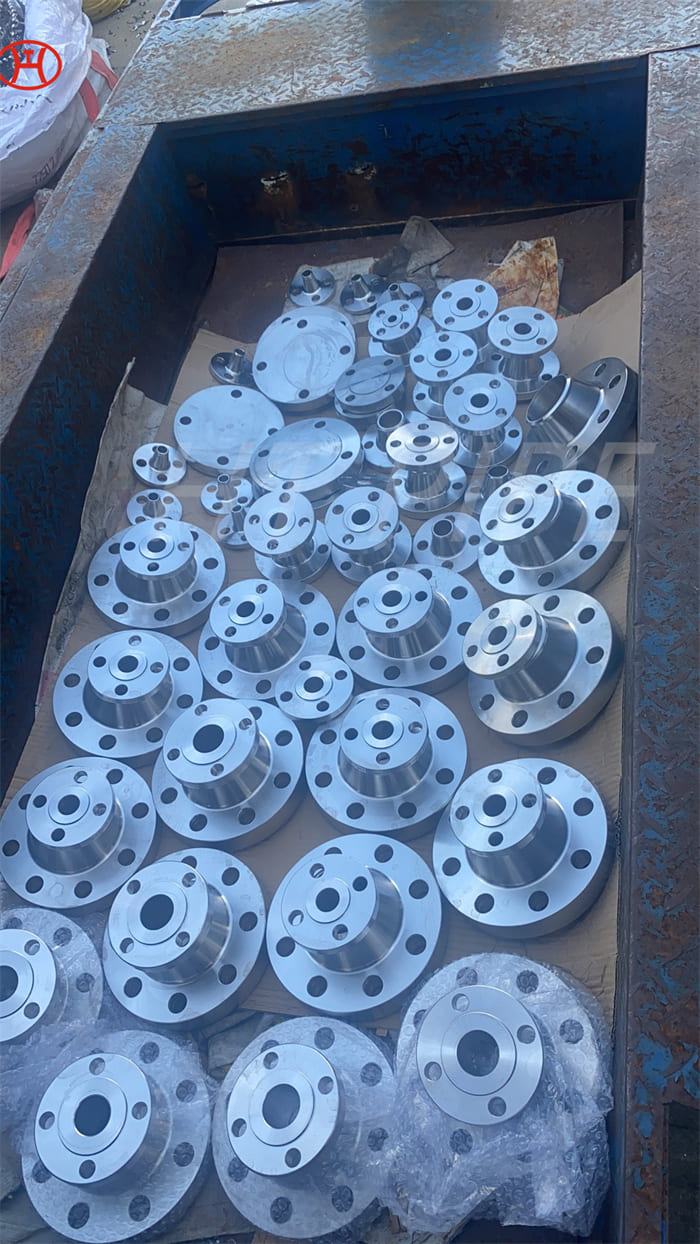
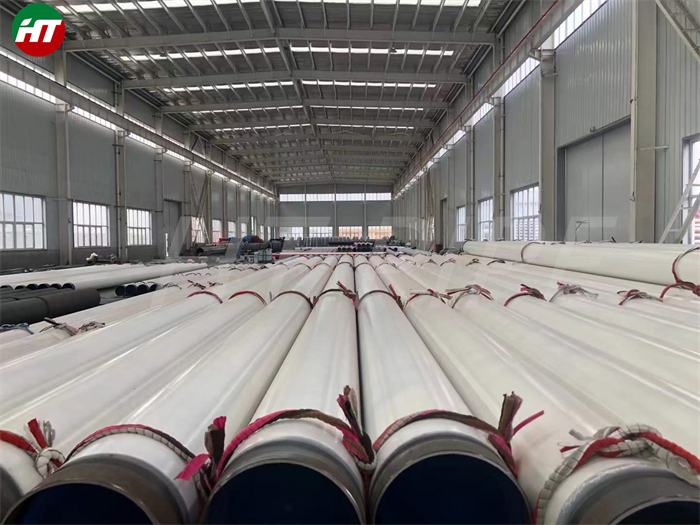
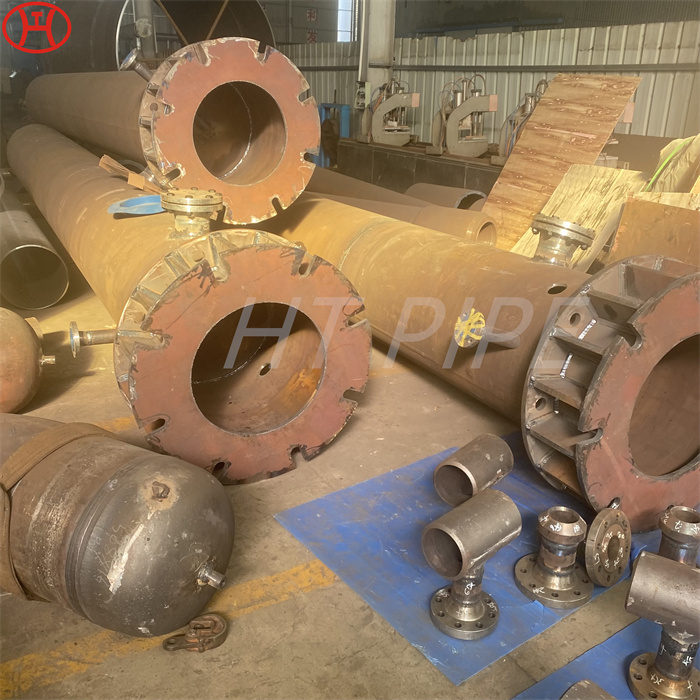
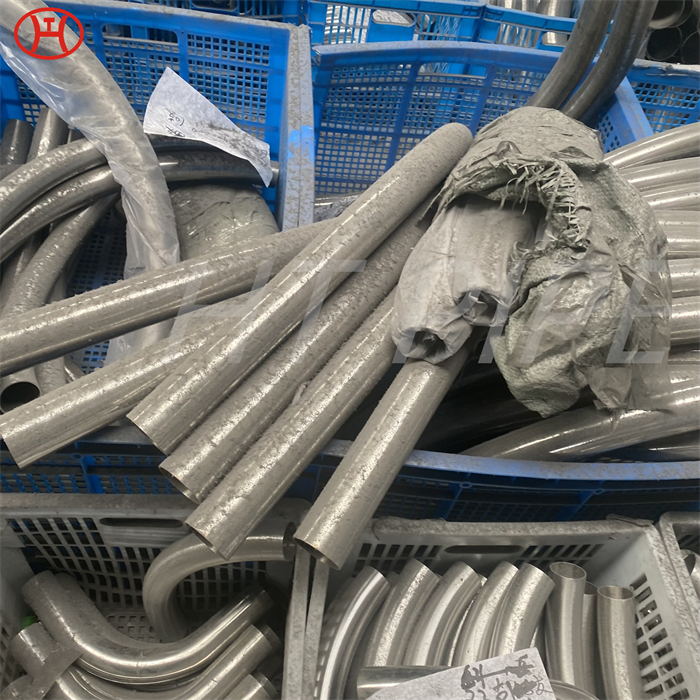
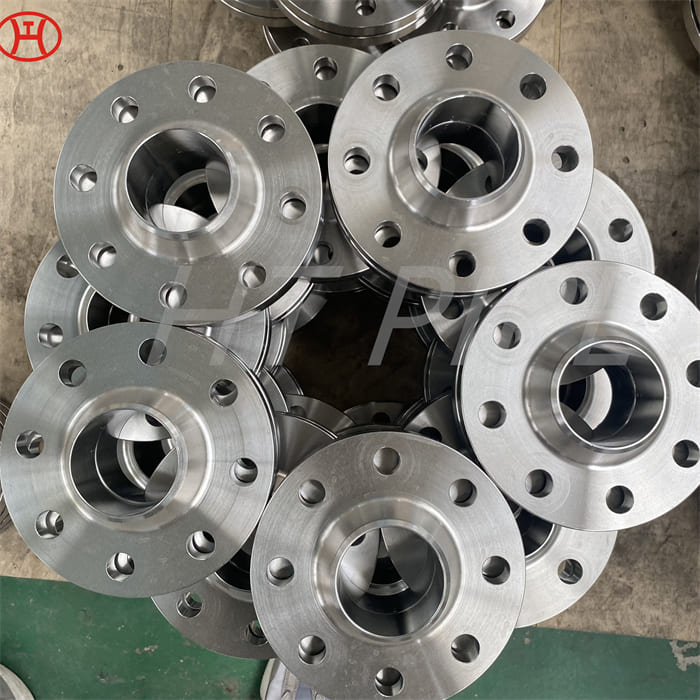
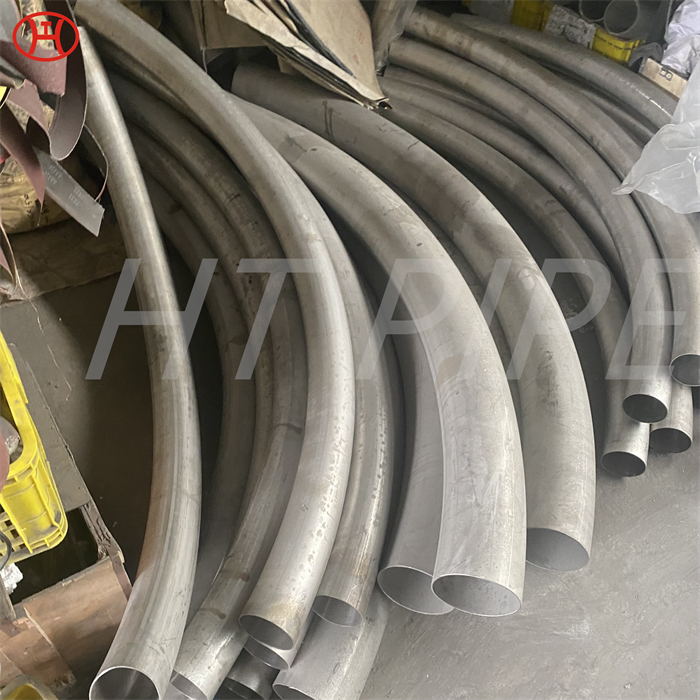
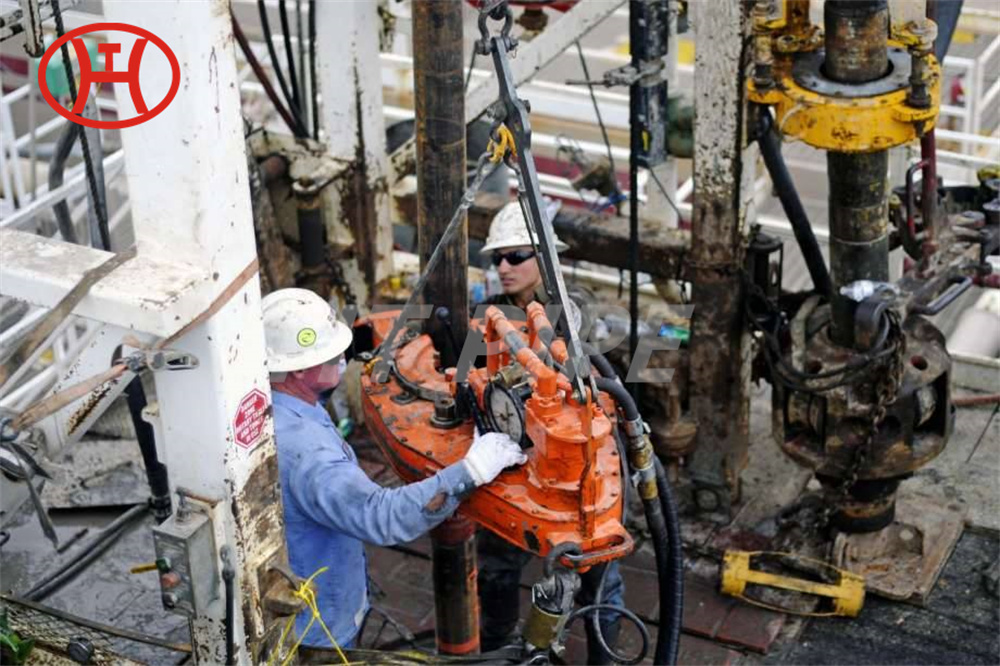
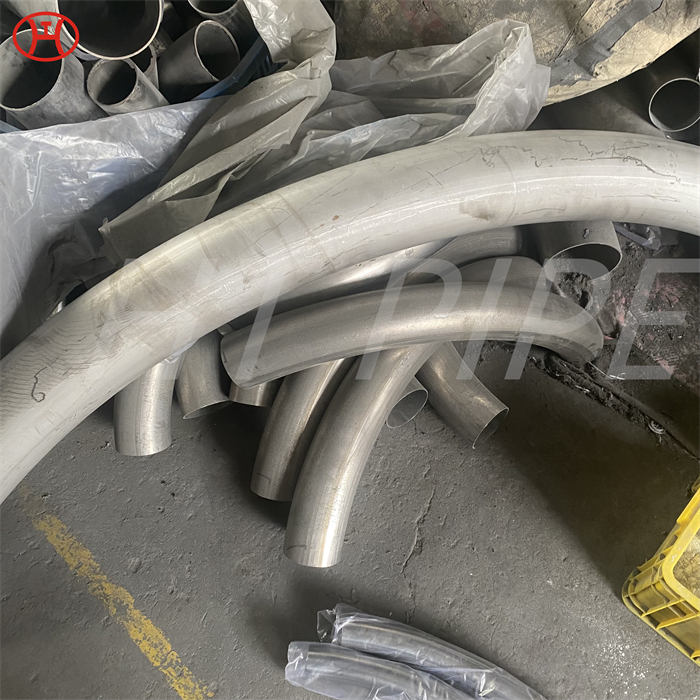
nickel alloy Hastelloy B2 2.4617 pipes with flanges
Hastelloy B2 is a nickel-molybdenum alloy with significant resistance to reducing environments such as hydrogen chloride gas and sulfuric, acetic and phosphoric acids. Hastelloy B2 is resistant to pure sulfuric acid and many non-oxidizing acids. This alloy should not be used in the presence of oxidative contaminants in oxidizing or reducing media. Premature failure may occur if Alloy B2 is used in the presence of iron or copper in systems containing hydrochloric acid.
Hastelloy B2 is a solid solution strengthened nickel-molybdenum alloy with significant resistance to reducing environments such as hydrogen chloride gas, sulfuric acid, acetic acid and phosphoric acid. Molybdenum is a major alloying element that provides significant corrosion resistance in reducing environments. This nickel steel alloy can be used in the as-welded condition because it resists the formation of grain boundary carbide deposits in the weld heat-affected zone.
HASTELLOY B-2 is a nickel-based alloy especially suitable for handling reducing acids at high concentrations and temperatures. The alloy resists the formation of grain boundary carbides in the heat affected zone of the weld, making it suitable for most chemical process conditions in the as-welded condition.
Since this alloy contains no significant chromium additions, it should not be used in oxidizing media or in the presence of oxidizing salts such as iron or copper. The latter may form when iron or copper is present in systems containing hydrochloric acid. Likewise, HASTELLOY B-2 is not resistant to wet chlorine or hypochlorite bleach.