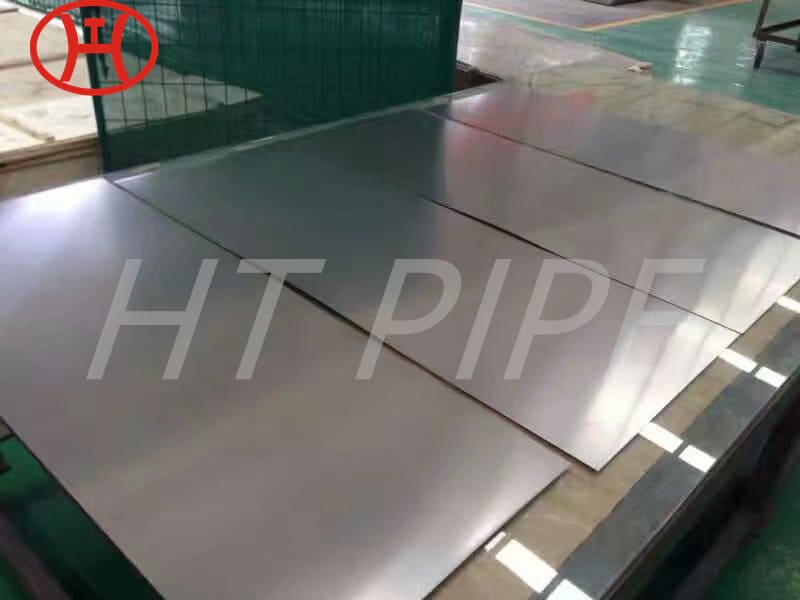
Stainless steel 304 408 409 410 plate
When selecting the 304 Stainless Steel that must endure corrosive environments, austenitic stainless steels are typically used. Possessing excellent mechanical properties, the high amounts of nickel and chromium in austenitic stainless steels also provide outstanding corrosion resistance.
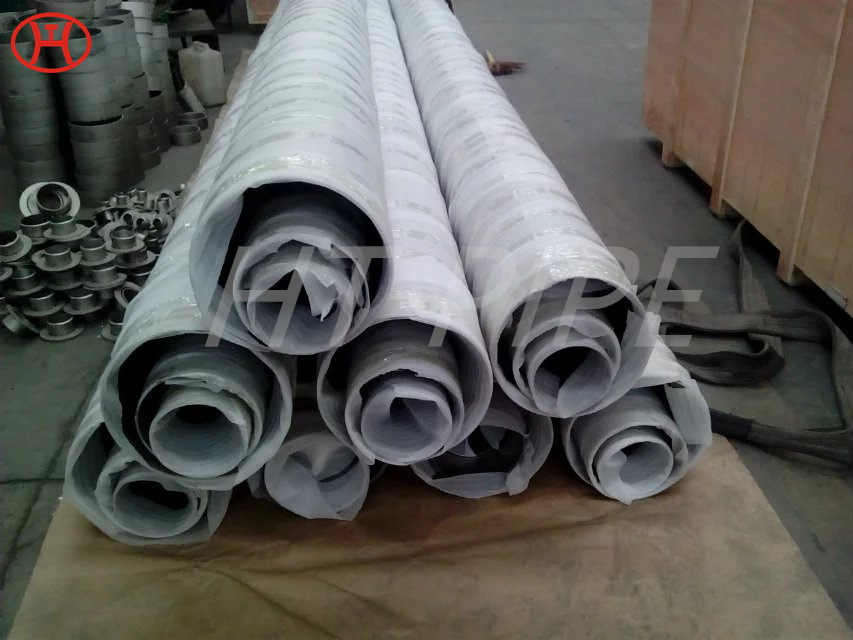
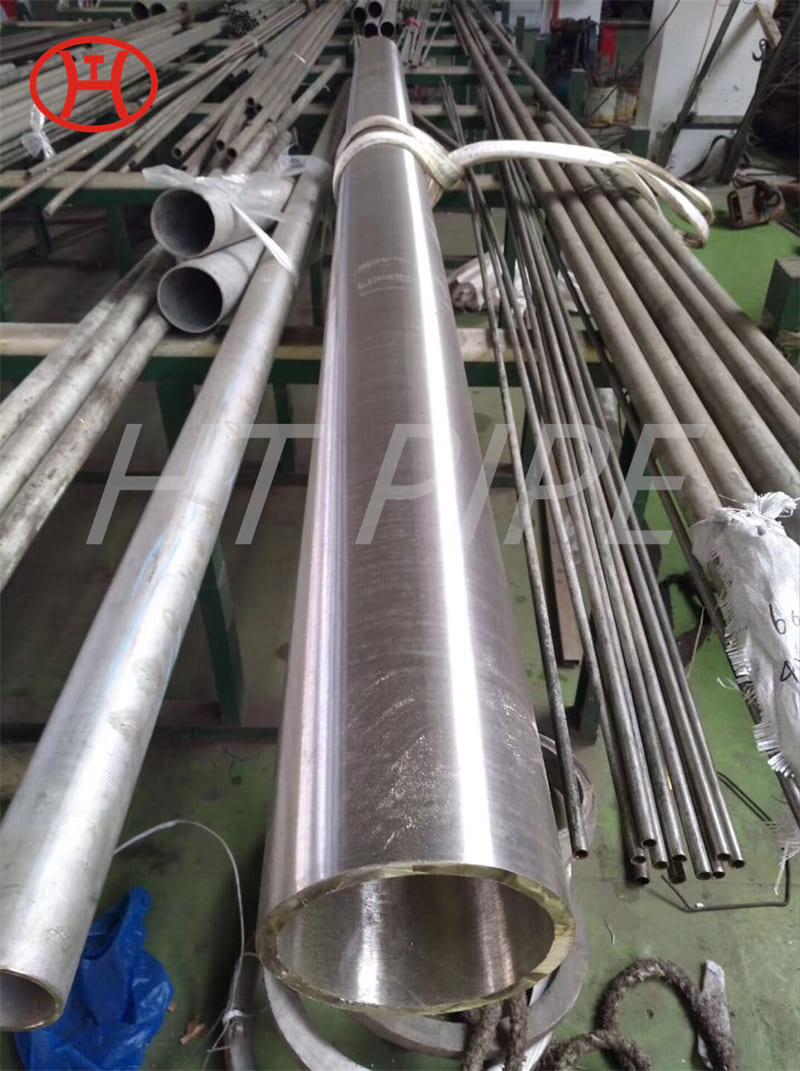
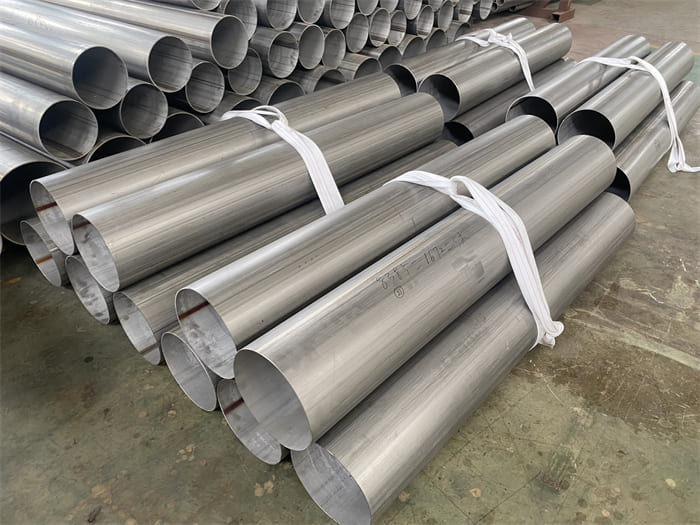
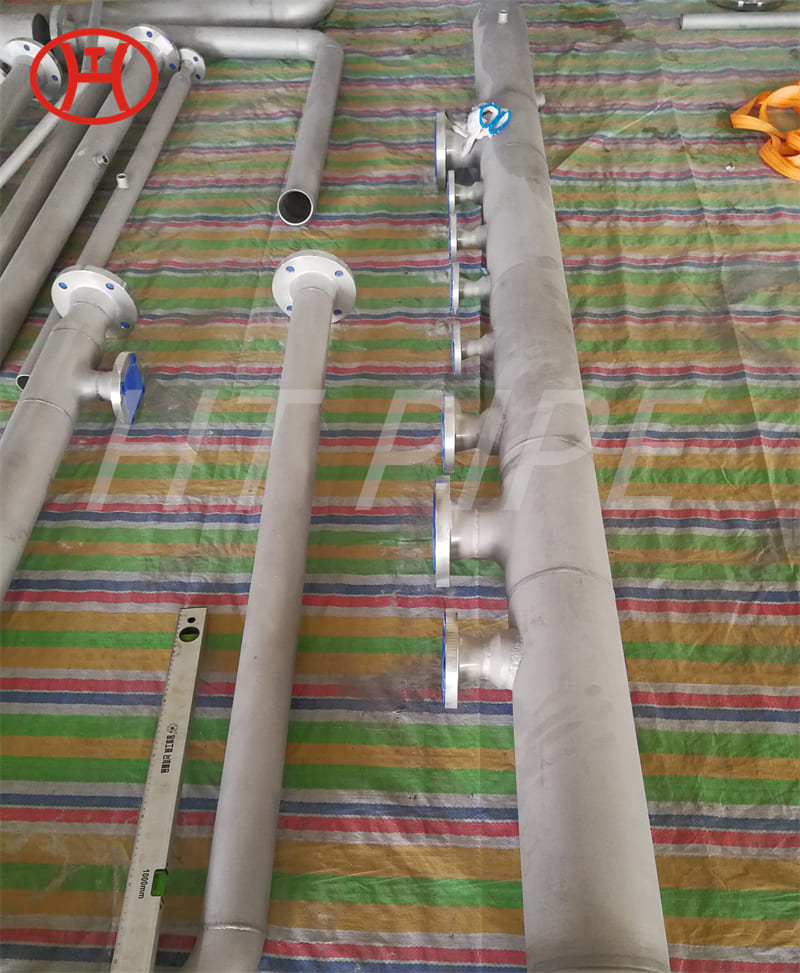
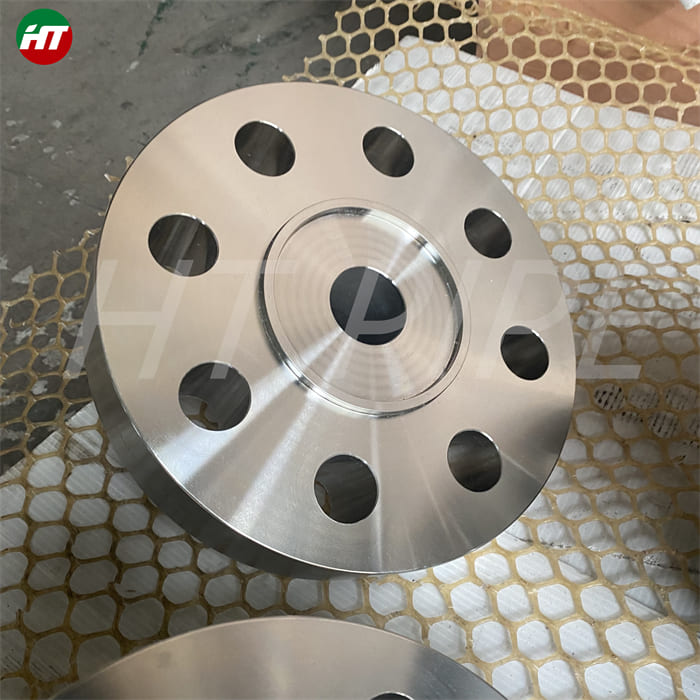
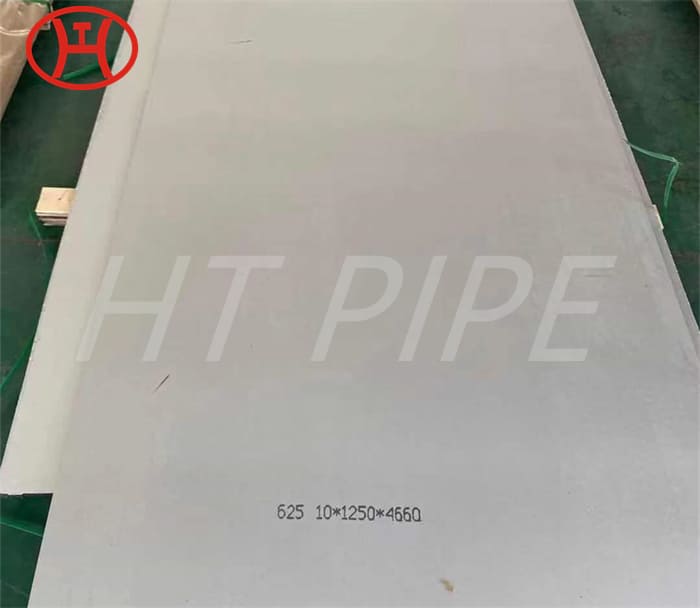
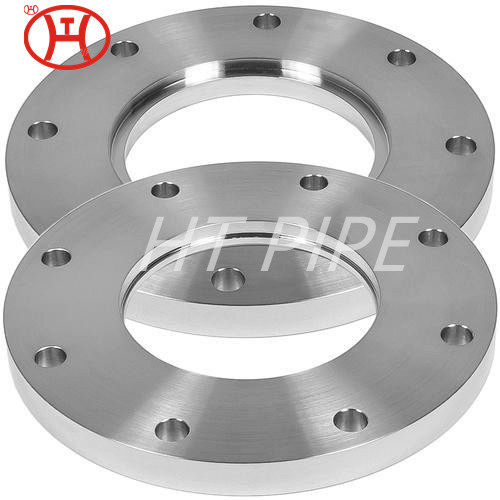
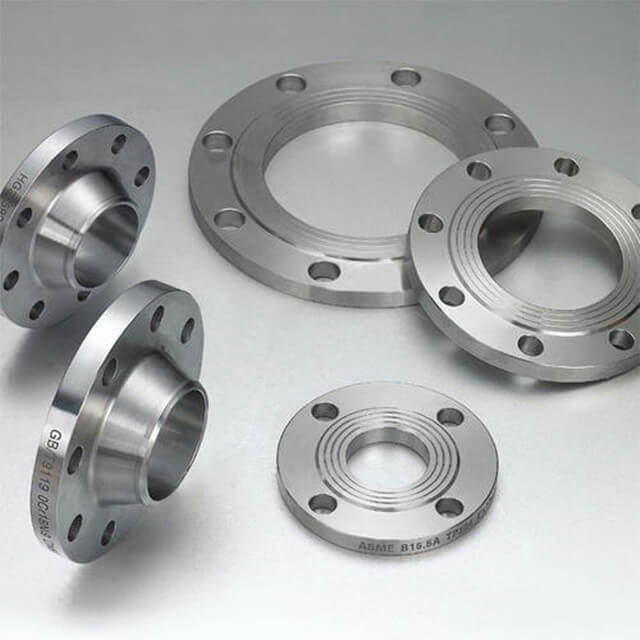
Stainless steel plate comes in a variety of thicknesses and tolerances, Stainless 304 & 304L stainless steel plate is often used in stamped and machined parts for processing equipment while 316 & 316L stainless steel plate are employed by the chemical, marine and power transmission industries.
ASTM A240 304 and 304L stainless steel plate is a standard 18-8 material – meaning it contains 18% chromium and 8% nickel. 304 stainless steel plate is an excellent candidate for most processing techniques as well as both indoor and outdoor applications. This product has a textured dull grey finish and sharp defined edges with accurate dimensions throughout length.
304 stainless steel is a high strength material with excellent corrosion resistance making it a great candidate for aerospace structures, pressure containment, base plates, gussets, structural support, and food and beverage industry applications. ASTM A240 is the standard specification for chromium and chromium-nickel stainless steel plate, sheet, and strip for pressure vessels and for general applications.
304 stainless steel plate is a commercial grade of stainless steel and the most widely used stainless steel. 304 stainless steel plate is a versatile, anti-rusting and heat resistant steel for general use. 304 stainless steel plate is austenitic, meaning it will not attract or hold a magnet.
Our 304 stainless steel plate is hot rolled, annealed and pickled. The 304 stainless steel plate does not have a polished or brushed finish and does not come with a protective PVC to prevent scratching as it is typically not used for aesthetic or cosmetic uses.
It is useful where sanitation and cleanliness are important. Non magnetic in the annealed condition. Hardness and tensile strength can be increased by cold working, but modified by lowered carbon content providing good resistance to corrosion in welded construction where subsequent heat treatment is not practical.
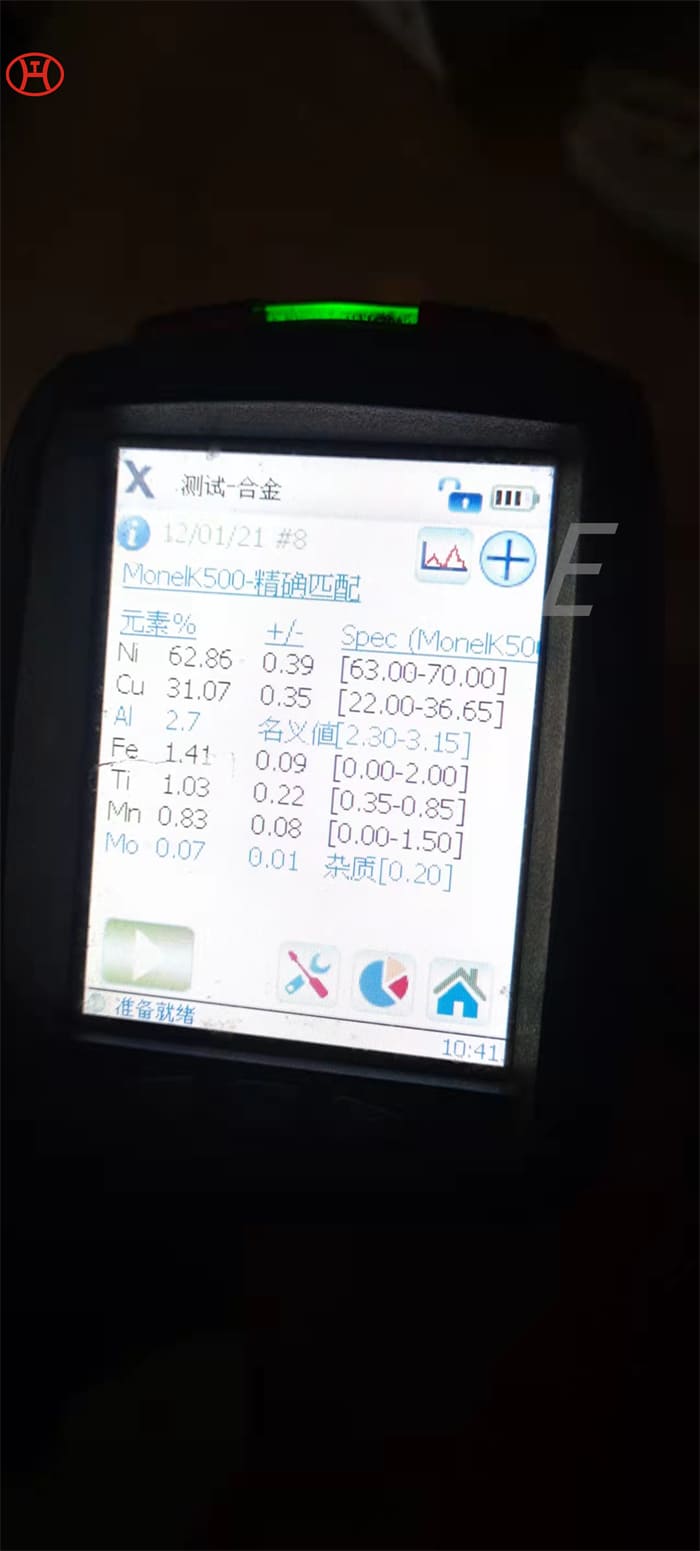
CHEMICAL COMPOSITION
| Element | Percentage |
| C | 0.08 max |
| Fe | 66.34 – 74 |
| Mn | 2 max |
| Ni | 8 – 10.5 |
| P | 0.045 max |
| S | 0.03 max |
| Si | 1 max |
| Cr | 20 |
MECHANICAL INFORMATION
| Imperial | Metric | |
| Density | 0.289 lb/in3 | 8.0 g/cc |
| Ultimate Tensile Strength | 73,200psi | 310 MPa |
| Yield Tensile Strength | 31,200psi | 276 MPa |
| Melting Point | 2,550 – 2,651°F | 1,400 – 1,455°C |