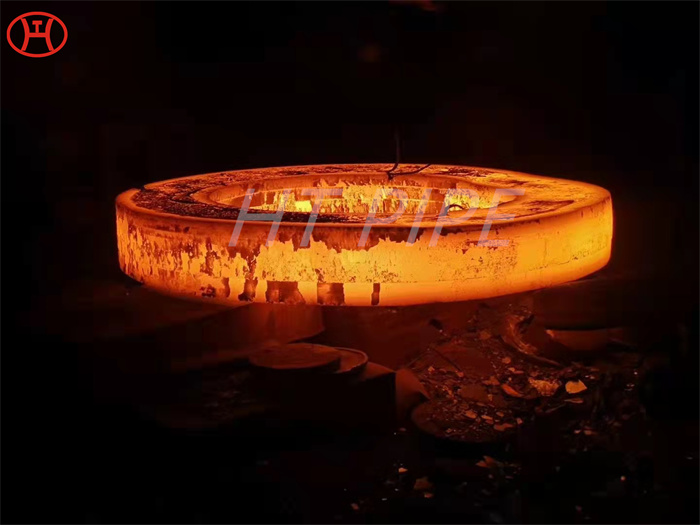
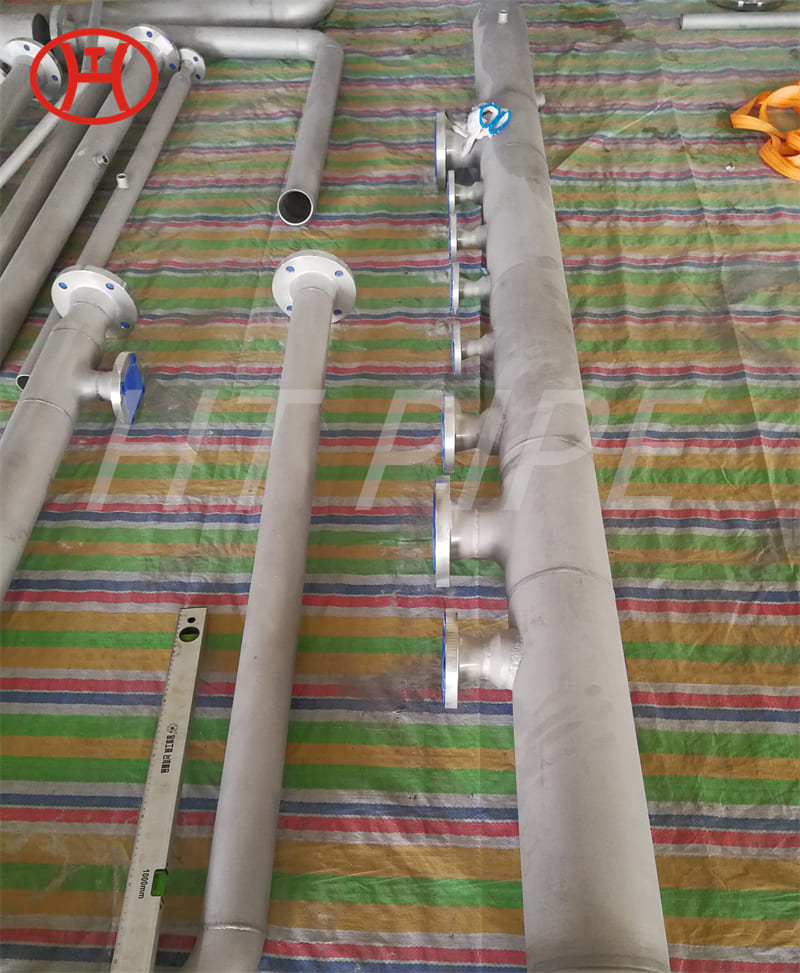
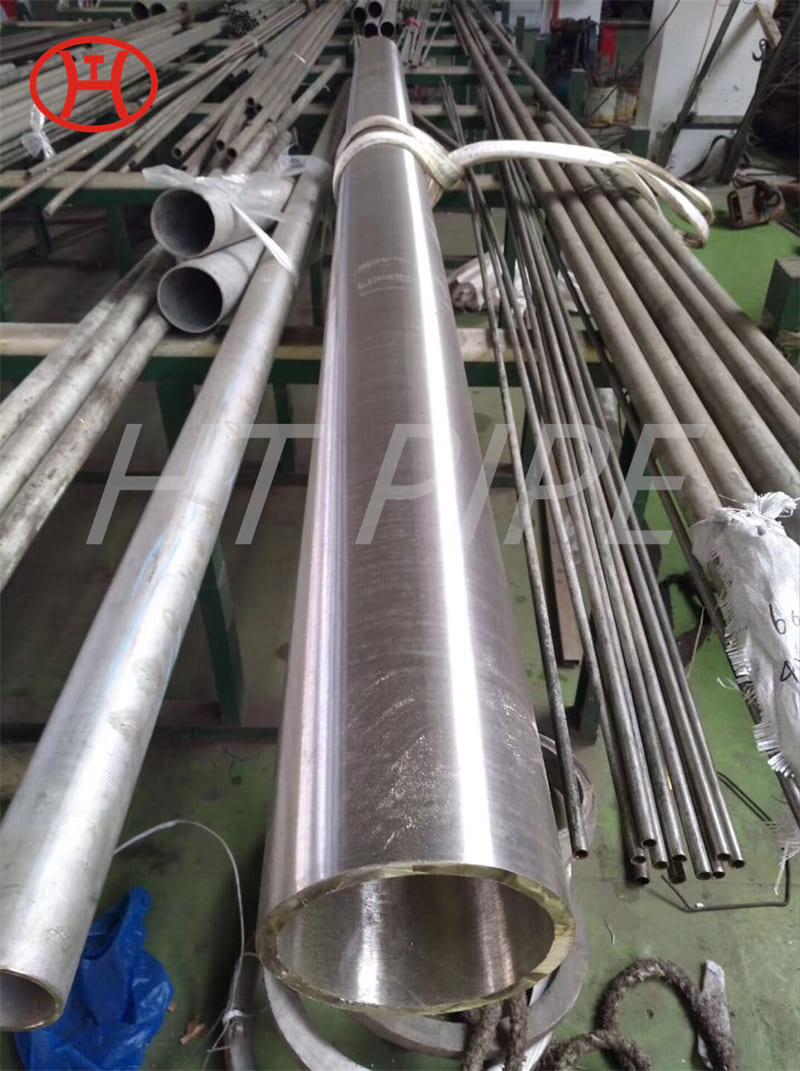
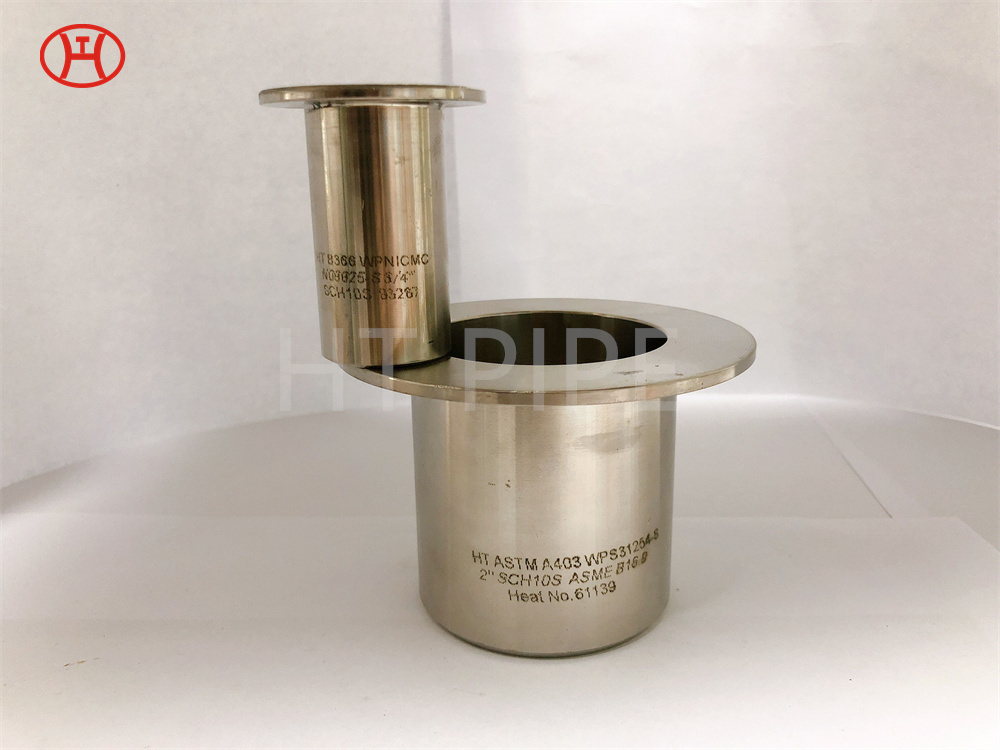
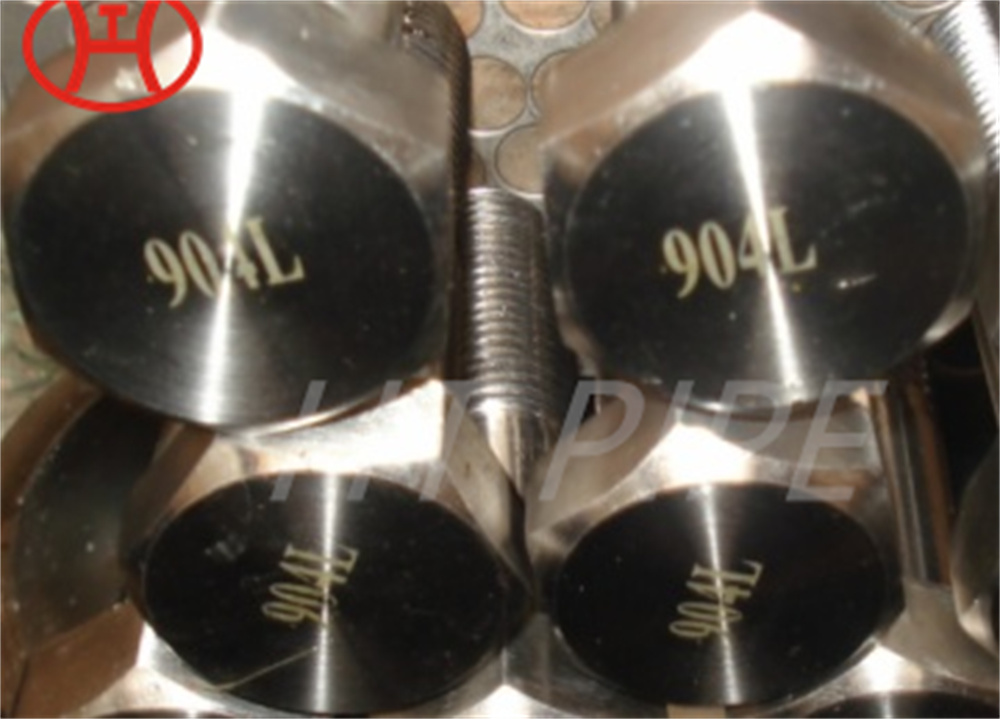
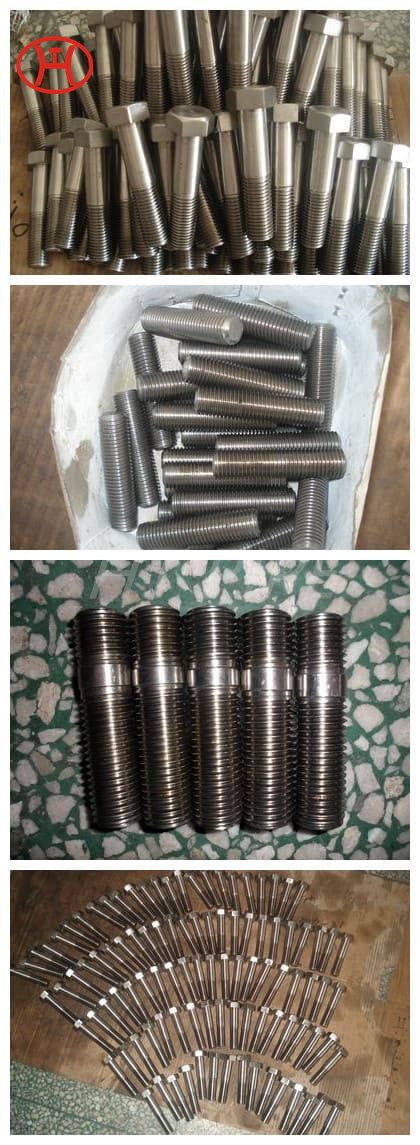
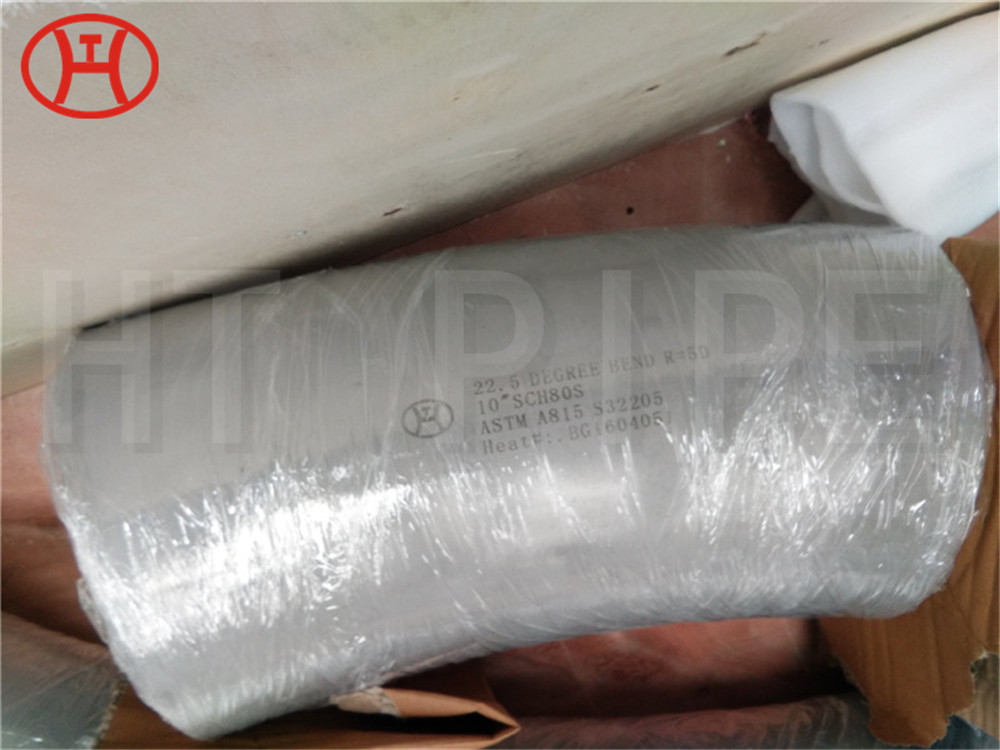
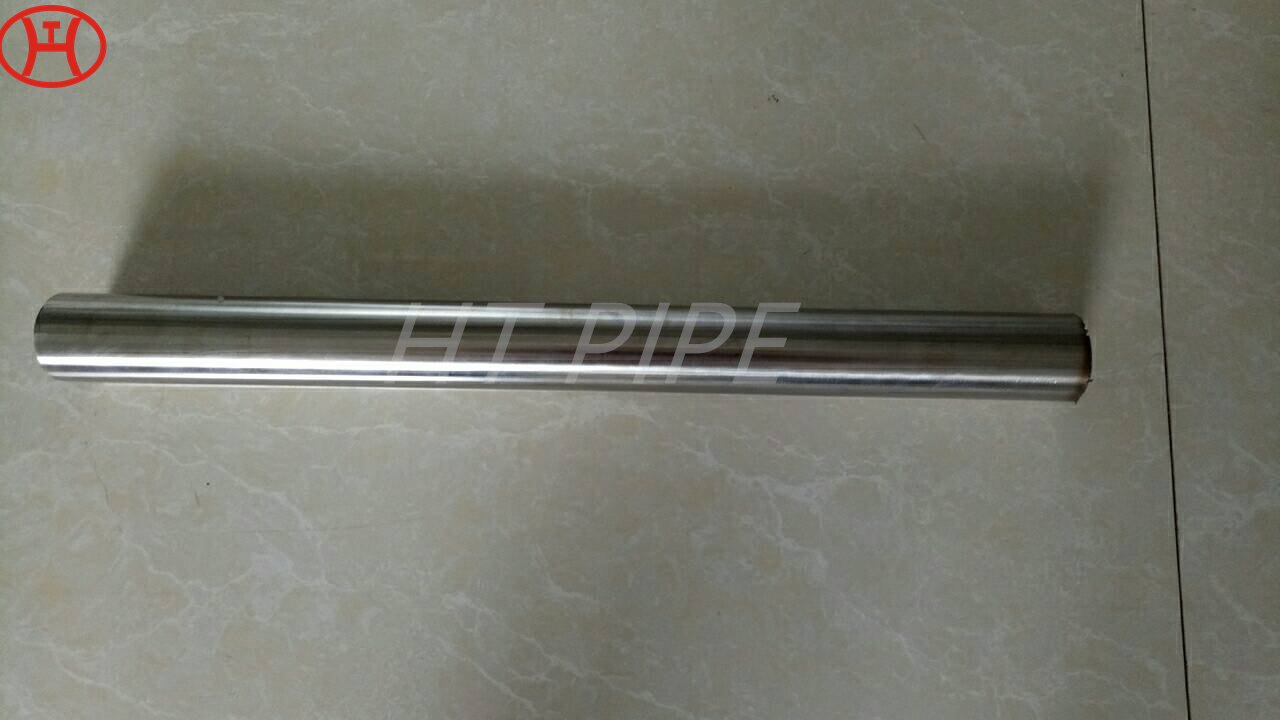
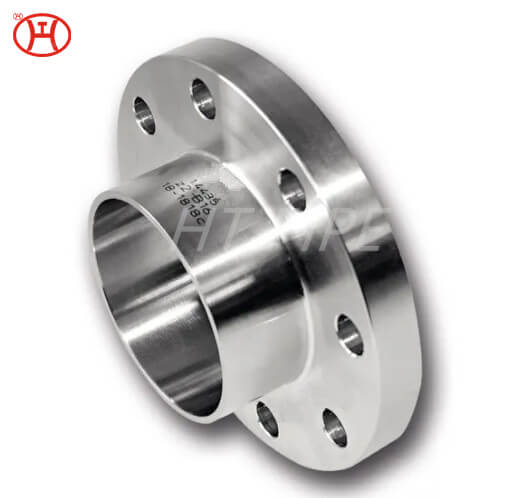
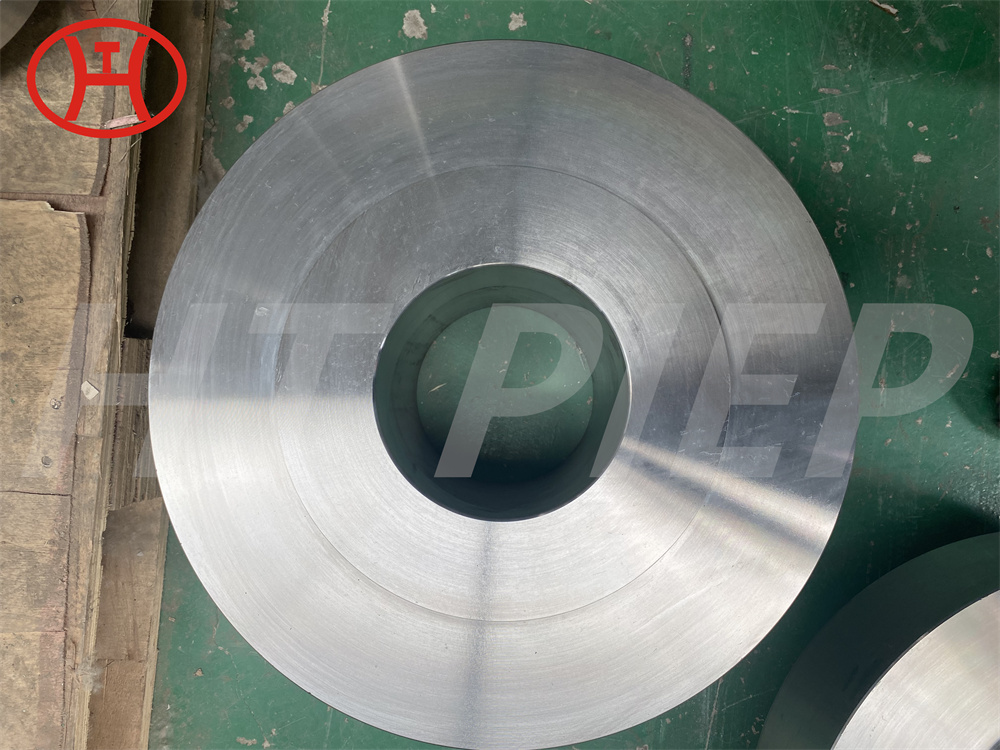
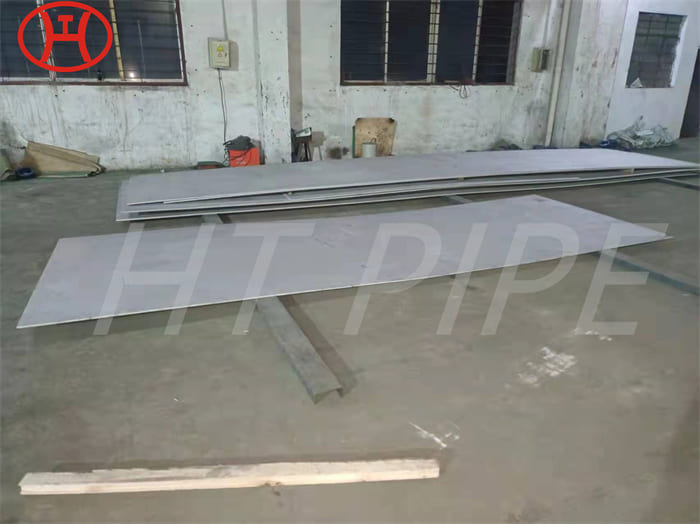
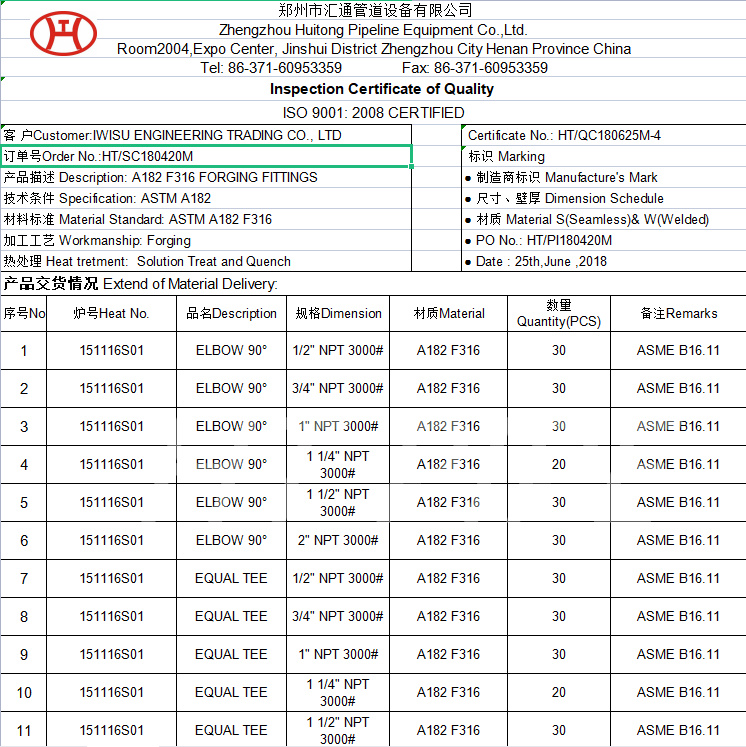
normalizing of 316L S31603 316S11 316S13 stainless steel flange
Applications and Materials
Normalizing is mainly used for normalizing the structure of carbon steel and low alloy steel after forging, hot rolling or casting. The hardness obtained after normalizing depends on the steel dimensional analysis and the cooling rate used (approximately 100-250 HB).
Process details
During normalizing, the material is heated to a temperature approximately equal to the hardening temperature (800-920¡ãC). At this temperature new austenite grains are formed. The austenite grains are much smaller than the previous ferrite grains. After heating and a short soak, the components are free to cool in air (gas). During the cooling process, new ferrite grains are formed and the grain size is further refined. In some cases, both heating and cooling are performed under protective gas to avoid oxidation and decarburization.